Infoworks Installation on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Prerequisites
| Package Installer | Version Used |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes | 1.25.x or above |
| Kubectl | 1.25.x or above |
| Helm | 3.7.x-3.9.x |
| Ingress-Controller | 4.2.5 |
| Python | 3.8 |
If you are using MAC OS to deploy Infoworks on to cluster, you must install the following package:
| Package Installer | Version Used |
|---|---|
| GNU-SED | 4.8 or more |
- Ensure that GKE Kubernetes cluster is connected to internet.
- Set up GKE Kubernetes cluster. For more information, refer to the Google Documentation.
- Ensure that Kubernetes version should be 1.25.x or above.
- Infoworks recommends creating the GKE Kubernetes cluster with private access and a VM as a Bastion host with Linux-based OS should be created within the VPC.
- If INGRESS_CONTROLLER_CLASS is set to nginx, then Infoworks recommends setting up ingress-controller externally with the required configuration. To set up nginx ingress-controller externally, refer to External Setup for Ingress Controller.
- If KEDA_ENABLED is set to true, then Infoworks recommends setting up KEDA externally with the required configuration. To set up KEDA externally, refer to External KEDA Setup.
- Install gcloud, Helm V3 and Kubectl on the Bastion host. Refer to official documentation for Helm and Kubectl installation instructions.
- Verify the following prerequisites
- Run
gcloud versionto ensure that gcloud is installed. - Run
helm versionto ensure that Helm is installed. - Run
kubectl versionto ensure that Kubectl is installed. - Run
python3 -Vto ensure that python (with venv) is installed. - Run
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-venvto install python pip and Virtual Environment package.
- Run
root@GKE-dev-qa-bastion:~$ gcloud version Google Cloud SDK 355.0.0 beta 2021.08.27 bq 2.0.71 core 2021.08.27 gsutil 4.67root@GKE-dev-qa-bastion:~$ helm versionversion.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.9.0", GitCommit:"7ceeda6c585217a19a1131663d8cd1f7d641b2a7", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.17.5"}root@GKE-dev-qa-bastion:~$ kubectl versionClient Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"22", GitVersion:"v1.22.6", GitCommit:"f59f5c2fda36e4036b49ec027e556a15456108f0", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2022-01-19T17:33:06Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.12", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"22", GitVersion:"v1.22.6", GitCommit:"07959215dd83b4ae6317b33c824f845abd578642", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2022-03-30T18:28:25Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.12", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}root@GKE-dev-qa-bastion:~# python3 -VPython 3.8.10- Set up Kubernetes Cluster in GKE for connection using gcloud by executing the following command:
Step 1: gcloud auth login--launch-browser
xxxxxxxxxxinfoworks@bastion-host-devqa:~$ gcloud auth login --launch-browserYou are running on a Google Compute Engine virtual machine.It is recommended that you use service accounts for authentication.You can run: $ gcloud config set account `ACCOUNT`to switch accounts if necessary.Your credentials may be visible to others with access to thisvirtual machine. Are you sure you want to authenticate withyour personal account?Do you want to continue (Y/n)? yGo to the following link in your browser: https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth?response_type=code&client_id=325559.apps.googleusercontent.com&redirect_uri=urn%3Aietf%3th%3A2.0%3Aoob&scope=openid+https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fuserinfo.email+https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fcloud-platform+https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fappengine.admin+https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fcompute+https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Faccounts.reauth&state=SAb9x0mF&prompt=consent&access_type=offline&code_challenge=QYUAZb16CNHSgS57B9Hc&code_challenge_method=S256Enter verification code:After successful verification, the following confirmation message appears.
xxxxxxxxxxYou are now logged in as [user@infoworks.io].Your current project is [iw-gcpdev]. You can change this setting by running: $ gcloud config set project PROJECT_IDStep 2: Identify the cluster name, zone/region, and project you want to connect to. Run the following command with these details:
xxxxxxxxxxgcloud container clusters get-credentials <clusterName> --zone <zoneName> --project <projectName>or
xxxxxxxxxxgcloud container clusters get-credentials <clusterName> --region <regionName> --project <projectName>xxxxxxxxxxFetching cluster endpoint and auth data.kubeconfig entry generated for <clusterName>.Persistent Storages
Persistence ensures to persist the data even if a pod restarts or fails due to various reasons. Infoworks needs the following persistent storages to be configured:
- Databases (MongoDB and Postgres) and RabbitMQ
- Infoworks Job Logs and Uploads
Run the following command to fetch the storage classes:
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl get storageclass --no-headersxxxxxxxxxxfilestore-nfs cluster.local/nfs-provisioner-nfs-subdir-external-provisioner premium-rwo pd.csi.storage.gke.io standard (default) kubernetes.io/gce-pd standard-rwo pd.csi.storage.gke.io| Storage Class Category | Comments |
|---|---|
| Standard | This is the default storage class category, which comes along with the cluster |
| premium-rwo & standard-rwo | Used when the Compute Engine Persistent Disk CSI Driver feature is enabled while creating the GKE Cluster. Check this setting in the Kubernetes cluster created above using Google Cloud Console. |
| filestore-client | This is a custom name. If Infoworks job logs and uploads are to be persisted. Infoworks installation automates creation of basic Google Filestore and configures the Filestore via NFS Client provisioner for the mounts in the Kubernetes Cluster. If you want to customize the Google Filestore as per your requirement , refer to Google FileStore documentation. To create a Filestore in shared VPC of service projects, refer to Google Filestore on Shared VPC Documentation. |
Filestore Mount Path
Step 1: Log in to Google Cloud console.
Step 2: Go to top-left of the navigation pane, under the Storage section, select Filestore > Instances.
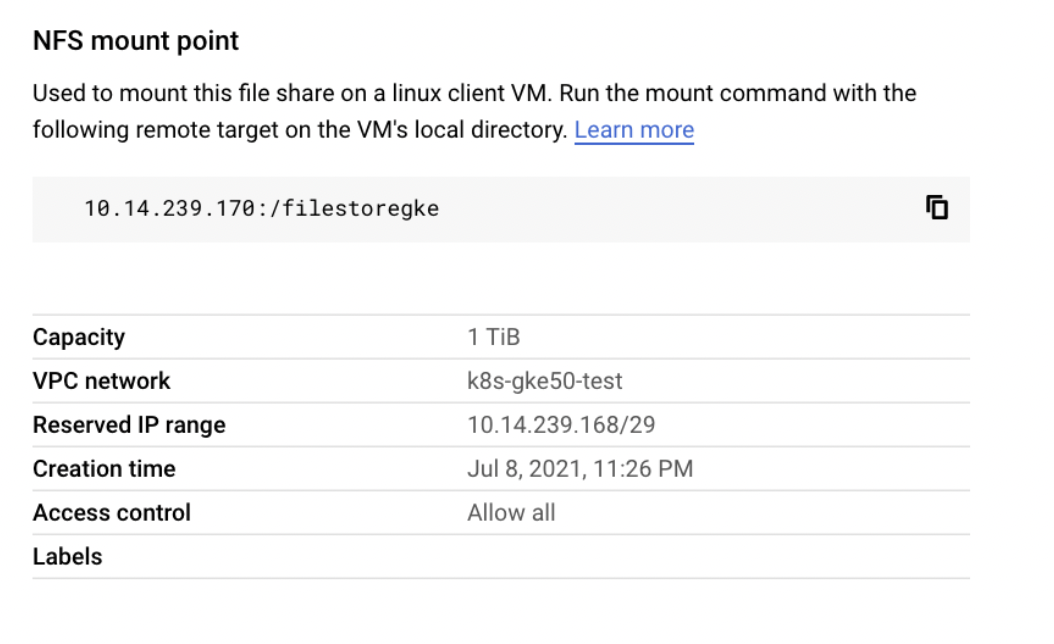
Step 3: Click the Filestore instances you created. Once the server is in READY state. Get the details of the NFS mount point as shown below.
Installing Infoworks on Kubernetes
Take a backup of values.yaml file before every upgrade. |
/opt/infoworks.
Step 1: Create Infoworks directory under /opt.
sudo mkdir -p /opt/infoworks
Step 2: Change permissions of /opt/infoworks directory
sudo chown -R <user>:<group/user> /opt/infoworks
Step 3: Change the directory path to /opt/infoworks.
cd /opt/infoworks
Step 4: To download Infoworks Kubernetes template, execute the following command:
xxxxxxxxxxwget https://iw-saas-setup.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/5.4/iwx_installer_k8s_5.4.1.tar.gzStep 5: Extract the downloaded file.
xxxxxxxxxxtar xzf iwx_installer_k8s_5.4.1.tar.gzStep 6: Navigate to the extracted directory iw-k8s-installer.
Step 7: Open configure.sh file in the directory.
Step 8: Configure the following parameters as described in the table, and then save the file
Generic Configuration
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| IW_NAMESPACE | Namespace of Infoworks Deployment | This field is autofilled. However, you can also customize the namespace as per your requirement. |
| IW_RELEASE_NAME | Release Name of Infoworks Deployment | This field is autofilled. However, you can also customize the release name as per your requirement. |
| IW_CLOUD_PROVIDER | Name of the cloud provider of Kubernetes cluster | Enter gcp. |
| NFS_STORAGECLASS_NAME | Name of the NFS storage class | Enter a valid Storage class name. Ex: filestore-client. |
| DB_STORAGECLASS_NAME | Name of the Database Storage Class | Enter a valid Storage class name. Ex: premium-rwo |
| INGRESS_ENABLED | This field indicates enabling Ingress for Infoworks Deployment | Select true or false. Default: true. Infoworks requires you to select true. |
| INGRESS_CONTROLLER_CLASS | Name of the ingress controller class | Default value: nginx. |
| INGRESS_TYPE | Name of the ingress type | Two values: external and internal. Default value: internal. external: Infoworks app is exposed to internet. internal: Infoworks app is restricted to internal network. |
| INGRESS_AUTO_PROVISIONER | This field indicates installing ingress controller provisioner | Select true or false. Default: true. If ingress-controller is already installed, set this as false. |
| IW_DNS_NAME | DNS hostname of the Infoworks deployment | Enter a valid DNS name. |
| IW_SSL_PORT | This field enables port and protocol for SSL communication | Select true or false. Default: true |
| IW_HA | This field enables high-availability of Infoworks deployment. | Select true or false. Default value: true. Infoworks recommendation: true i.e. enabling HA. |
| IW_HOSTED_REGISTRY | This field indicates if the Container Registry hosted by Infoworks. | Enter true |
| USE_GCP_REGISTRY | This field enables separate registry for cloud. GCR is being used by Infoworks by default. To override cloud specific registry images, provide input "false". | Select true or false. Default value: true. |
Autoscaling Configuration
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| KEDA_ENABLED | This field enables to configure autoscaling to Infoworks deployment using KEDA. | Select true or false. Default value: false. |
| KEDA_AUTO_PROVISIONER | This field enables installing KEDA Kubernetes deployment automatically by Infoworks deployment | Select true or false. Default value: false. |
num_executors in conf.properties. If the number of Hangman instances changes due to autoscaling, then the total number of jobs Infoworks handles also changes. To fix the total number of concurrent Infoworks jobs, you must disable the autoscaling on the Hangman service and set the number of Hangman replicas manually as described in the Enabling Scalability#enabling-scalability section.
Service Mesh Configuration for Security
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| SERVICE_MESH_ENABLED | This field enables to configure service mesh to Infoworks deployment | Enter false. |
| SERVICE_MESH_NAME | This field is the name of the service mesh. | Keep this field empty. |
MongoDB Configuration
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| EXTERNAL_MONGO | This field enables external mongoDB support for Infoworks deployment | Select true or false. Default value: false. |
The following fields are applicable if EXTERNAL_MONGO= true.
| Fields | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| MONGO_SRV | This field enables DNS connection string for MongoDB Atlas | Select true or false. Default value: true (If external MongoDB Atlas is enabled) |
| MONGODB_HOSTNAME | The Mongo Host URL to connect to | Enter the Mongo Server or Seed DNS hostname (without prefix) |
| MONGODB_USERNAME | The Mongo User to authenticate as. | Enter a user that has at least read/write permissions over the databases mentioned. |
| MONGODB_USE_SECRET_PASSWORD | This field enables user to configure MongoDB password in the secrets before installing Infoworks. Steps will be documented | Select true or false. Default Value: false. If value is false then we need ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD field to be filled, else secret name is required. (Optional value). |
| MONGODB_SECRET_NAME | This is the name of the MongoDB encrypted password stored in secrets. (Manual Creation) | User will create the secret and has to provide the name of the secret. (Optional value) Keep it empty if not sure. For more information, refer to the "For MongoDB" section mentioned below. |
| MONGODB_ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD | The Password of the aforementioned MONGODB_USERNAME | Enter the Password of the MONGO_USER |
| MONGO_FORCE_DROP | This field delete all the data in the MongoDB Atlas and initialize the data freshly. | Select true or false. Default value: false. Infoworks recommends to keep the value to false always. |
| INFOWORKS_MONGODB_DATABASE_NAME | This field indicates the name of the Infoworks MongoDB database in Atlas. | Provide the name of the database for Infoworks setup. |
| INFOWORKS_SCHEDULER_MONGODB_DATABASE_NAME | This field indicates the name of the Infoworks scheduler MongoDB database in Atlas | Provide the name of the scheduler database for Infoworks setup. |
PostgresDB Configuration
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| EXTERNAL_POSTGRESDB | This field enables external PostgresDB support for Infoworks deployment | Select true or false. Default value: false. |
The following fields are applicable if EXTERNAL_POSTGRESDB= true
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| POSTGRESDB_HOSTNAME | The PostgresDB Host URL to connect to | Enter the PostgresDB Server hostname (without prefix) |
| POSTGRESDB_USERNAME | The PostgresDB User to authenticate as. | Enter a user that has at least read/write permissions over the databases mentioned. |
| POSTGRESDB_USE_SECRET_PASSWORD | This field enables user to configure Postgres password in the secrets before installing Infoworks. Steps will be documented | Select true or false. Default Value: false. If value is false then we need ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD field to be filled, else secret name is required. (Optional value). |
| POSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME | This is the name of the Postgres encrypted password stored in secrets. (Manual Creation) | User will create the secret and has to provide the name of the secret. (Optional value) Keep it empty if not sure. For more information, refer to the "For Postgres" section mentioned below. |
| POSTGRESDB_ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD | The Password of the aforementioned POSTGRESDB_USERNAME | Enter the Password of the POSTGRESDB_USER |
| INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME | This field indicates the name of the Infoworks Postgres database in the Postgres server. | Provide the name of the database for Infoworks setup. |
Filestore Configuration
Enable the following configuration to set up FileStore automatically using Infoworks installation.
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| FILESTORE_CREATION | This field automatically enables the Filestore setup. | Select true or false. Default value: true. |
If FILESTORE_CREATION is set to true, then the below mentioned fields become valid.
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| FILESTORE_NAME | Name of the Filestore instance | This field is autofilled. However, you can also customize the Filestore as per your requirement. |
| FILESTORE_PROJECT | Name of the GCP Project ID to create Filestore instance | Provide Project ID. To locate Project ID, refer to Locating Project ID. |
| FILESTORE_ZONE | Name of the GCP zone to create Filestore instance | Provide zone name. |
| FILESTORE_NETWORK | Name of the GCP network to create FIlestore instance. | Provide the network detail. |
| FILESTORE_AUTO_PROVISIONER | This field indicates installing NFS provisioner. | Select true or false. Default value: true |
| FILESTORE_INSTANCE_MOUNTPATH | Mount Path of the Filestore instance | This field is autofilled. However, you can also customize the namespace as per your requirement. |
If FILESTORE_CREATION is false and FILESTORE_AUTO_PROVISIONER is true.
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| FILESTORE_INSTANCE_IP | IP Address of the Filestore instance | Provide a valid IP Address |
Step 9 (Optional): Enable NodeSelector/Toleration and Custom annotations etc. by editing values.yaml file manually before deploying Infoworks deployment.
Step 10 (Optional): To run Infoworks jobs on separate workloads, edit values.yaml file under infoworks folder. Specifically, you need to edit jobnodeSelector and jobtolerations fields based on the node pool you created in the Node Pools
nodeSelector and tolerations fields.
workernodeSelector andworkertolerations fields.
xxxxxxxxxxnodeSelector: {}tolerations: []jobnodeSelector: group: developmentjobtolerations: - key: "dedicated" operator: "Equal" value: "iwjobs" effect: "NoSchedule"Step 11 (Optional): To define the PaaS passwords, there are two methods:
First method
The password must be put in pre-existing secrets in the same namespace.
For MongoDB
(i) Set MONGODB_USE_SECRET_PASSWORD=true
(ii) To create the custom secret resource, run the following commands from the iw-k8s-installer directory.
xxxxxxxxxx$ encrypted_mongo_password=$(./infoworks_security/infoworks_security.sh --encrypt -p "<mongo-password>" | xargs echo -n | base64 -w 0)$ IW_NAMESPACE=<IW_NAMESPACE> $ MONGODB_SECRET_NAME=<MONGODB_SECRET_NAME>$ kubectl create ns ${IW_NAMESPACE}$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOFapiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata: name: ${MONGODB_SECRET_NAME} namespace: ${IW_NAMESPACE}data: MONGO_PASS: ${encrypted_mongo_password}type: OpaqueEOFMONGODB_SECRET_NAME and IW_NAMESPACE according to the inputs given to the automated script. <mongo-password> is the plaintext password.
For Postgres
(i) Set POSTGRESDB_USE_SECRET_PASSWORD=true
(ii) To create the custom secret resource, run the following commands from the iw-k8s-installer directory.
xxxxxxxxxx$ encrypted_postgres_password=$(./infoworks_security/infoworks_security.sh --encrypt -p "<postgres-password>" | xargs echo -n | base64 -w 0)$ IW_NAMESPACE=<IW_NAMESPACE> $ POSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME=<POSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME>$ kubectl create ns ${IW_NAMESPACE}$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOFapiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata: name: ${POSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME} namespace: ${IW_NAMESPACE}data: POSTGRES_PASS: ${encrypted_postgres_password}type: OpaqueEOFPOSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME and IW_NAMESPACE according to the inputs given to the automated script. postgres-password is the plaintext password.
Second Method
You can give the password to the Automated Script, which will encrypt it to store it in the templates.
Step 12: To run the script, you must provide execute permission beforehand by running the following command.
xxxxxxxxxxchmod 755 iw_deploy.shStep 13: Run the script
xxxxxxxxxx./iw_deploy.shxxxxxxxxxxNOTE: (Optional) Enable NodeSelector/Toleration and Custom annotations etc., by editing values.yaml file manually before deploying infoworks app Checking for basic Prerequisites.Found HELMv3Found KUBECTLTesting Kubernetes basic cluster connectionValidation is done: Kubernetes Cluster is Authorized Enter kubernetes namespace to deploy Infoworksv1Enter release name for infoworks v1Creating v1 namespace on kubernetes cluster namespace/v1 createdInput the Kubernetes Cluster Cloud Provider Environment- aws/gcp/azure gcpList of available StorageClass in Kubernetes Cluster enterprise-multishare-rwxenterprise-rwxfilestore-nfs-devfilestore-nfs-newfilestore-sharedvpc-examplemy-scpremium-rwopremium-rwxstandardstandard-rwostandard-rwxINFO: NFS and Database (Disk) persistance is recommended and always set to True Enter NFS StorageClass: Select StorageClass from listfilestore-nfs-devEnter DATABASE StorageClass: Select StorageClass from liststandard-rwoENABLE INGRESS: true or false Default: "true"trueSelect Ingress Controller Class: cloud native "cloud" or external "nginx" Default: "nginx"nginxSelect Ingress type: internal or external Default: "internal"externalProvisioning Nginx Ingress controller automatically.NOTE: If the Ingress-Nginx is already provisioned manually skip this by selecting 'N' Do you want to continue y/n? Default: "y"nEnter DNS Hostname to access Infoworks: for example: iwapp.infoworks.local sample.infoworks.technologyENABLE SSL for the Infoworks Ingress deployment (This enables port and protocol only): true or false Default: "true"trueENABLE HA for Infoworks Setup: true or false Default: "true"falseENABLE external MongoDB access for Infoworks Setup: true or false Default: "false"trueENABLE SRV connection string for MongoDB access for Infoworks Setup: true or false, MongoDB Atlas default is true Default: "true"trueInput MongoDB DNS connection string for Infoworks Setup: Private link ex - {DB_DEPLOYMENT_NAME}-pl-0.{RANDOM}.mongodb.net mongo-pl-0.1234.mongodb.netInput the database name of MongoDB for Infoworks Setup. default: infoworks-db infoworks-newInput the scheduler database name of MongoDB for Infoworks Setup. default: quartzio quartzioENABLE external PostgresDB access for Infoworks Setup: true or false Default: "false"trueInput postgresDB Username for Infoworks Setup. Assuming the user have permissions to create databases if doesn't exist. infoworksInput the Postgres user password for Infoworks database Setup. Infoworks will encrypt the Postgres password. Input the database name of Postgres for Infoworks Setup. default: airflow airflowENABLE Service mesh for Infoworks Setup, Only Linkerd supported: true or false Default: "false"falsehelm upgrade -i v1 ./infoworks -n v1 -f ./infoworks/values.yamlSince the above installation was configured for ingress-controller, run the following command to get the domain mapping done.
xxxxxxxxxxNAME: intrueLAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 2 17:25:20 2021NAMESPACE: intrueSTATUS: deployedREVISION: 1xxxxxxxxxxkubectl get ingress --namespace samplexxxxxxxxxxNAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGEv1-ingress <none> sample.infoworks.technology 43.13.121.142 80 3m43sGet the application URL by running these commands: http://sample.infoworks.technology.
Enabling SSL
If you set INGRESS_CONTROLLER_CLASS to nginx, add SSL Termination in the TLS section of values.yaml file either before running the automated script or after the deployment.
Step 1: Log in to Linux machine on the latest Debian-based OS.
Step 2: Ensure libssl-dev package is installed.
Step 3: Provide DNS Name for Infoworks deployment
Generating Self-Signed SSL Certificate:
To generate SSL, run the following commands:
xxxxxxxxxxmkdir certificatesxxxxxxxxxxcd certificatesxxxxxxxxxxopenssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048 # Creates a RSA keyxxxxxxxxxxopenssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -key ca.key -subj "/C=CN/ST=CA/L=US/O=Infoworks, Inc./CN=Infoworks Root CA" -out ca.crtxxxxxxxxxxopenssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout server.key -subj "/C=CN/ST=CA/L=US/O=Infoworks, Inc./CN=*.infoworks.domain" -out server.csrxxxxxxxxxxopenssl x509 -req -extfile <(printf "subjectAltName=DNS:infoworks.domain,DNS:subdomain.infoworks.domain") -days 365 -in server.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crtKeep a note of server.crt and server.key files for self-signed certificates for Nginx SSL Termination and provide the valid values for ingress_tls_secret_name and namespace_of_infoworks.
Run the following command to add the tls certificates to the Kubernetes cluster.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl create secret tls <ingress_tls_secret_name> --cert=server.crt --key=server.key -n <namespace_of_infoworks>Edit values.yaml file to look similar to the following sample file.
xxxxxxxxxxingress: enabled: true protocol: https port: 443 hostname: subdomain.infoworks.cloud ingressClassName: "nginx" annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 10m nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: "300" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "300" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "300" tls: - hosts: - subdomain.infoworks.cloud secretName: <ingress_tls_secret_name>It is suggested to make changes in the values.yaml file and add the below parameters as annotations in the ingress block, replacing <URL> to the DNS of your deployment, as defined in IW_DNS_NAME.
xxxxxxxxxxnginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors: "true"nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: | proxy_hide_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin; add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Origin" "<URL>" always; add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Methods" "GET, PUT, POST, OPTIONS" always; add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Headers" "DNT,X-CustomHeader,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Authorization" always; add_header "Access-Control-Expose-Headers" "Content-Length,Content-Range" always;nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-credentials: "true"After adding the annotations, the values.yaml file should look as shown below.
xxxxxxxxxxingress: enabled: true protocol: https port: 443 hostname: subdomain.infoworks.cloud ingressClassName: "nginx" annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 10m nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: "300" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "300" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "300" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors: "true" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: | proxy_hide_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin; add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Origin" "subdomain.infoworks.cloud" always; add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Methods" "GET, PUT, POST, OPTIONS" always; add_header "Access-Control-Allow-Headers" "DNT,X-CustomHeader,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Authorization" always; add_header "Access-Control-Expose-Headers" "Content-Length,Content-Range" always; nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-credentials: "true" tls: - hosts: - subdomain.infoworks.cloud secretName: <ingress_tls_secret_name>Enabling High-Availability and Scalability
Enabling High-Availability
Infoworks installation enables high-availability configuration while setting up Infoworks in Kubernetes. You can enable high-availability by editing the helm file called values.yaml.
Step 1: To edit values.yaml file, perform the action given in the following snippet.
xxxxxxxxxxglobal: haEnabled: true replicas: 2Step 2: Run HELM upgrade command.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade <release_name> infoworks/ --values infoworks/values.yaml -n <namespace>This enables the high availability for Infoworks.
Enabling Scalability
Infoworks installation supports auto-scaling of pods.
For a scalable solution:
- There must be a minimum of two replicas, if HA is enabled.
- They can be scaled to any number based on available resources (CPU and memory).
- Infoworks supports scalability of source, pipeline, and workflow jobs out of the box. Ensure that there are available resources in the Kubernetes cluster.
Infoworks services will scale automatically based on the workloads and resource utilization for the running pods.
To modify any autoscaling configuration, edit the horizontalPodScaling sub-section under global section in the values.yaml file.
xxxxxxxxxxglobal: ... ... horizontalPodScaling: hpaEnabled: true hpaMaxReplicas: 5 scalingUpWindowSeconds: 20 hpaScaleUpFreq: 45 scalingDownWindowSeconds: 300| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| hpaEnabled | By default, hpa is enabled for the install/upgrade. Set the value to false to disable hpa. |
| hpaMaxReplicas | This field indicates the number of maximum replicas the pod can scale out horizontally. |
| scalingUpWindowSeconds | This field indicates the duration a pod must wait before scaling out activity. |
| hpaScaleUpFreq | This field indicates the duration HPA must wait before scaling out. |
| scalingDownWindowSeconds | This field indicates the duration a pod should wait before scaling in the activity. |
However, there are three pods which require manual scaling based on workload increase, namely platform-dispatcher, hangman, and orchestrator-scheduler.
There are two ways to enable scalability:
1. By editing the values.yaml file.
Step 1: Edit the values.yaml file.
xxxxxxxxxxinfoworks(deploymentname): replicas: 4platform-dispatcher, hangman, or orchestrator-scheduler with actual name.
For example:
xxxxxxxxxxinfoworksHangman: replicas: 4Step 2: To increase the scalability manually, run HELM upgrade command:
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade <release_name> infoworks/ --values infoworks/values.yaml -n <namespace>2. Using Kubectl
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl scale --replicas=3 rs/<deploymentName>For example:
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl scale --replicas=3 rs/releasename-hangman-id -n <namespace>Optional Configuration
For setting up Pod Disruption Budget
A Pod Disruption Budget (PDB) defines the budget for voluntary disruption. In essence, a human operator is letting the cluster be aware of a minimum threshold in terms of available pods that the cluster needs to guarantee in order to ensure a baseline availability or performance. For more information, refer to the PDB documentation.
To set up PDB:
Step 1: Navigate to the directory IW_HOME/iw-k8s-installer .
Step 2: Edit the values.yaml file.
xxxxxxxxxxvi infoworks/values.yamlStep 3: Under the global section and pdb sub-section, set the enabled field to true.
xxxxxxxxxxglobal: image:= pdb: enabled: true minAvailable: 1Step 4: Run HELM upgrade command.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade <release_name> infoworks/ --values infoworks/values.yaml -n <namespace>For setting up PodAntiAffinity
If the anti-affinity requirements specified by this field are not met at the scheduling time, the pod will not be scheduled onto the node. If the anti-affinity requirements specified by this field cease to be met at some point during pod execution (e.g. due to a pod label update), the system may or may not try to eventually evict the pod from its node. For more information, refer to the PodAntiAffinity documentation.
To set up PodAntiAffinity:
Step 1: Navigate to the directory IW_HOME/iw-k8s-installer .
Step 2: Edit the values.yaml file.
xxxxxxxxxxvi infoworks/values.yamlStep 3: Under the global section, set the podAntiAffinity field to true.
xxxxxxxxxxglobal: image:= pdb:= podAntiAffinity: falseStep 4: Run HELM upgrade command.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade <release_name> infoworks/ --values infoworks/values.yaml -n <namespace>xxxxxxxxxxglobal: haEnabled: true replicas: 2Increasing the Size of PVCs
To scale the size of PVCs attached to the pods:
Step 1: Note the storage class of the PVCs to be scaled.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl -n <namespace> get pvcStep 2: Ensure allowVolumeExpansion is set to true in the storageClass.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl edit storageClass <storage-class-of-pvc>allowVolumeExpansion: trueStep 3: Delete the managing statefulset without deleting the pods.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl -n <namespace> get stskubectl -n <namespace> delete sts --cascade=orphan <statefulset name>Step 4: For each PVC, upscale the size (ensure all PVCs attached managed by a single statefulset have the same size. For example, all Postgres managed PVCs must have the same size).
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl -n <namespace> get pvckubectl -n <namespace> edit pvc <pvc-name>Step 5: Navigate to the helm chart used for Infoworks deployment.
Step 6: Edit the values.yaml file to update the size of the corresponding database to the new value.
Step 7: Run the helm upgrade command.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade --recreate-pods --reuse-values -f <path-to-your-values.yaml> <your-release-name> <path-to-your-chart> -n <your-namespace>Above upgrade command will recreate all pods with the same PVCs.
Updating the MongoDB and PostgresDB Credentials
To update the MongoDB and/or PostgresDB credentials in the Infoworks deployment, follow the below given procedure.
Updating the MongoDB Credentials
Updating Encrypted Passwords Stored in values.yaml
There are two methods to update password:
Method 1
To update MongoDB encrypted passwords that are stored in values.yaml file, with the existing configure.sh file, use the IW_DEPLOY script to populate values.yaml:
Step 1: Download and untar the Infoworks kubernetes template, if not already present, according to the iwx-version in your existing deployment.
xxxxxxxxxxversion="5.4.1"major_version=$(echo $version | cut -d '.' -f 1,2)wget https://iw-saas-setup.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/$major_version/iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gztar xzf iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gzStep 2: If a new template was downloaded, replace the iw-k8s-installer/configure.sh as well as iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yaml with the older file.
xxxxxxxxxxmv /path/to/older/configure.sh iw-k8s-installer/configure.shmv /path/to/older/values.yaml iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yamlStep 3: Change the directory path to iw-k8s-installer.
xxxxxxxxxxcd iw-k8s-installerStep 4: Replace the following values with a blank string in the configure.sh file.
xxxxxxxxxxMONGODB_USERNAME=""MONGODB_ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD=""Step 5: Run iw_deploy.sh. Once you receive "Seems like you have already configured Infoworks once. Do you want to override? y/n Default: n", enter “Y”. This will prompt the user to provide input for the values that were blank in the previous step. The script will then replace the infoworks/values.yaml file with the updated values.
xxxxxxxxxxinfoworks@bastion-host:~/iw-k8s-installer$ ./iw_deploy.sh NOTE: (Optional) Enable NodeSelector/Toleration and Customannotations etc., by editing values.yaml file manually before deploying infoworks app Seems like you have already configured Infoworks once. Do you want to override? y/n Default: nyChecking for basic Pre requisite.Found HELMv3Found KUBECTLTesting Kubernetes basic cluster connectionValidation is done: Kubernetes Cluster is Authorized qa-541 Namespace already existsInput MongoDB Username for Infoworks Setup. Assuming the user have permissions to create databases if doesn't exist. updated-mongouserInput the MongoDB password for Infoworks database Setup. Infoworks will encrypt the MongoDB password. Upgrade INFOWORKS helm upgrade release-name ./infoworks --values ./infoworks/values.yaml -n namespaceStep 6: Run the following command to upgrade by specifying your namespace and helm release name according to the values given in the configure.sh file.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade $IW_RELEASE_NAME ./infoworks --values ./infoworks/values.yaml -n $IW_NAMESPACEMethod 2
To update MongoDB encrypted passwords, you can directly modify the values.yaml file.
Step 1: Download and untar the Infoworks Kubernetes Template, if not already present, according to the iwx-version in your existing deployment.
xxxxxxxxxxversion="5.4.1"major_version=$(echo $version | cut -d '.' -f 1,2)wget https://iw-saas-setup.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/$major_version/iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gztar xzf iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gzStep 2: If a new template was downloaded, replace the iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yaml with the older file.
xxxxxxxxxxmv /path/to/older/values.yaml iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yamlStep 3: Change the directory path to iw-k8s-installer directory.
xxxxxxxxxxcd iw-k8s-installerStep 4: Generate the encrypted passwords as needed. To generate any encrypted string, execute the following command.
xxxxxxxxxxencrypted-mongo-password=$(./infoworks_security/infoworks_security.sh --encrypt -p "<password>")This generates your passwords in a secure encrypted format, which has to be provided in the following steps.
Step 5: Replace the following yaml keys with the new values in the infoworks/values.yaml file, if needed.
xxxxxxxxxxdatabases:metaDB: auth: username: "mongo-username" encryptedMongoPass: "encrypted-mongo-password"Step 6: Run the following command to upgrade by specifying your namespace and helm release name according to the installed kubernetes deployment specifications.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade $IW_RELEASE_NAME ./infoworks --values ./infoworks/values.yaml -n $IW_NAMESPACEUpdating Encrypted Passwords Stored as a Separate Secret
To update the MongoDB password:
Step 1: Run the following commands from the iw-k8s-installer directory.
xxxxxxxxxx$ encrypted_mongo_password=$(./infoworks_security/infoworks_security.sh --encrypt -p "<mongo-password>" | xargs echo -n | base64 -w 0)$ IW_NAMESPACE=<IW_NAMESPACE> $ MONGODB_SECRET_NAME=<MONGODB_SECRET_NAME>$ kubectl patch secret -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} ${MONGODB_SECRET_NAME} --type='json' -p="[{'op' : 'replace' ,'path' : '/data/MONGO_PASS ,'value' : '${encrypted_mongo_password}'}]"Step 2: Restart all pods except the databases.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl get pods -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} --no-headers=true | awk '!/-rabbitmq-|-postgres/{print $1}' | xargs kubectl delete -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} podUpdating the PostgresDB Credentials
Updating Encrypted Passwords Stored in values.yaml
There are two methods to update password:
Method 1
To update PostgresDB passwords that are stored in values.yaml file, with the existing configure.sh file, use the IW_DEPLOY script to populate values.yaml.
Step 1: Download and untar the Infoworks Kubernetes Template, if not already present, according to the iwx-version in your existing deployment.
xxxxxxxxxxversion="5.4.1"major_version=$(echo $version | cut -d '.' -f 1,2)wgethttps://iw-saas-setup.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/$major_version/iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gztar xzf iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gzStep 2: If a new template was downloaded, replace the iw-k8s-installer/configure.sh as well as iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yaml with the older file.
xxxxxxxxxxmv /path/to/older/configure.sh iw-k8s-installer/configure.shmv /path/to/older/values.yaml iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yamlStep 3: Change the directory path to iw-k8s-installer.
xxxxxxxxxxcd iw-k8s-installerStep 4: Replace the following values with a blank string in the configure.sh file.
xxxxxxxxxxPOSTGRESDB_USERNAME=""POSTGRESDB_ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD=""Step 5: Run iw_deploy.sh. Once you receive "Seems like you have already configured Infoworks once. Do you want to override? y/n Default: n", enter “Y”. This will prompt the user to provide input for the values that were blank in the previous step. The script will then replace the infoworks/values.yaml file with the updated values.
xxxxxxxxxxinfoworks@bastion-host:~/iw-k8s-installer$ ./iw_deploy.sh NOTE: (Optional) Enable NodeSelector/Toleration and Custom annotations etc., by editing values.yaml file manually before deploying infoworks app Seems like you have already configured Infoworks once. Do you want to override? y/n Default: nyChecking for basic Pre requisite.Found HELMv3Found KUBECTLTesting Kubernetes basic cluster connectionValidation is done: Kubernetes Cluster is Authorized qa-541 Namespace already existsInput postgresDB Username for Infoworks Setup. Assuming the user have permissions to create databases if doesn't exist. updated-postgresuserInput the Postgres user password for Infoworks database Setup. Infoworks will encrypt the Postgres password.Upgrade INFOWORKS ... helm upgrade release-name ./infoworks --values ./infoworks/values.yaml -n namespaceStep 6: Run the following command to upgrade by specifying your namespace and helm release name according to the values given in the configure.sh file.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade $IW_RELEASE_NAME ./infoworks --values ./infoworks/values.yaml -n $IW_NAMESPACEMethod 2
To update PostgresDB encrypted passwords, you can directly modify the values.yaml file.
Step 1: Download and untar the Infoworks Kubernetes Template, if not already present, according to the iwx-version in your existing deployment.
xxxxxxxxxxversion="5.4.1"major_version=$(echo $version | cut -d '.' -f 1,2)wget https://iw-saas-setup.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/$major_version/iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gztar xzf iwx_installer_k8s_$version.tar.gzStep 2: If a new template was downloaded, replace the iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yaml with the older file.
xxxxxxxxxxmv /path/to/older/values.yaml iw-k8s-installer/infoworks/values.yamlStep 3: Change the directory path to iw-k8s-installer.
xxxxxxxxxxcd iw-k8s-installerStep 4: Generate the encrypted passwords as needed. To generate any encrypted string, execute the following command.
xxxxxxxxxxencrypted-postgres-password=$(./infoworks_security/infoworks_security.sh --encrypt -p "<password>")This generates your passwords in a secure encrypted format, which has to be provided in the following steps.
Step 5: Replace the following yaml keys with the new values in the infoworks/values.yaml file, if needed.
xxxxxxxxxxdatabases:postgresDB auth: username: "postgres-username" encryptedPostgresPass: "encrypted-postgres-password"Step 6: Run the following command to upgrade by specifying your namespace and helm release name according to the installed kubernetes deployment specifications.
xxxxxxxxxxhelm upgrade $IW_RELEASE_NAME ./infoworks --values ./infoworks/values.yaml -n $IW_NAMESPACEUpdating Encrypted Passwords Stored as a Separate Secret
To update the PostgresDB password:
Step 1: Run the following commands from the iw-k8s-installer directory.
xxxxxxxxxx$ encrypted_postgres_password=$(./infoworks_security/infoworks_security.sh --encrypt -p "<postgres-password>" | xargs echo -n | base64 -w 0)$ IW_NAMESPACE=<IW_NAMESPACE> $ POSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME=<POSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME>$ kubectl patch secret -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} ${POSTGRESDB_SECRET_NAME} --type='json' -p="[{'op' : 'replace' ,'path' : '/data/POSTGRES_PASS' ,'value' : '${encrypted_postgres_password}'}]"Step 2: Restart the orchestrator and orchestrator-scheduler pods.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl get pods -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} --no-headers=true | awk '/-orchestrator-/{print $1}' | xargs kubectl delete -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} podLimitations
MongoDB Limitations
With HA enabled, scaling the pods from higher to lower has the following limitations:
- Pods need to be manually deleted from replication configuration.
- Disabling HA to Non-HA is not supported once HA is enabled.
Database Limitations
Applicable to PostgresDB, MongoDB, and RabbitMQ.
- PVC’s size can’t be decreased.
- Increasing a PVC’s size requires downtime.
- After downscaling pods, the extra PVCs needs to be manually deleted.
PostgresDB Limitations
In the current HA architecture, on Postgres connection disruption, airflow is unable to reconnect via new connection. Furthermore, the current Postgres proxy is too simplistic to handle connection pools. Hence, if a Postgres master goes down, all running workflows will fail.