Onboarding Data from Parquet
Parquet is an open-source file format for Hadoop. Parquet stores nested data structures in a flat columnar format. Compared to traditional approaches where data is stored in a row-oriented approach, Parquet is more efficient in terms of storage and performance. |
The Infoworks Parquet Ingestion feature allows users to migrate data from Hadoop/Hive to Databricks.
Infoworks supports the following types of Parquet files:
- Parquet files that have been ingested by Infoworks or created by Infoworks transformations in the source data lake.
- Parquet files for which Spark can obtain partitioned metadata (with folder structure format,
$table_path/<partition_column>=<partition_value>/).
Demo
Here is a demo on ingesting data in the Parquet file format.
Setting a Parquet Source
For setting a Parquet source, see Creating a Source. Ensure that the Source Type selected is Parquet.
Configuring a Parquet Source
For configuring a Parquet source, see Setting Up a Source.
Parquet Configurations
- Select either of the following storage locations depending on where the files are stored: Databricks File System (DBFS), Cloud Storage.
Databricks File System (DBFS) is a distributed file system mounted into a Databricks workspace and available on Databricks clusters. DBFS is an abstraction on top of scalable cloud object storage. For more details, see Databricks Documentation.
Infoworks allows you to access files from cloud storage, ingest the data, and perform analytics on them. Cloud storage refers to data stored on remote servers accessed from the internet, or cloud.
For preparing data for ingestion from Databricks File System (DBFS), enter the following:
- Source Base Path: The path to the base directory in DBFS where all the Parquet files to be accessed are stored. The other files are relative from this path. For example, if the file is stored in iw/filestorage/ingestion/sample in DBFS, the base path refers to iw/filestorage/ingestion.
Infoworks allows you to access files from cloud storage, ingest the data, and perform analytics on them. Cloud storage refers to data stored on remote servers accessed from the internet, or cloud.
For preparing data for ingestion Cloud Storage, enter the following:
- Cloud Type: The options include Azure Blob Storage (WASB) or Amazon S3.
Windows Azure Storage Blob (WASB), also known as Blob Storage, is a file system for storing large amounts of unstructured object data, such as text or binary data. For more details, see Azure Blob Storage Documentation.
For Azure Blob Storage (WASB), enter the following:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Container name | The name of the container in the storage account, in which the files are stored. A container organizes a set of blobs, similar to a directory in a file system. For more details, see Create a container. |
| Storage Account name | The unique name of the storage account. You can obtain the name from the For more details, see Create a storage account. |
| Authentication Mechanism | The mechanism using which the security information is stored. The options include Account Key and None. Account key refers to the access key to authenticate applications when making requests to this Azure storage account. You can choose None to access data from public cloud storage folders. |
| Enable Support for Azure Government Cloud Regions | Select this check box to enable ingestion from a source available in the Government Cloud regions. This option is not editable if the data source tables are already created. |
| Storage Account key | The access key to authenticate applications when making requests to this Azure storage account. For more details, see Manage storage account access keys. |
| Source Base Path | The path to the base directory in the file system where all the Parquet files to be accessed are stored. The other files are relative from this path. The default value is /, which indicates the base path of the following format: wasbs://<container_name>@<account_name>.blob.core.windows.net/ |
Amazon S3 or Amazon Simple Storage Service is a service offered by Amazon Web Services that provides object storage through a web service interface. For more details, see Amazon S3 Documentation.
For Amazon S3, enter the following:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication Mechanism | The mechanism using which the security information is stored. |
| Access ID | The access ID uniquely identifies an AWS account. You can use the access ID to send authenticated requests to Amazon S3. The Access ID is a 20-character, alphanumeric string, for example, AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE. For the access ID details, contact your AWS Cloud admin. |
| Secret key | The secret key to send requests using the AWS account. The secret access key is a 40-character string, for example, wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY. For the secret key details, contact your AWS Cloud admin. For more details, see AWS Account Access Keys. |
| Source Base Path | The bucket where all the Parquet files to be accessed are stored. For more details, see Creating a bucket. |
For Azure DataLake Storage (ADLS) Gen2, enter the following:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Scheme | Scheme used to access ADLS Gen2. The available options are abfs:// and abfss:// |
| Authentication Mechanism | The mechanism using which the security information is stored. The options include Access Key and Service Principal. Access key refers to the key to authenticate applications when making requests to this Azure storage account. Service Principal functions as the identity of the application instance. |
| File System | Provide a file system where all the data of an artifact will be stored. |
| Storage Account Name | Provide the name of Azure storage account. |
| Access Key | Provide the storage access key to connect to ADLS. |
| Application ID | Provide the ID that uniquely identifies the user application. |
| Directory ID | Provide the ID that uniquely identifies the Azure AD instance. |
| Service Credential | Provide the credential string value that the application uses to prove its identity. |
File Mapping
This page allows you to map individual files stored in the file system. You can add tables to represent each file, crawl them, and map the file details based on the preview.
- Click the File Mappings tab and click Add Table.
- Enter the following file location details:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Table Name | The name to represent the table in the Infoworks User Interface. |
| Target Table Name | The name for the target table to be created in the data lake. |
| Source Relative Path | The path to the directory (relative to source base path) where the Parquet files are stored. For example, if the file is stored in iw/filestorage/ingestion/sample, the relative path refers to /sample. |
| Target Relative Path | The target directory path (relative to the target base path) to store the crawled output. Hive external tables will be created on this directory. |
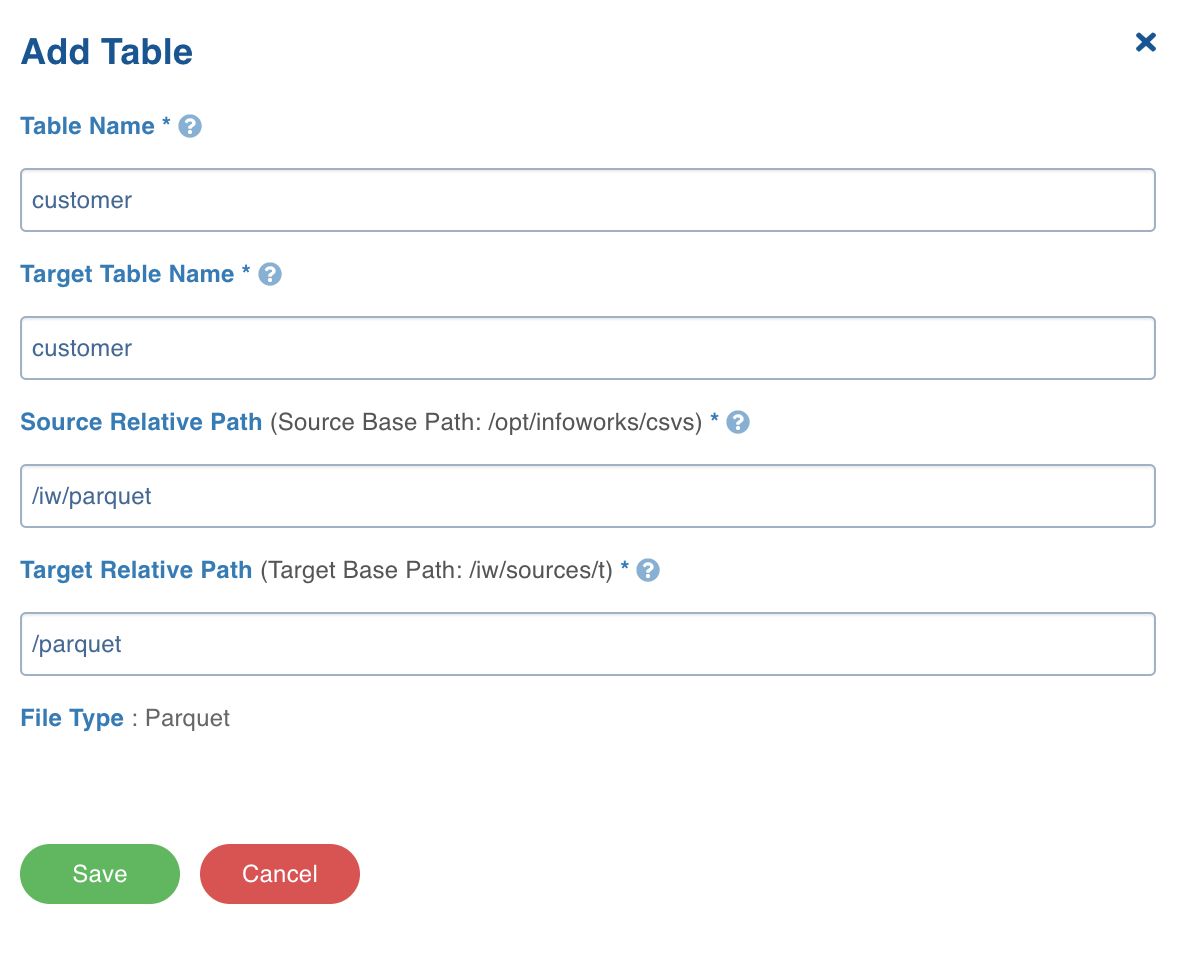
3. Click Save.
- Select the table and click Crawl Schema.
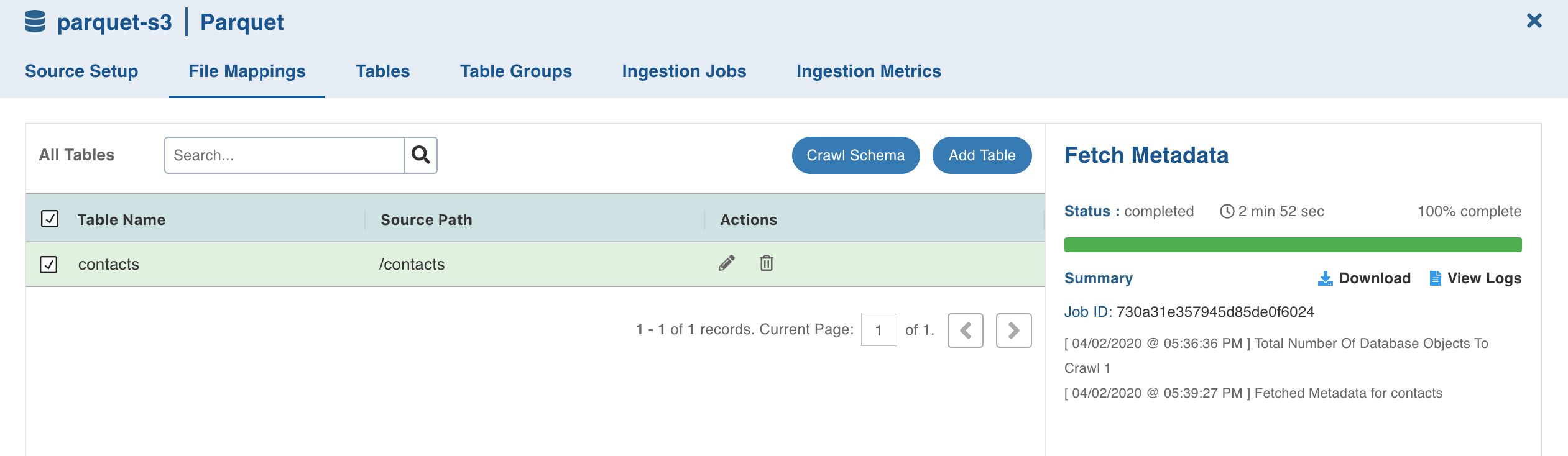
The metadata will be crawled and the job status will be displayed.
Ingesting Parquet Data
For ingesting a Parquet source, see Onboarding Data.
- Infoworks does not support parquet file ingestion when column name has space characters.
- Infoworks does not support handling of non-standard Spark partition data, unless the Parquet files are created by Infoworks.
- Infoworks does not support reading data, for which the folder name in the partitioned table data is not of the
part_col=valformat.
Editing Schema
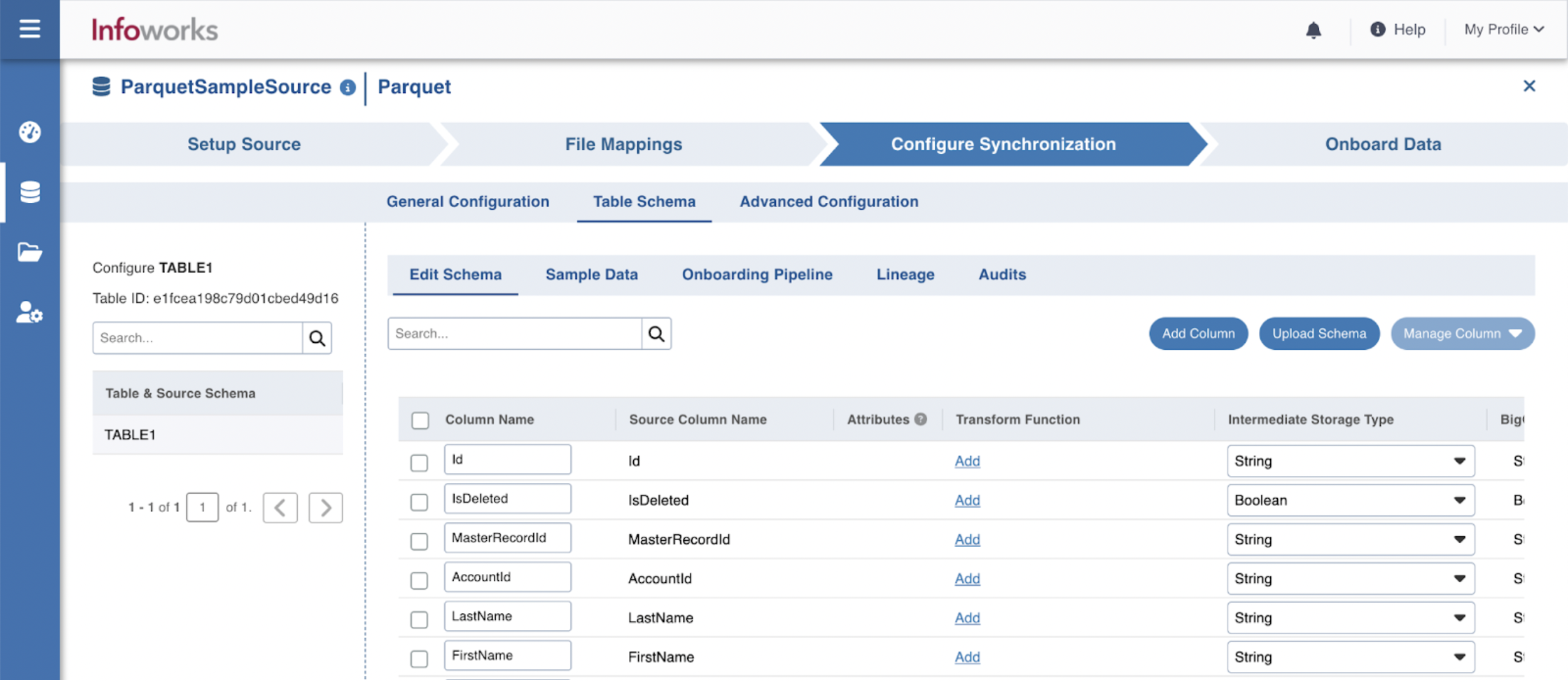
To edit the schema:
Step 1: Click the Details button for the required table.
Step 2: In the Edit Schema section, click the required column and perform the required changes. You can also add columns, upload schema, and perform bulk edit.
Additional Information
- If records are not adhering to schema and there is a datatype mismatch, the job will fail.