Joining Tables/Nodes
The Join node allows you to join two or more tables/nodes. |
Following are the steps to apply the Join node in a pipeline:
- Drag and drop the Join node from the Transformations section to the pipeline editor page.
- Connect the source node to the Join node.
- Double-click the Join node. The properties page is displayed.

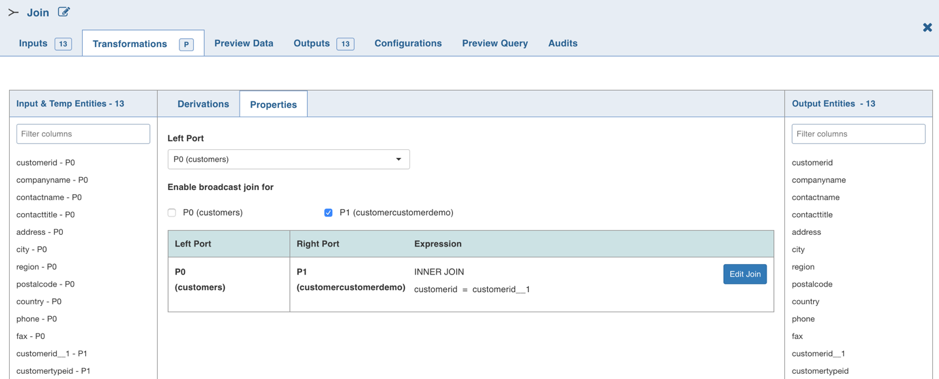
- Select the left port and click Edit Join. Enter the following details and click Save:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Left Port | Select the Left Port main table. | All the other tables will have one or more join conditions with the left table. |
| Join Type | The join node creates a new result table by combining columns from multiple tables. | Inner Join: Returns all the rows where the selected columns from left and right tables match. Left Outer Join: Creates a new result table that returns all the rows in the left table and only those rows in the right table where the selected column values of left and right tables match. Right Outer Join: Creates a new result table that returns all the rows in the right table and only those rows in the left table where the selected column values match. Full Outer Join: Creates a new result table that returns the intersecting rows joined together, as well as the non-intersecting rows from both tables, with null values for fields of the other table. Cross Join: Produces a cross product of two tables. The number of records in the resulting table is equal to the number of rows in the left table multiplied by the number of rows in the right table. This does not require any join condition. Anti Join: Anti-join between two tables returns rows from the first table where no matches are found in the second table. Semi-Join: A semi join between two tables returns values from the left side of the table that have a match with the right table. |
| Join Conditions | The columns in Port0 and Port1 on which the join function will be performed. | Select the columns for Port0 and Port1. |
- To set the join expression, select the Advanced mode and enter the join expression and click Save.
A sample expression is as follows:
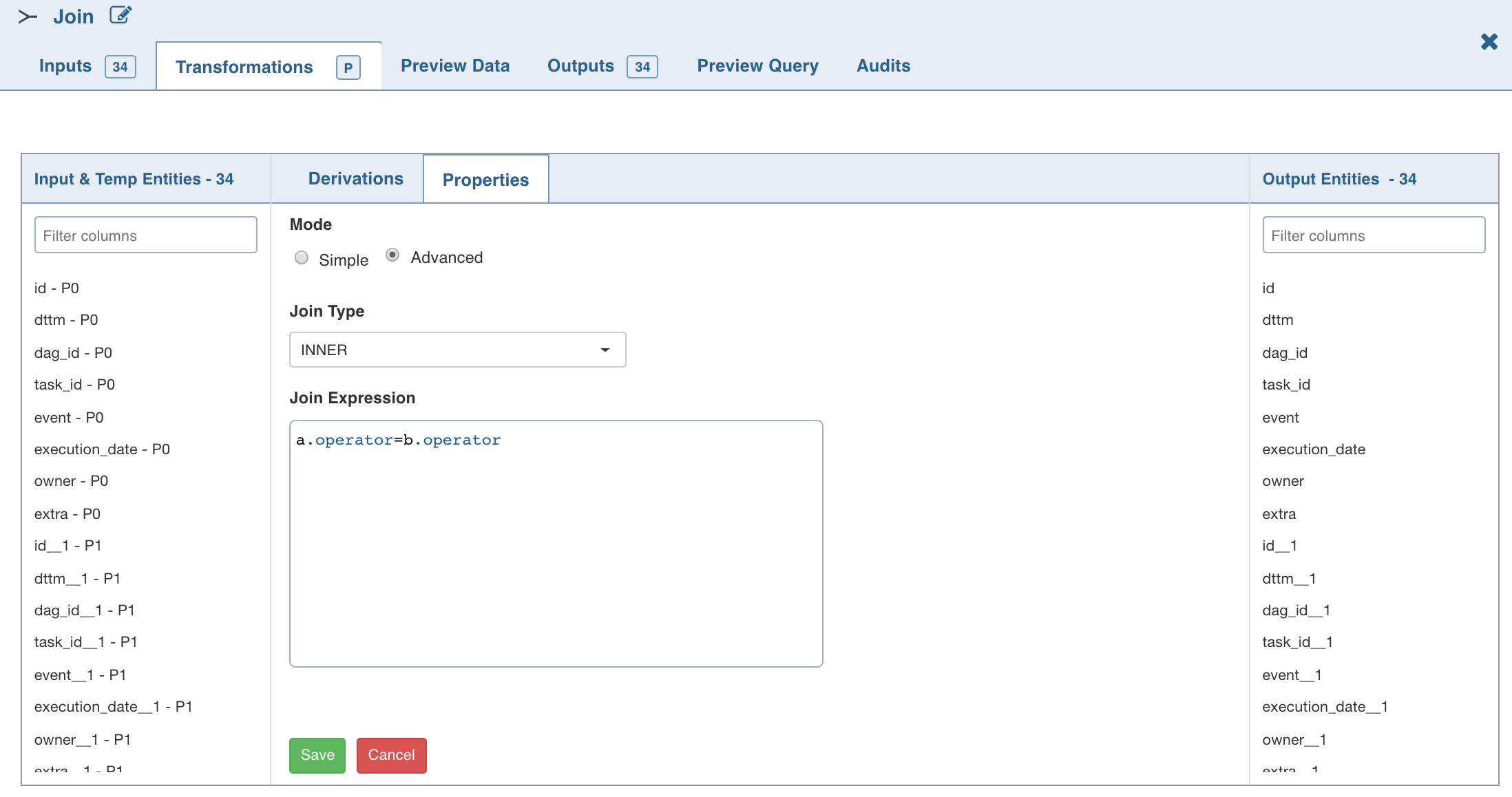
The join conditions are validated and added to the read-only view. Errors if any, will be displayed at the top of the transformation page.
Even after renaming a column in the Schema section, the original column name will be displayed in the Properties window. However, the renamed column will be propagated in the downstream nodes.
For Spark execution engine, to use the Join node and cross join between any two columns, the spark.sql.crossJoin.enabled configuration must be set to true in the Spark configuration file.
Post Processing Configuration
For details, see Configurations - Post Processing.
Broadcast Join
- This feature is available only for Spark execution engine.
- This feature is not supported for pipelines created in Snowflake data environment.
Spark SQL uses Broadcast Join (Broadcast Hash Join) instead of Hash Join to optimize join queries when the size of one side data is below the spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold value.
Broadcast join can be efficient for joins between a large table (fact) with relatively small tables (dimensions) that could then be used to perform a star-schema join. This avoids sending all data of the large table over the network.
Following are the steps to enable Broadcast join for the join node in pipeline:
- Double-click the Join node. The properties page is displayed.
- Select the port for which broadcast join is required. The selection will be autosaved.
The selected port(s) will be broadcasted when the execution occurs.