Extensions
Extensions can be used to extend the functionality of IWX features in a predefined way.
The following table illustrates the different extensions supported, along with the programming languages. Each of these extensions are run on specific clusters during the execution of workflow, pipeline, or ingestion. The extensions that are executed depends on the IWX version used.
| Extension | Where it Runs | When it Runs | Programming Language | IWX Version | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bash node | IWX edge node | As part of workflow | bash | 4.x+ | ||
| Pipeline Extension/Custom Target | Data plane/Spark Cluster | As part of pipeline | Java, Python | 4.x+ | ||
| Source Extension (Pre-ingestion hook) | Data plane/Spark Cluster | As part of ingestion, before data is read, before data is written | Java | 5.0+ | ||
| Pre/post job hook | Data plane/Spark Cluster | Before/after job/pipeline | Python, bash | 5.4+ |
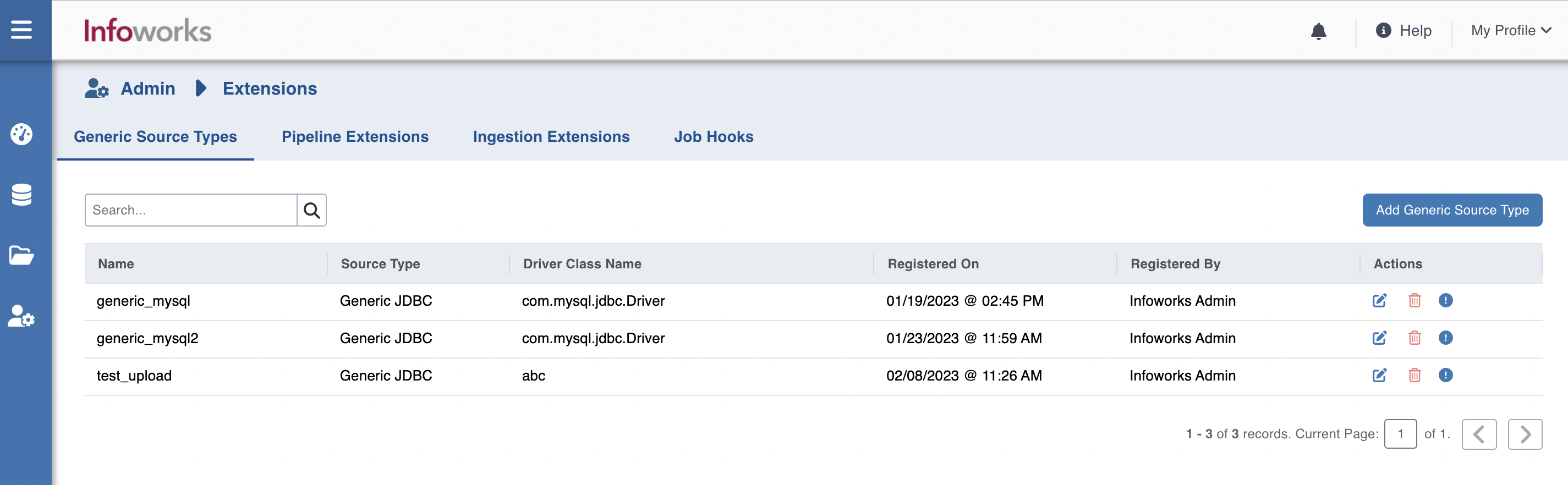
Managing Generic Source Type
To manage the generic source type, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to Admin > Extensions > Generic Source Types.
- Click the Add Generic Source Type button.
Managing Pipeline Extensions
To manage the Pipeline Extensions, perform the following steps:
- In Infoworks, navigate to Admin > Extensions > Pipeline Extensions.
- Click Create Pipeline Extension.
- In the Add Pipeline Extension page, enter the following details:
- Extension Type: Choose Custom Transformation or Custom Target.
- Execution Type: Select Java.
- Name: A user-friendly name for the group of transformations under one project. For example, SampleExtension.
- Upload the files or enter the path to the folder where the jars have been uploaded. For example, /home//pivottransformation/.
- The classes implementing the SparkCustomTransformation API which must be available as transformations within Infoworks.
- Alias: A user-friendly alias name for the transformations. For example, Sample.
- ClassName: A fully qualified class name. For example, io.infoworks.awb.extensions.sample.SparkCustomTfmSample.
- Additional config parameters: these are user configurable parameters that can be configured to retrieve secrets from secret store and will be available in custom target implementation.
- You can click Add to add multiple pairs of Alias and Class Names.
- Click Save.
Managing Ingestion Extensions
This procedure allows users to integrate custom code/third party data masking/obfuscation to allow users to secure the data before it lands in the data lake for all source types. These extensions may be used with all data source types.
In the Infoworks left navigation pane, navigate to Admin > Extensions > Ingestion Extensions.
- Click Create Ingestion Extension.
- In the Add Ingestion Extension page, enter the following details:
Extension Type: Select Source Extension or Streaming Extension.
Extension Subtype:
- If the extension type is Streaming Extension, select Custom Deserializer.
- If the extension type is Source Extension, select Custom Extension or Hive UDF.
i.* If the Extension Subtype is selected as Custom Extension, enter the following details:
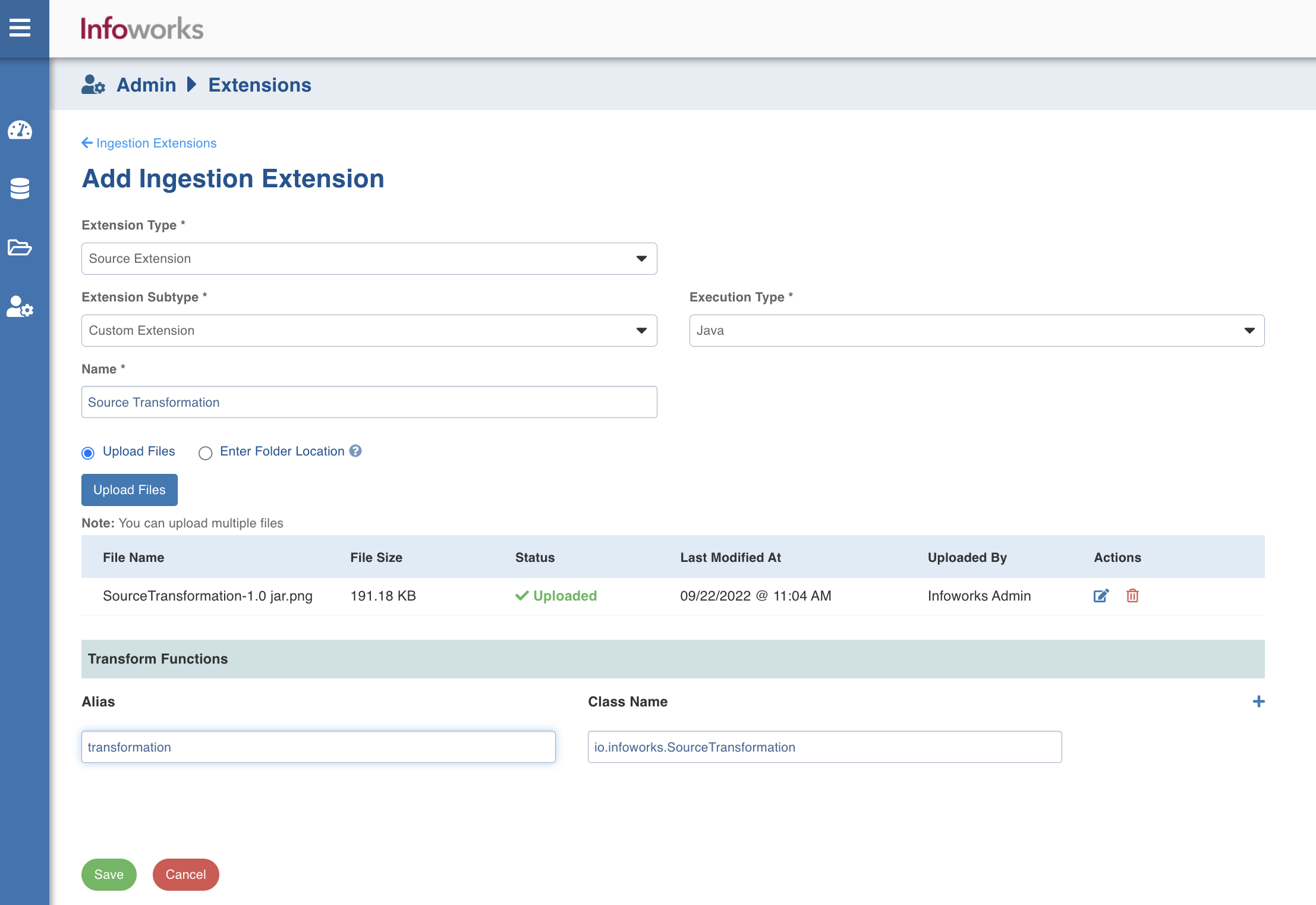
- Execution Type: Select Java.
- Name: A user-friendly name for the group of transformations under one project. For example, Source Transformation.
- Upload the jar files or enter the path to the folder where the jars have been uploaded. For example, /home/source_transformation.
- When the Extension type is Source Extension, in the Transform Functions section, enter the fields in the Alias and Class Name.
- When the Extension type is Streaming Extension, in the Deserializers section, enter the fields in the Alias and Class Name.
- Click Add to add a new Transform function, if required.
- Click Save to save the changes.
ii. If the Extension Subtype is selected as Hive UDF, enter the following details:
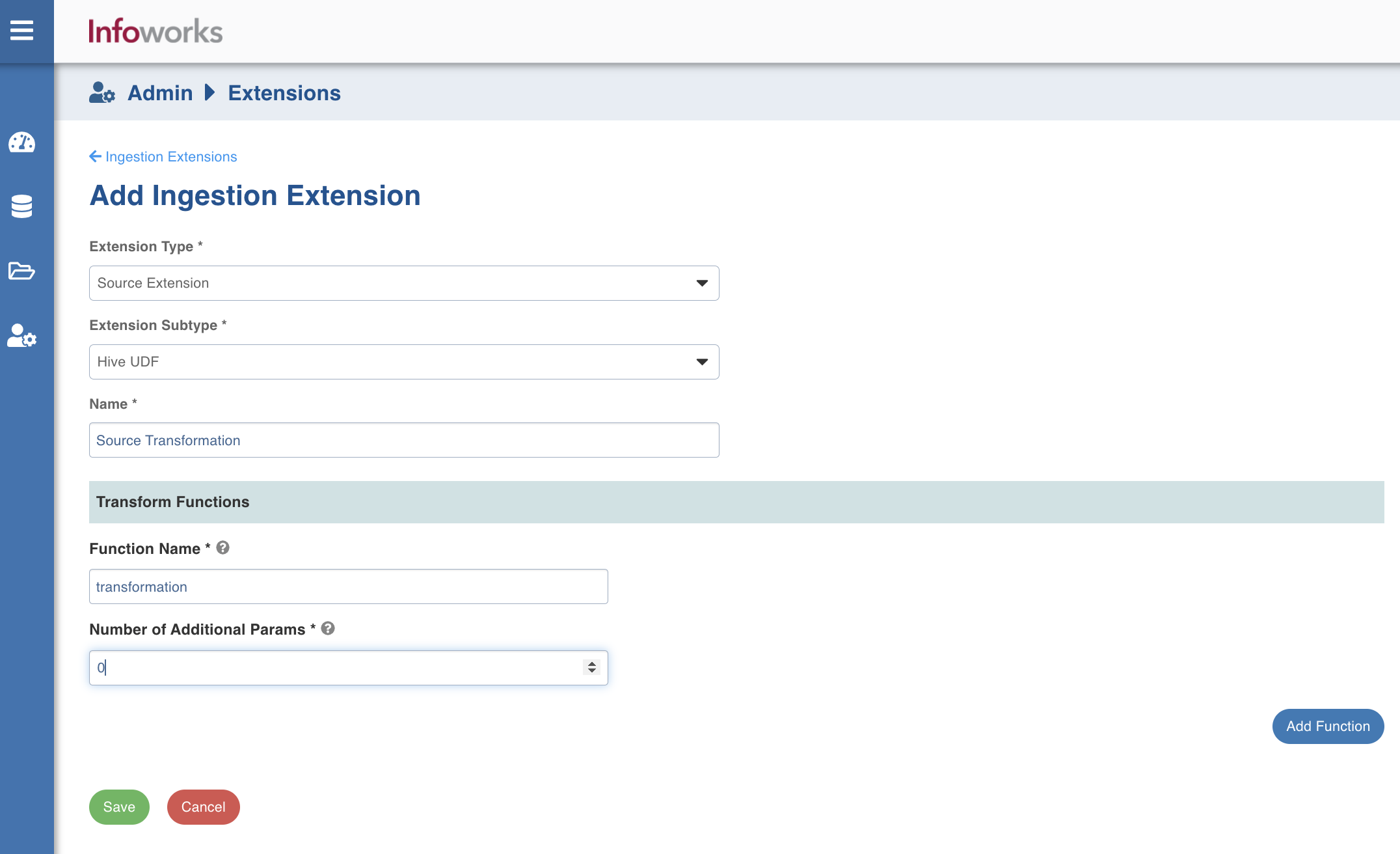
- Name: A user-friendly name for the group of transformations under one project. For example, Source Transformation.
- In the Transform Functions section, enter the following details:
- Function Name: Name of the function with schema included which is registered at hive metastore. For example, dwu_edw_iwx_0820.encryptConfidentialENT
- Number of Additional Params: Number of parameters needs to be passed other than source column. For example, for dwu_edw_iwx_0820.encryptConfidentialENT(PAYER_LVL_1_ID, 'ACCOUNT_MVP', count will be 1)
- Click Add Function to add a new transform function, if required.
- Click Save to save the changes.
Registering Hive UDFs on Spark Cluster
To register Hive UDFs on Spark Cluster:
Step 1: Navigate to the ingestion core folder cd /opt/infoworks/lib/ingestion/core/.
/opt/infoworks/lib/ingestion/connectors/<source>/lib/dist-jobs/
For example: if the hive udf has to be added to csv source the path should be: /opt/infoworks/lib/ingestion/connectors/csv/lib/dist-jobs/
Step 2: Place your Jar which contains the classes that implement UDFs.
Step 3: Enter the following configuration either in the Admin or in the Source Setup page.
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| should_register_hive_udfs | true |
| hive_udfs_to_register | <functionName1>:<fullyQualifiedclassNameImplementingFunction1>;<functionName2>:<fullyQualifiedclassNameImplementingFunction2> |
Deregistering Hive UDFs on Spark Cluster (if needed)
Step 1: Enter the following configuration either in the Admin or in the Source Setup page.
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| should_deregister_hive_udfs | true |
| hive_udfs_to_deregister | <functionName1>:<functionName2> |
Procedure to Build the Jar for Upload
Perform the following steps to build the jar for upload.
- Create a java Class in which you must implement Function and Serializable Interface similar to following code, where:
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| Function<T,R> | Represents the function that accepts one argument and produces a result. This is a functional interface whose functional method is apply(Object). The arguments of this function (T,R) will be the datatype of column on which it is intended to use. |
| Serializable | Is the interface present in the java.io package. It is a marker interface. A Marker Interface does not have any methods and fields. Thus classes implementing it do not have to implement any methods. Classes implement it if they want their instances to be Serialized or Deserialized. |
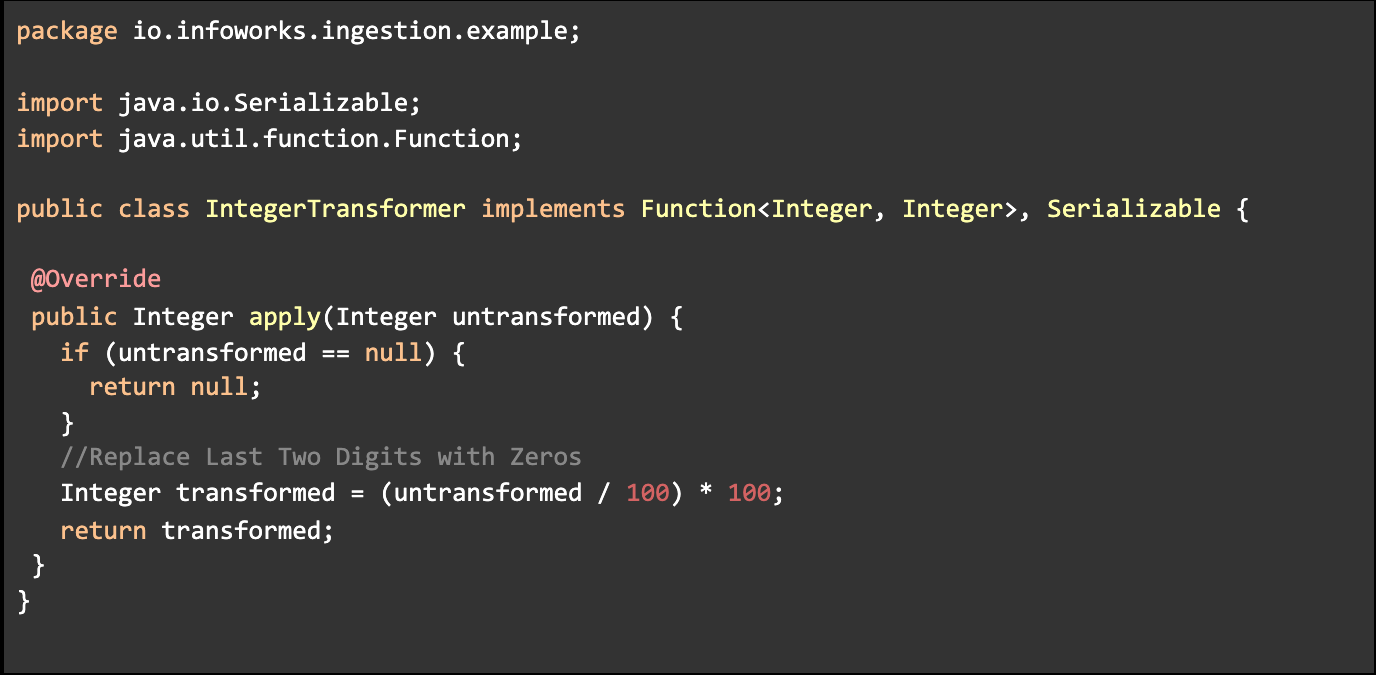
- Implement the apply function as per your requirements.
- Build the Jar file for classes.
- Upload Jar file In UI or upload file on control plane and provide path for that in UI.
- Provide any Alias name and fully qualified Class Name. In above example,
- Alias: replace_last_two_digits_with_zeros
- ClassName: io.infoworks.ingestion.example.IntegerTransformer
Using Transform Functions
To view the Transform Function that is set, perform the following steps:
- Click Data Sources -> View Source -> Source Setup.
- Navigate to the Ingestion Extensions section and select the ingestion extension which is required for this source.
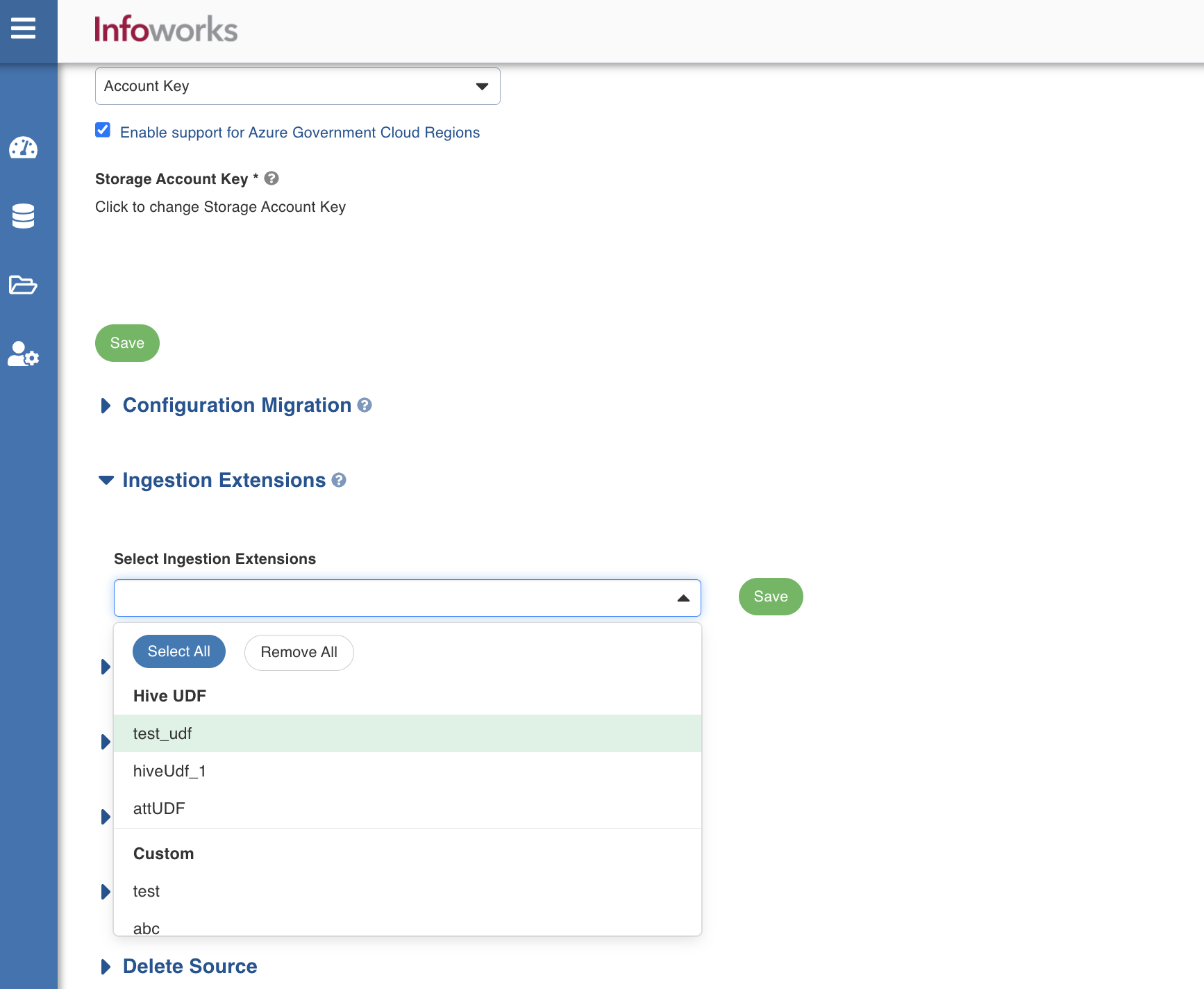
- Click Save to save the source extension.
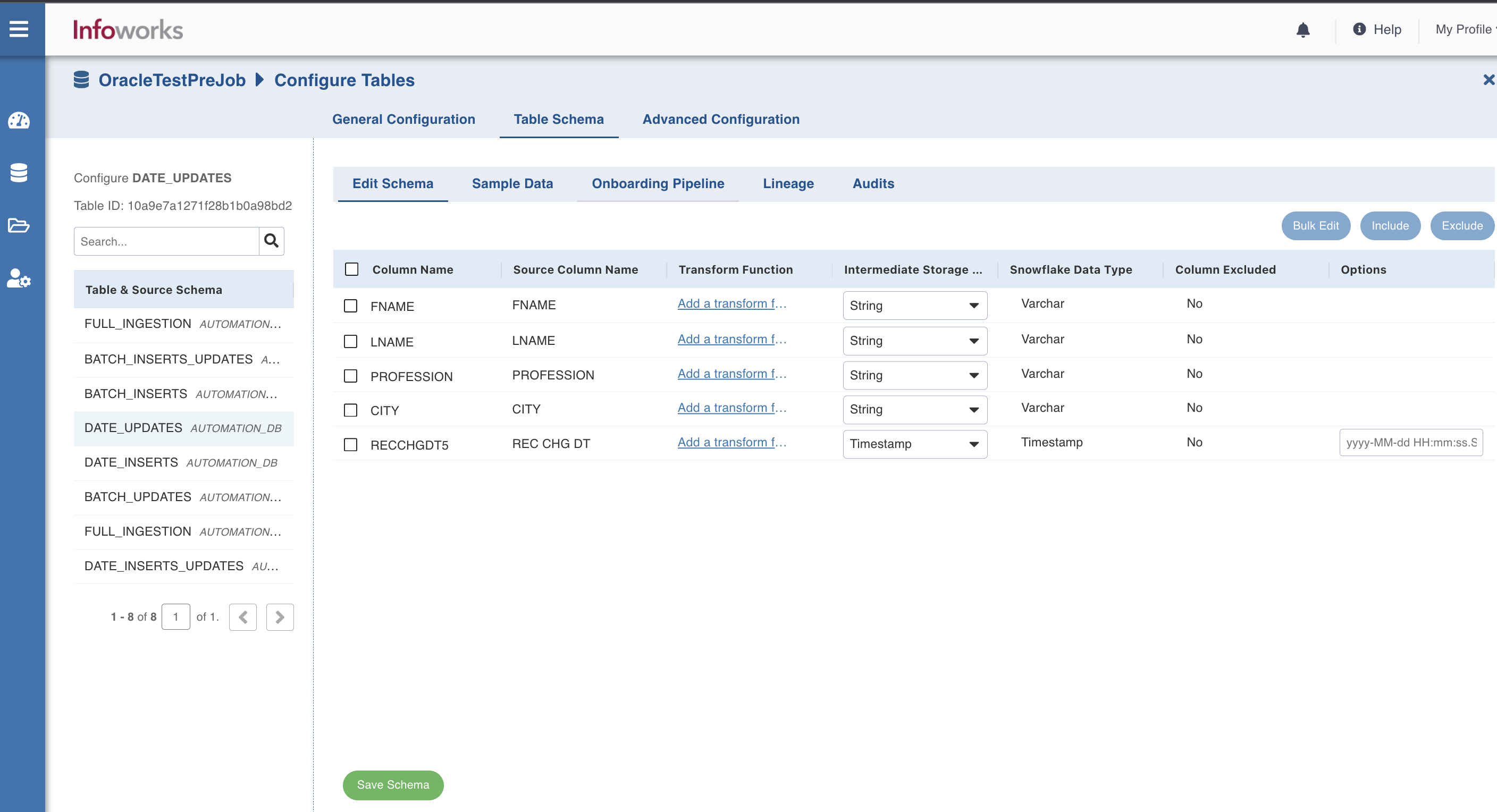
- Navigate to the Tables tab and click Configuration for any of the tables. The General Configuration section appears.
- Navigate to the Table Schema tab, and under the Transform function column, click Add a transform function for the columns for which transformation is required.
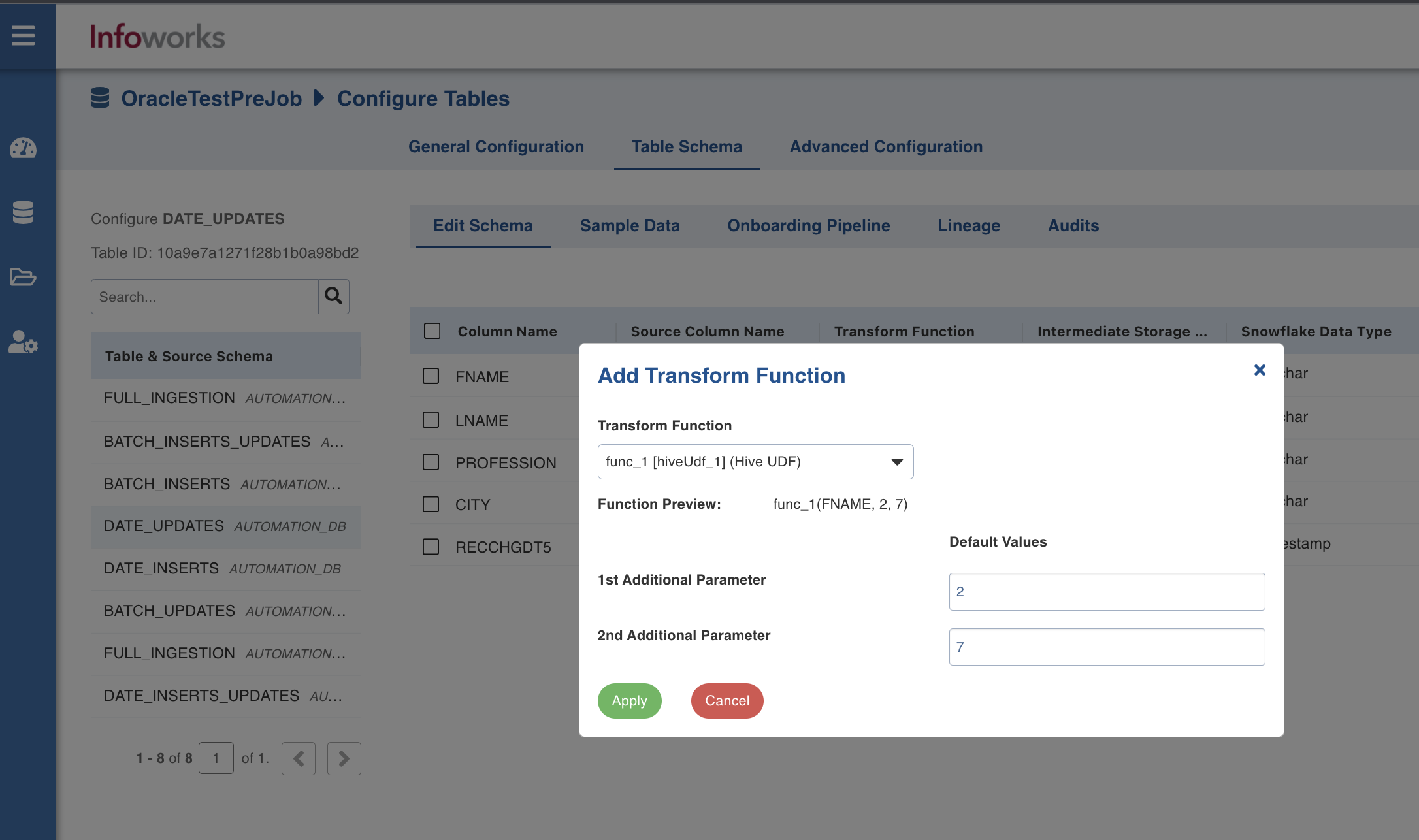
- In the Add Transform Function window, perform the following:
- In case of Hive UDF, select the transform function and enter the default values for 1st Additional Parameter and 2nd Additional Parameter fields. Click Apply.
- In case of Custom Extension, select the transform function and click Apply.
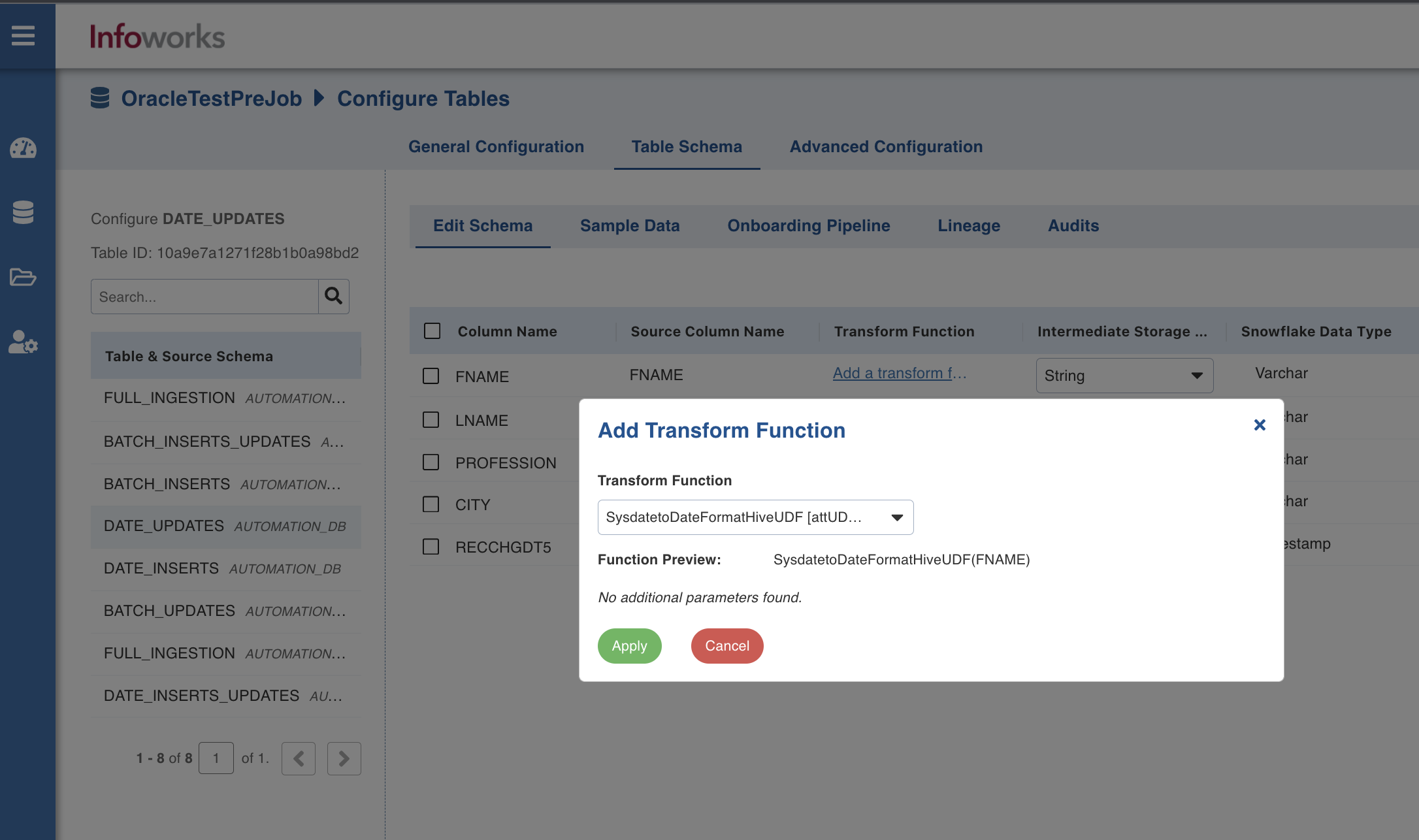
- Click Save Schema. The schema is updated successfully for the columns.
- To view the updated sample data, click the Sample Data tab.
Configuring Deserializers
To configure deserializers, the jar needs to be built the same way as in Procedure to Build the Jar for Upload.
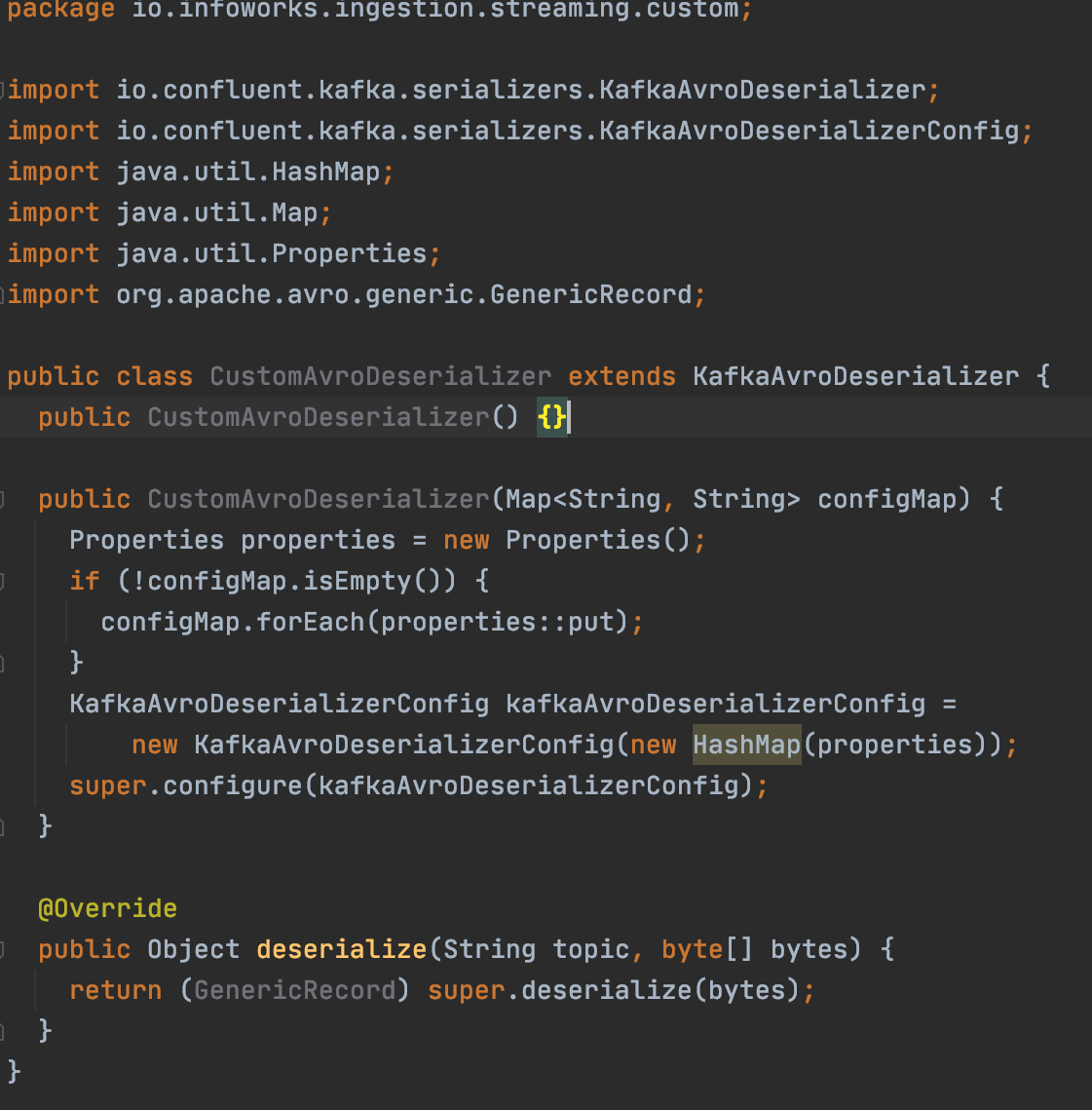
- For Confluent Cloud source with message type as avro, CustomAvroDeserializer is the reference image. You must extend KafkaAvroDeserializer and implement the deserialize method. Return type for this is java.lang.Object.
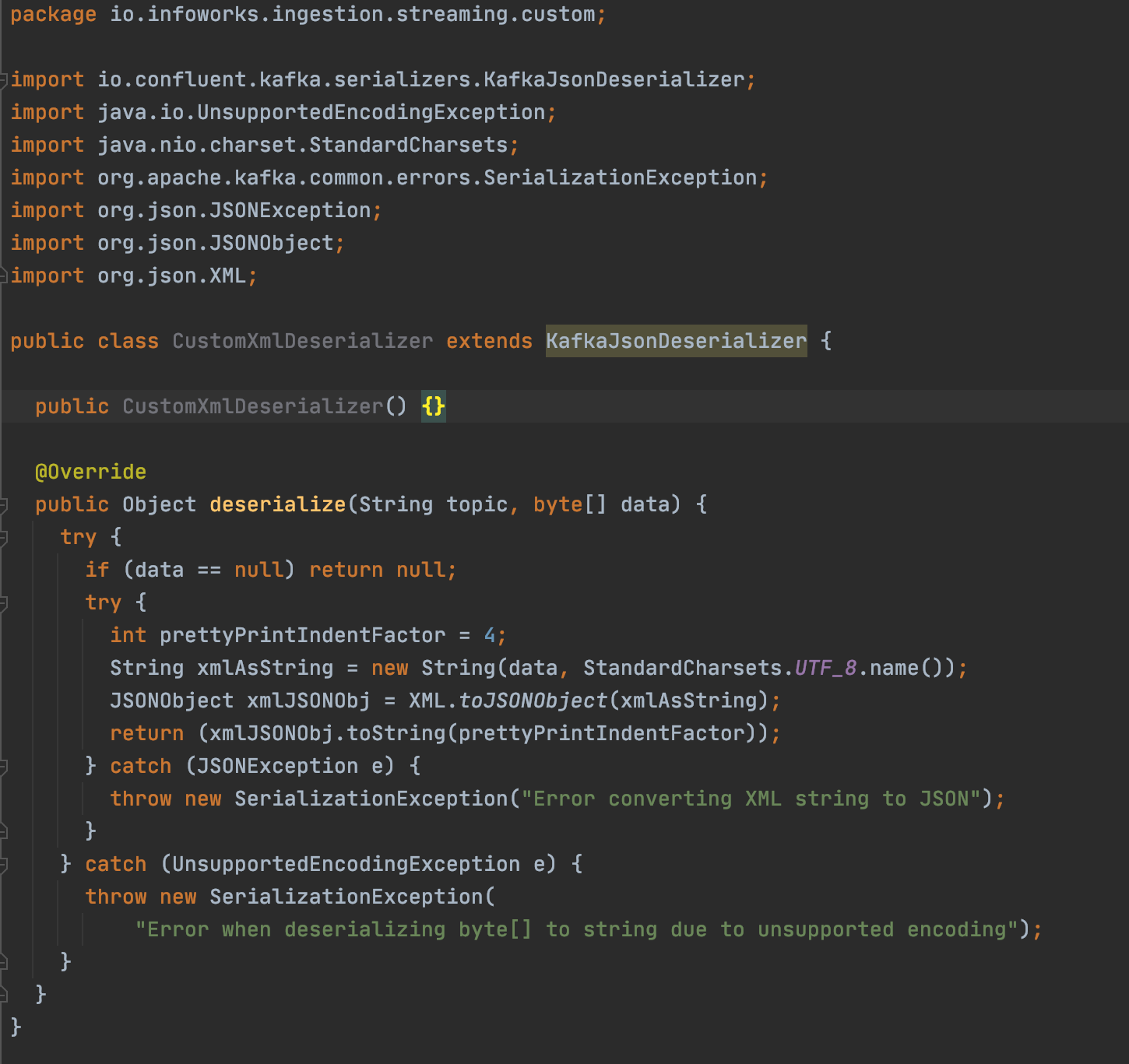
- For Confluent Cloud source with message type as Json, CustomXmlDeserializer is the reference image. You must extend KafkaJsonDeserializer and implement the deserialize method. Return type for this is java.lang.String.
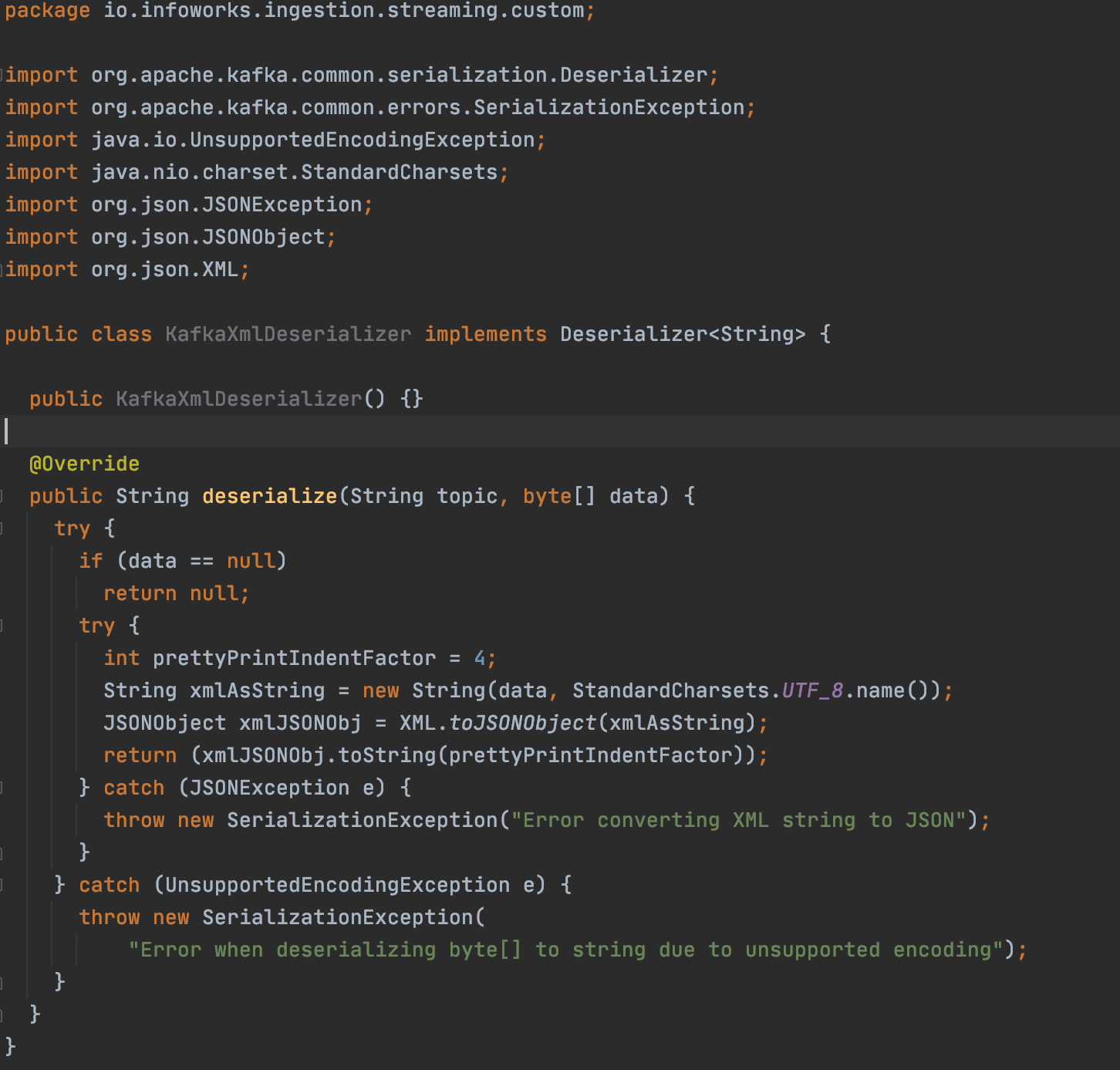
- For Kafka source with message type Json, KafkaXmlDeserializer is the reference image. You must implement Deserializer<String> and implement the deserialize method. Return type for this is java.lang.String.
For more information, refer to the following sample project to understand how deserializer should be implemented.
Using Deserializers
Deserializers needs to be added as a part of Source Setup page.
- Deserializers are only applicable for streaming sources.
- Infoworks uses the default deserializers if no deserializer is selected.
- Fully qualified class name should be unique for each case.
To view the Deserializers that is set, perform the following steps:
- In the left-navigation pane, click Data Sources.
- Select a data source with Kafka or Confluent source type, and click View Source. The Tables section of the source appears.
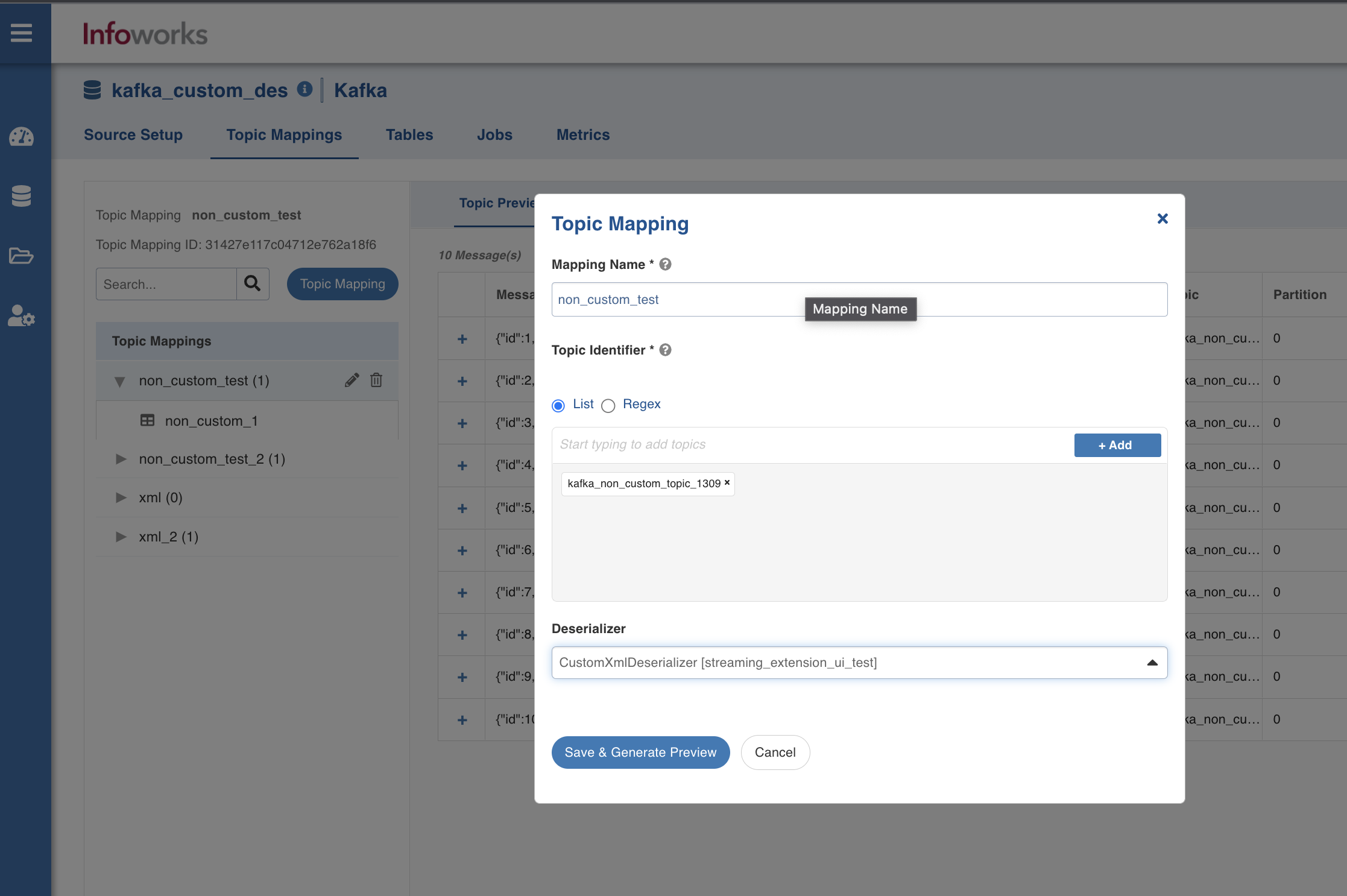
- Navigate to the Topic Mappings tab, and in the Topic Mappings section, click the
icon. - In the Topic Mapping window, enter the following details:
- Mapping Name: Name for the topic mapping to be configured.
- Topic Identifier: List or regex pattern of the topics to be subscribed. Select List or Regex.
- Regular expression: Expression when the topic identifier is selected as regex.
- Deserializer: Select a deserializer from the drop-down. The format is Alias [extension name].
6. Click Save & Generate Preview.
Managing Job Hooks
Job hooks may be used to execute predefined scripts before/after data is ingested or running a pipeline job. They can be used to perform additional steps such as encrypting or decrypting source files, moving or deleting files, integrating with third party tools, and so on. Scripts may be written in bash or python 3.x. The scripts are executed on the data plane (compute cluster) where the job runs.
To manage the job hooks, perform the following steps:
- In Infoworks, navigate to Admin > Extensions > Job Hooks.
- Click Create Job Hook.
- In the Add Job Hook page, enter the following details:
- Name: A user-friendly name for the job hook. For example, SampleJobHook.
- Execution Type: Choose Python or Bash.
- Upload the external scripts. Multiple files can be uploaded.
- Executable File Name: Select one of the uploaded external scripts.
- Parameters: Any external parameters that should be passed to the executable script.
- Additional environment variables: these are user configurable environment variables that can be configured to retrieve secrets from secret store and will be available in job hook process with specified name.
- Fail Job if hook fails: If the check box is selected, job status fails if the hook fails.
- Click Save.
You can view the details of the created job hook by clicking the Audits icon in the Actions column.
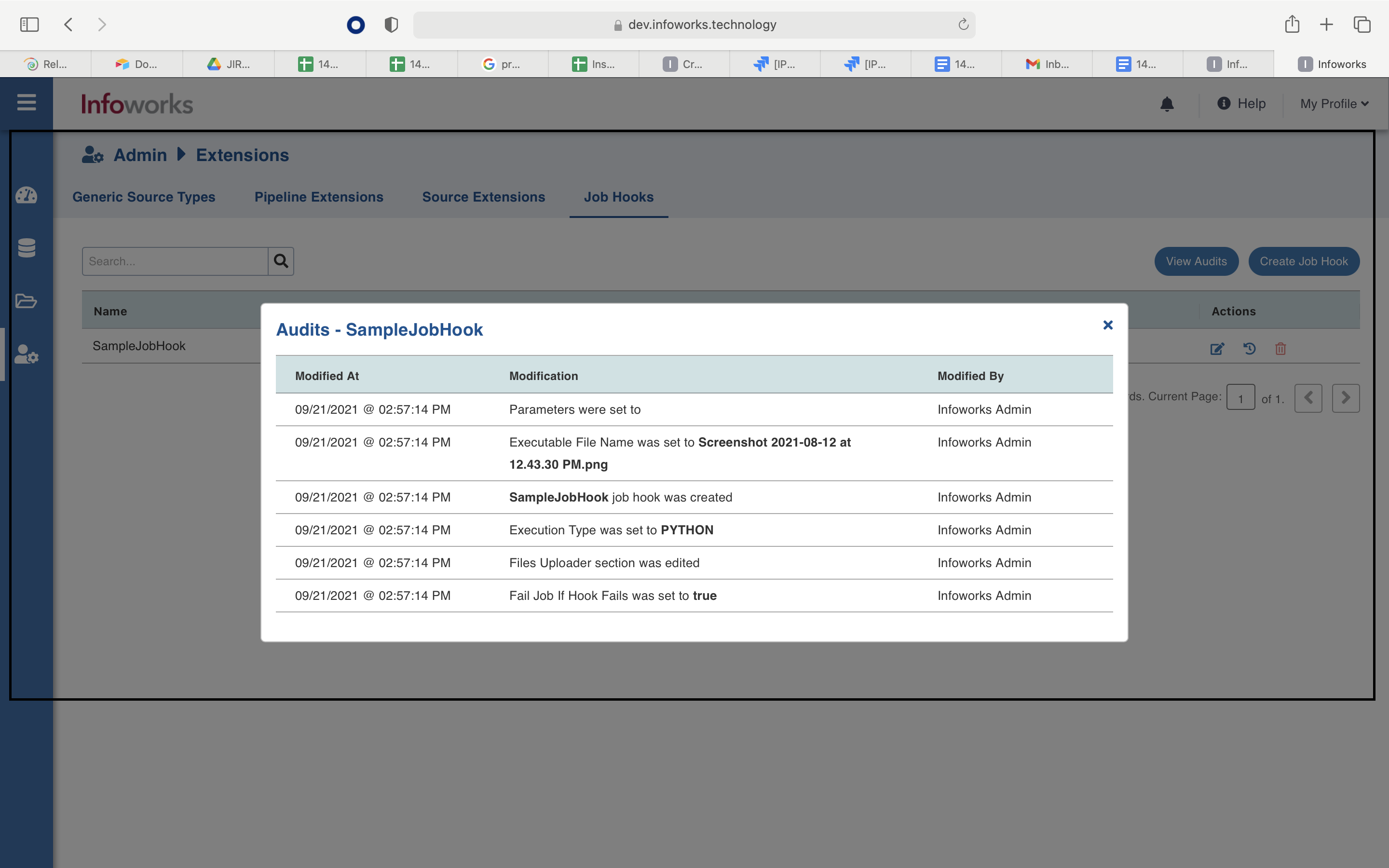
Using a Job Hook
You can associate job hooks to
- an existing data source while onboarding new data.
- to new/existing pipeline
Setting up a Job Hook for Ingestion
To set up a job hook, perform the following steps:
- In Infoworks, navigate to Data Sources > View Source > Source Setup. Alternatively, you can also navigate to Data Sources > Onboard New Data, and click a source connector.
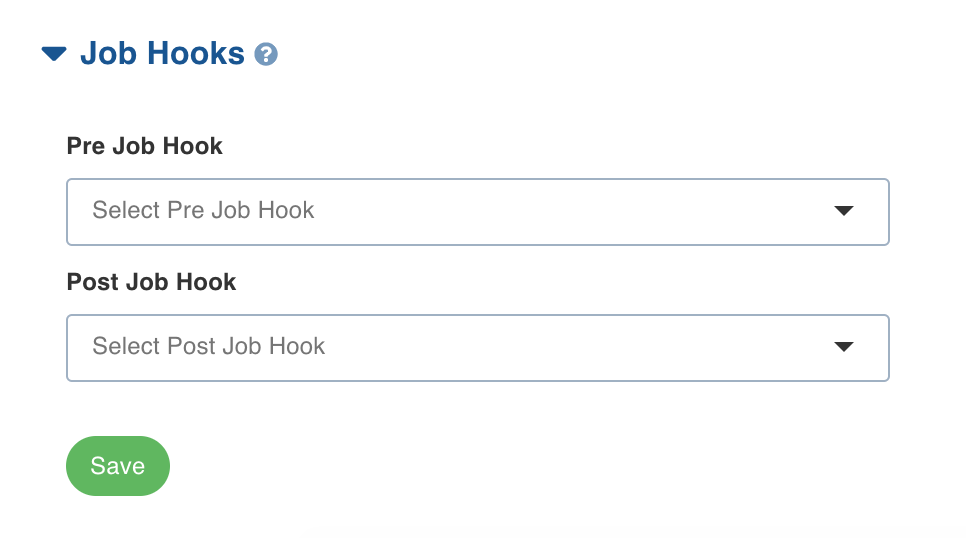
- Scroll down to the bottom, and expand the Job Hooks section.
- If you need to run a hook before ingesting a data source, select it in the Pre Job Hook drop-down.
- If you need to run a hook after ingesting a data source, select it in the Post Job Hook drop-down.
- Click Save. The job hooks are saved successfully.
Supported Dynamic Environment Variables
User can use the following variables in the pre-post job hook scripts assuming they will be available as environment variables.
- jobId
- tableNameAtSource
- schemaNameAtSource
- catalogNameAtSource
- targetTableName
- targetSchemaName
- sourceId
- sourceName
- tableId
- workflowId
- workflowRunId
- sourceBasePath (for file sources)
- targetTablePath
- jobType
- jobStatus (only accessible from post hook)
Setting up a Job Hook for Pipeline
To set up a job hook, perform the following steps:
Step 1: In Infoworks, go to Domains and click the respective domain name
Step 2: Click the Pipelines tab and click the respective pipeline.
Step 3: Under the Settings tab, scroll-down to the Job Hooks section.
- If you need to run a hook before running a pipeline job, select it in the Pre Job Hook drop-down.
- If you need to run a hook after running a pipeline job, select it in the Post Job Hook drop-down.
Step 4: Click Save. The job hooks are saved successfully.

Supported Dynamic Environment Variables for Pipelines
User can use the following variables in the running the pre-post pipeline job assuming they will be available as environment variables.
- jobId
- jobType
- jobName
- pipelineId
- pipelineName
- workflowId
- workflowRunId
- remoteJobBasePath
- remoteJobConfBasePath
- jobStatus (only accessible from post hook)