PostgresDB PaaS for Azure
Setup Postgres Service on Azure Portal
An Azure Database for PostgreSQL server is created with a configured set of compute and storage resources. The server is created within an Azure resource group.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are necessary for setting up Postgres Database on Azure.
- A Microsoft account is required to work with Azure Cloud Platform. Sign up for a Microsoft account, if you do not have one.
- Ensure that you have an Azure subscription with a billing account.
PostgreSQL Database
Azure Database for PostgreSQL is a managed service that you use to run, manage, and scale highly available PostgreSQL databases in the cloud. To set up Postgres Database, refer to the official Azure Documentation.
Setup Postgres
Step 1: To set up Postgres, navigate to Azure Console, search for Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible servers, and click it.
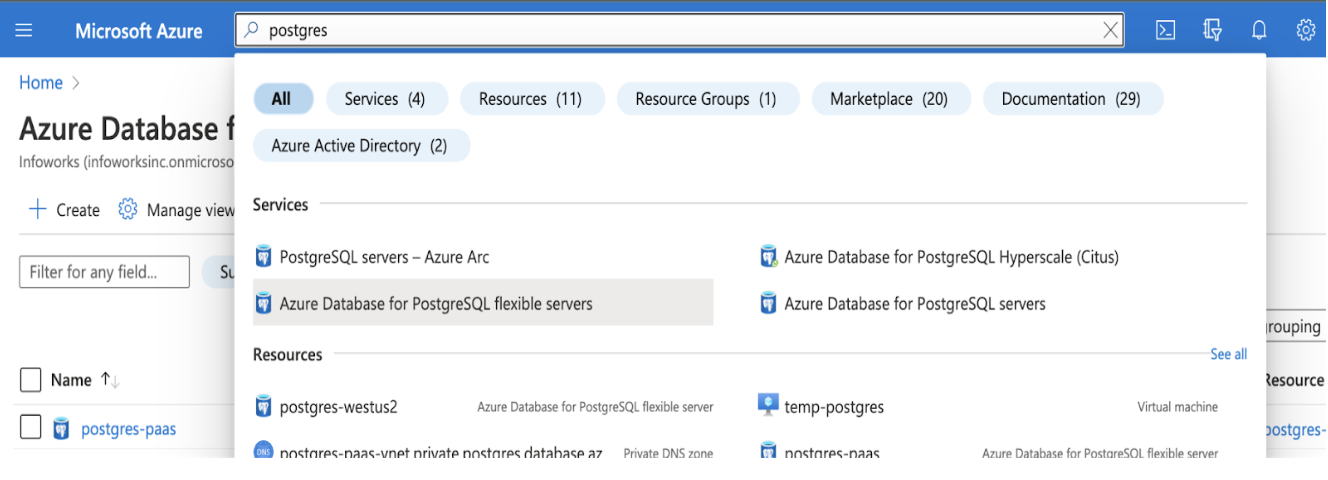
Step 2: Click Create.
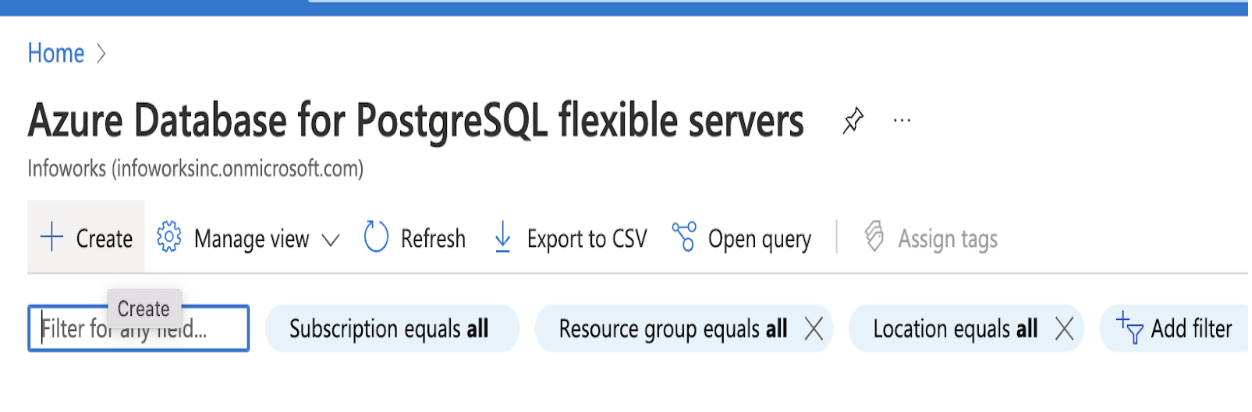
PostgreSQL Basics
This section provides basic information about your Postgres database
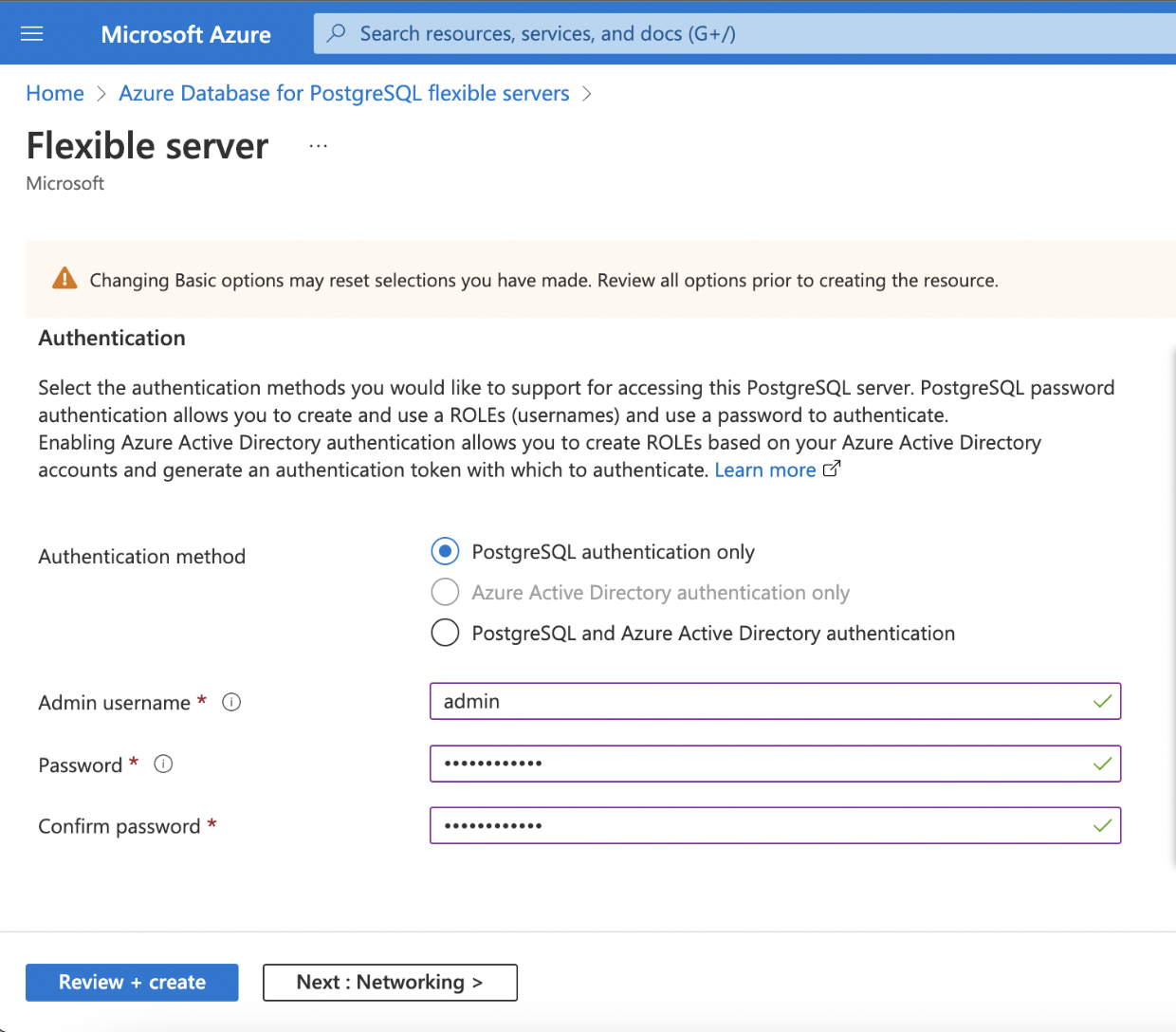
Step 1: Enter the required details for the following mandatory fields.
- Subscription
- Resource Group
- Server Name
- Region
- PostgreSQL Version
- Admin Username
- Password
- Confirm Password
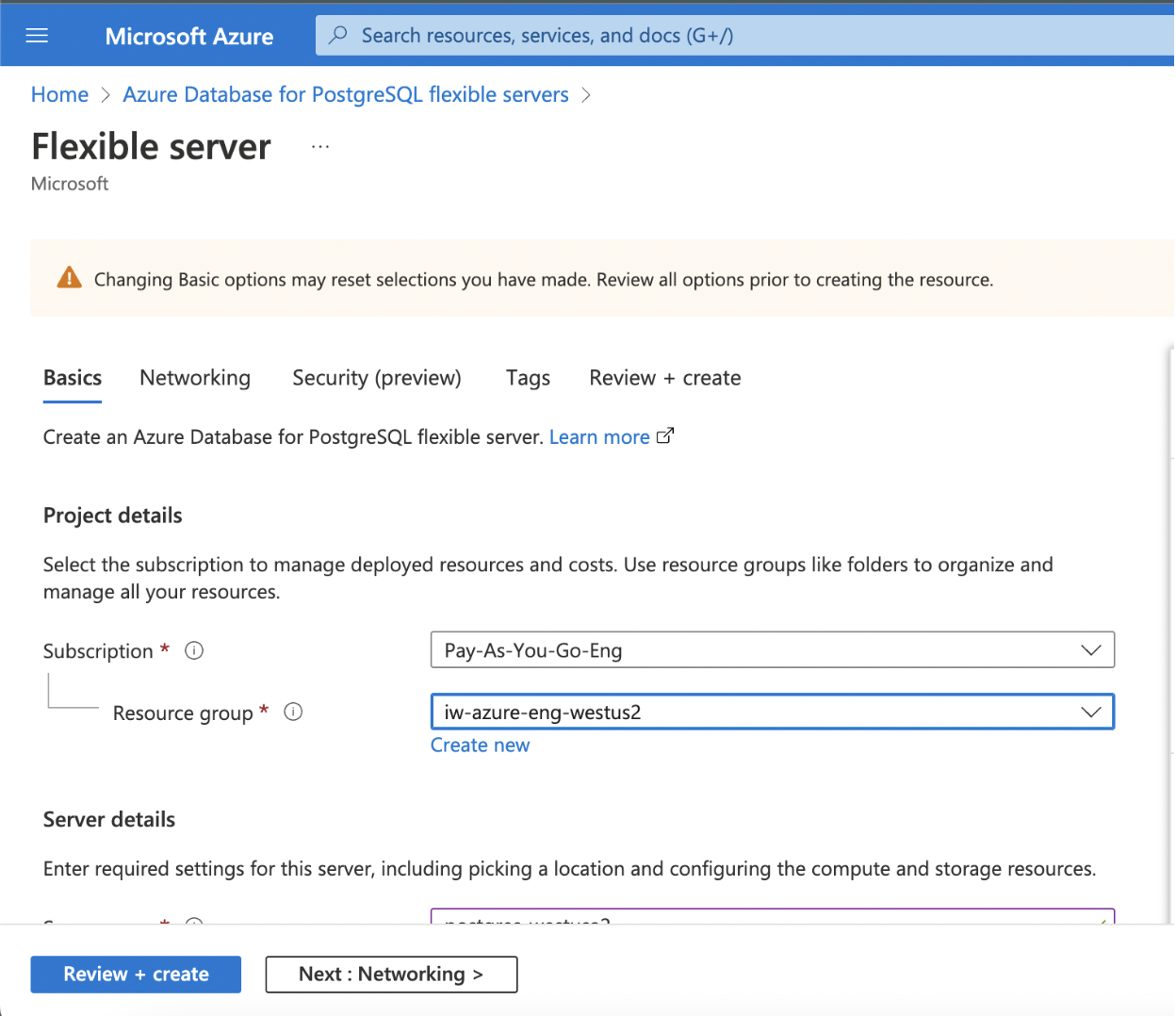
(contd.)
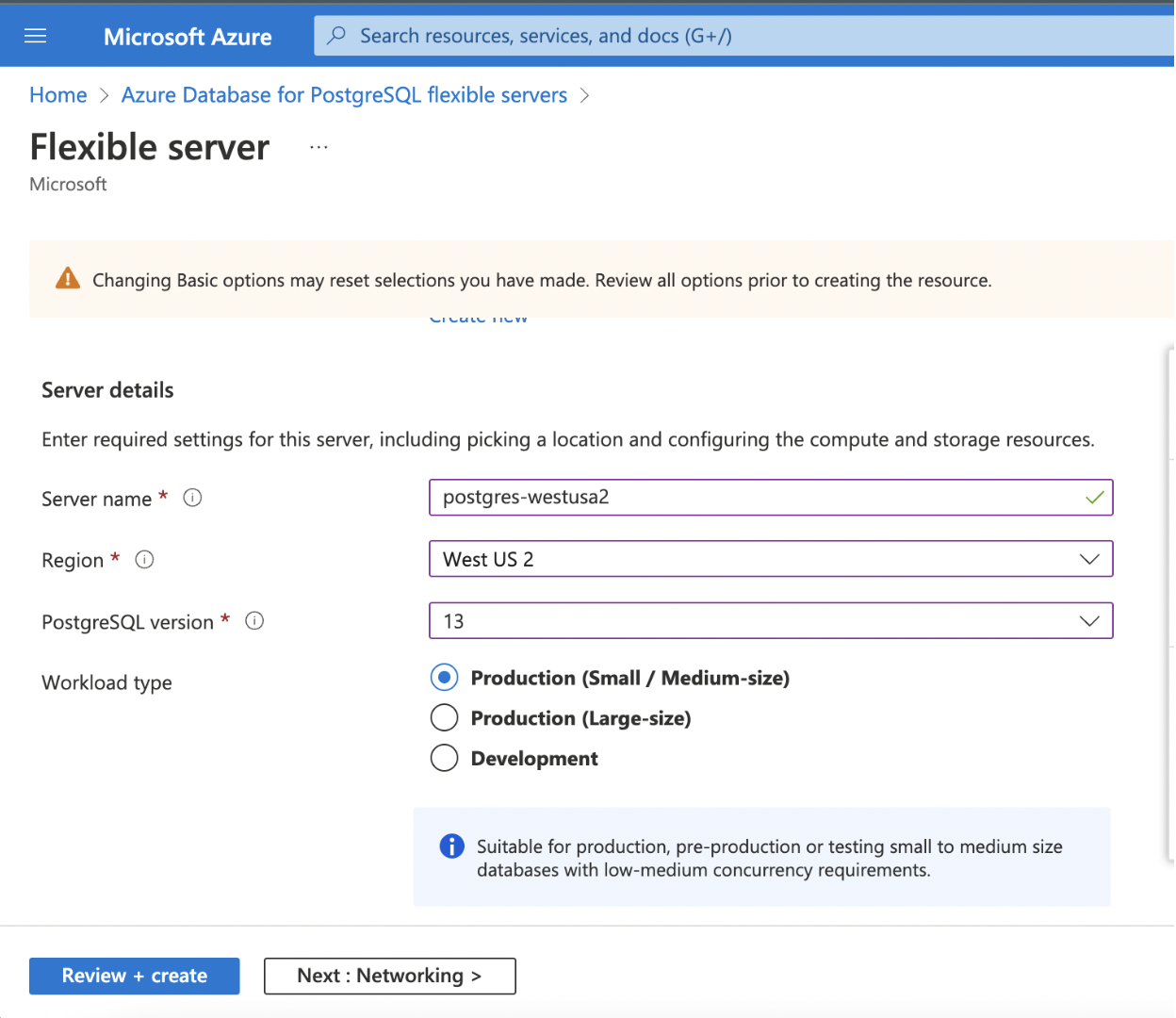
(contd.)
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Subscription | The name of your Subscription(Account) in which the PostgreSQL database is to be set up. |
| Resource Group | Name of the Group under which the PostgreSQL database should be available |
| Server Name | A unique name that identifies your Azure Database for PostgreSQL server. |
| Region | Name of the Region in which the cluster is to be setup. |
| PostgreSQL Version | Infoworks recommends using PostgreSQL Version 13. |
| Workload Type | Select the environment (Development or Production) for your Postgres DB, whichever it will be used for. If the database instance is set up for a critical application, depending upon the usage and the size of data which will be ingested, select the appropriate Size (Small/Medium or Large). |
| Authentication Method | Select the type of Authentication you want to set up. Infoworks supports PostgreSQL authentication only. |
| Admin Username/ Password | Your own login account to use when you connect to the server. The admin login name can't be azure_superuser, azure_pg_admin, admin, administrator, root, guest, or public. It can't start with pg_. Set a strong password using uppercase letters, English lowercase letters, numbers, and non-alphanumeric characters |
Step 2: Click Next: Networking>.
Networking
Networking in the scenario mentioned below describes securing the database and accessing it privately without exposing it to the outside world.
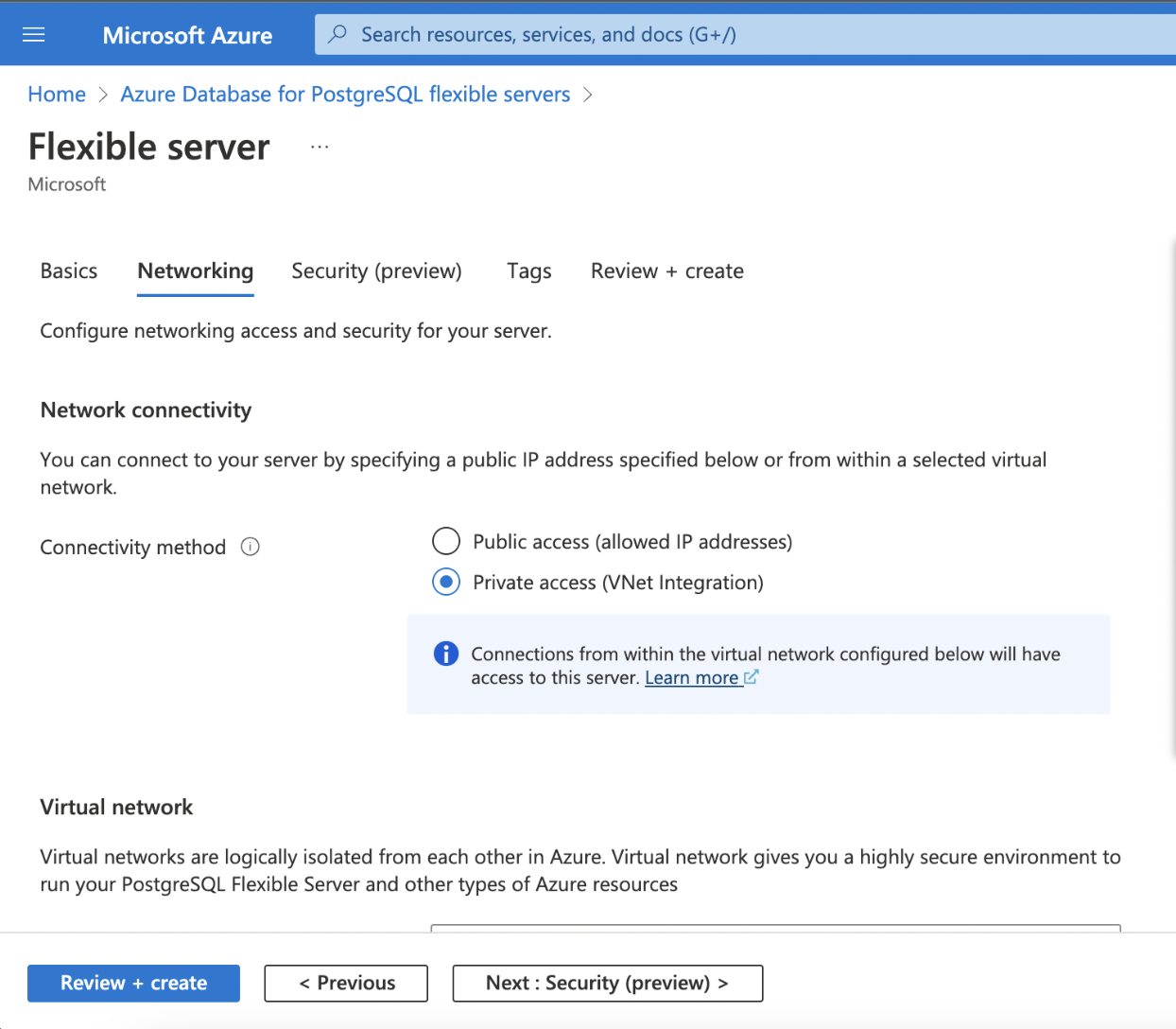
Step 1: Fill in the required details for setting up the networking.
- Connectivity Method
- Subscription
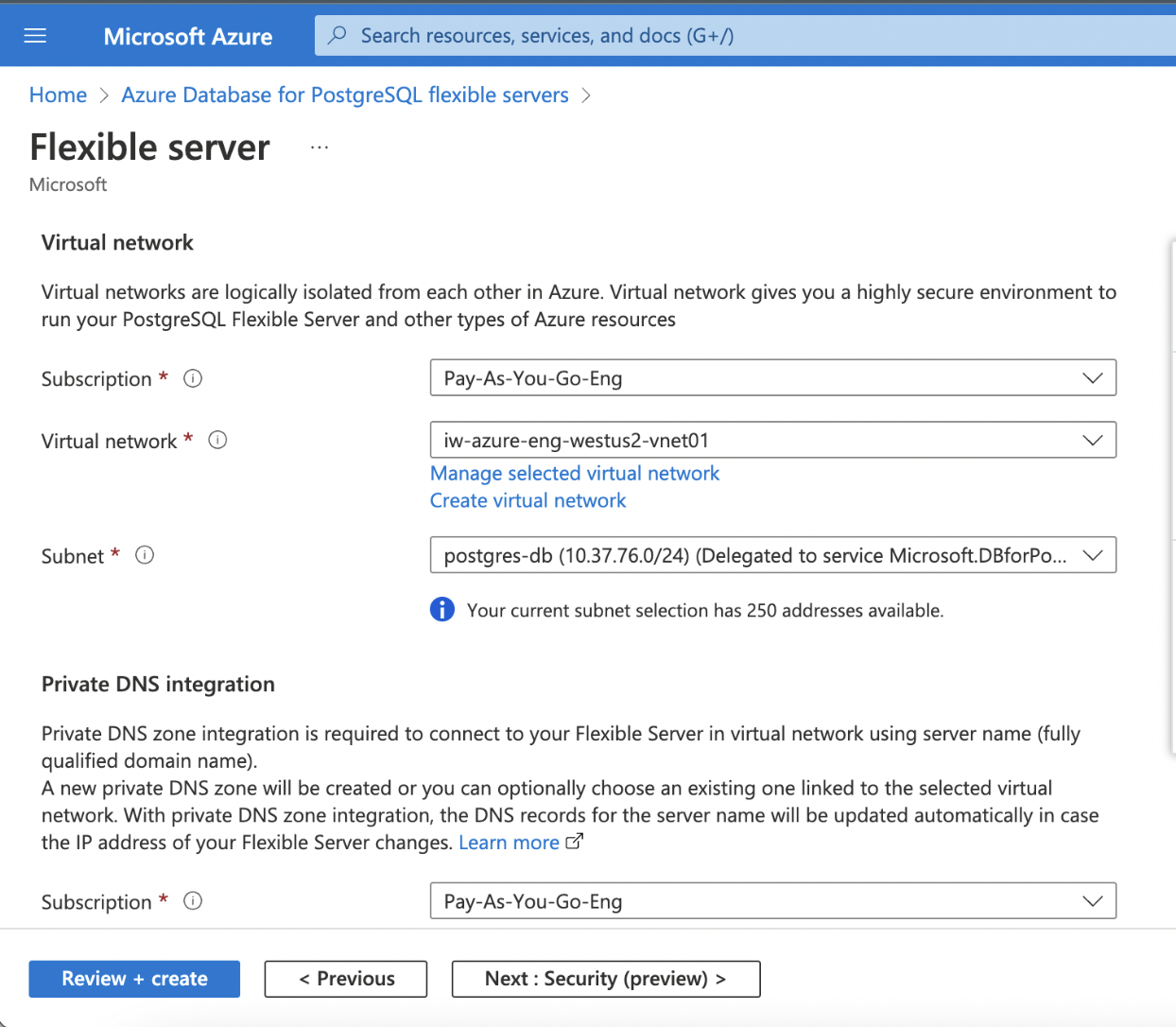
- Virtual Network
- Subnet
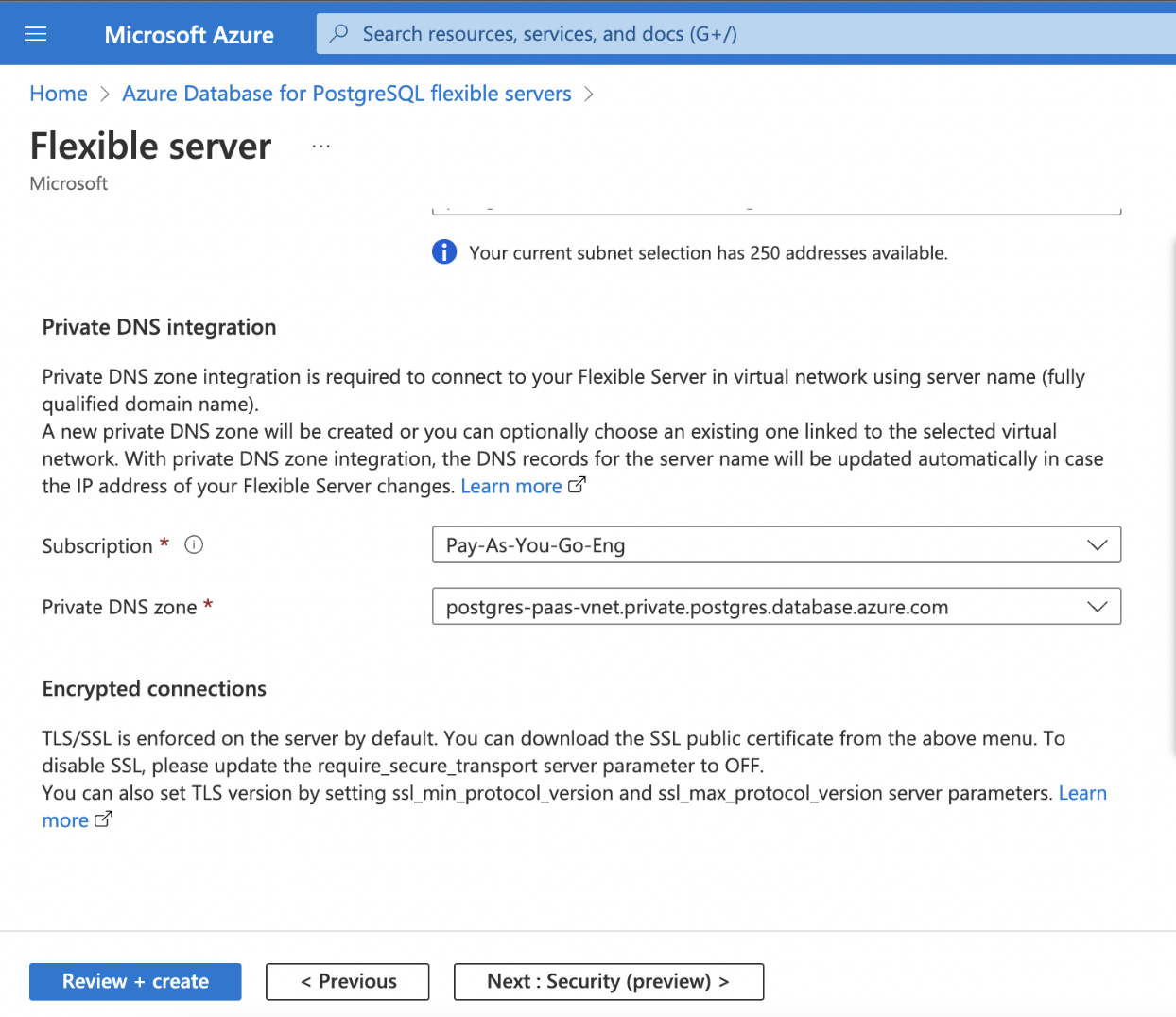
- Private DNS Zone
(contd.)
(contd.)
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Connectivity Method | Choose whether the database should be accessible over a public or private network. Infoworks recommends to set up connectivity over private network |
| Subscription | The name of your Subscription (account) in which the PostgreSQL database is to be set up. |
| Virtual Network | Select the Virtual Network to be associated with the database |
| Subnet | Select the appropriate subnet within the VNet. |
| Private DNS Zone | Create a new Zone or select an existing DNS Zone. This will create a FQDN for the Postgres database. |
Step 2: Click Next: Security (preview).
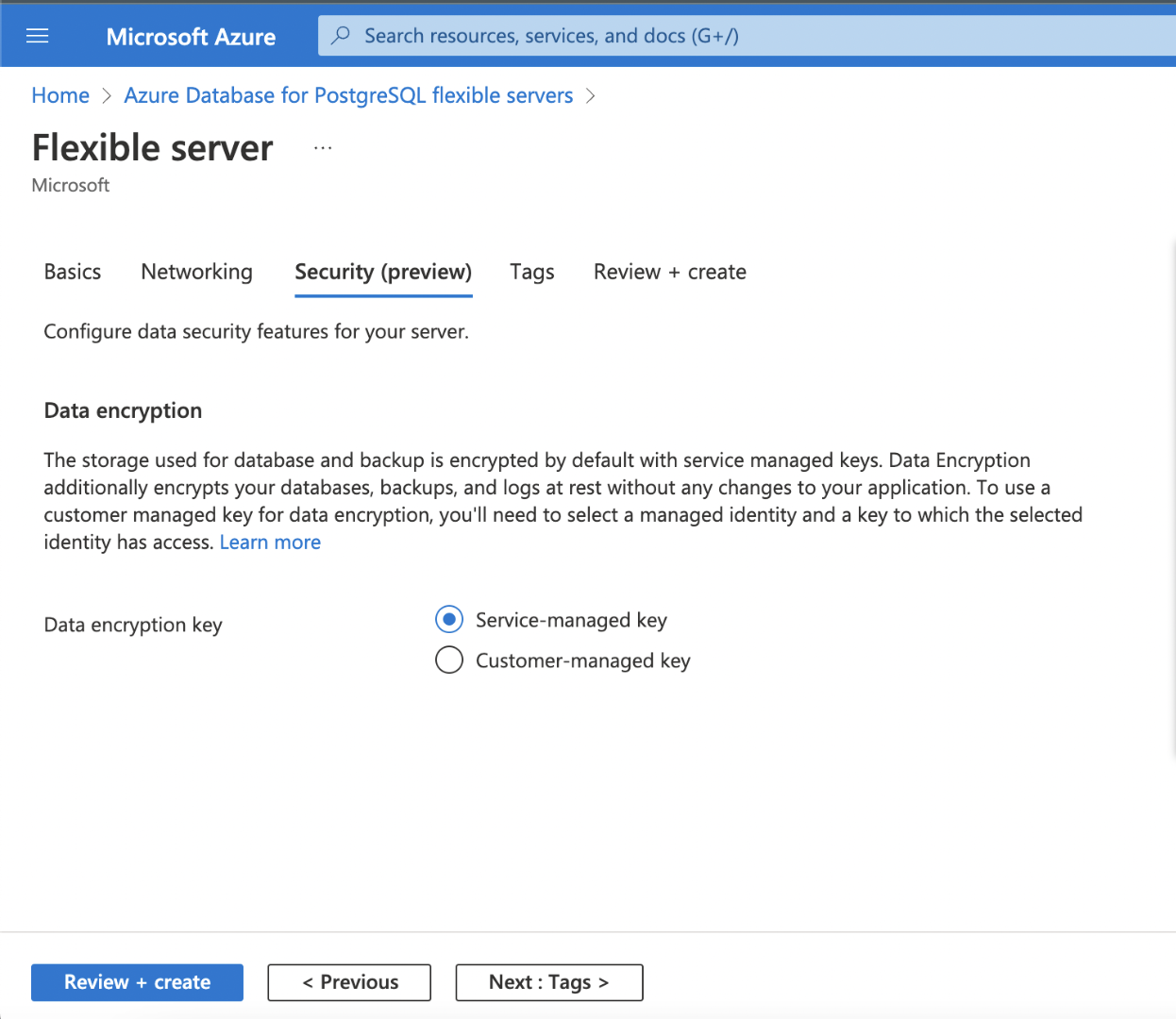
Security Preview
The storage used for the database and backup is encrypted by default with service-managed keys. Data Encryption additionally encrypts your databases, backups, and logs at rest without any changes to your application.
Step 1: Keep the default settings and click Next: Tags >.
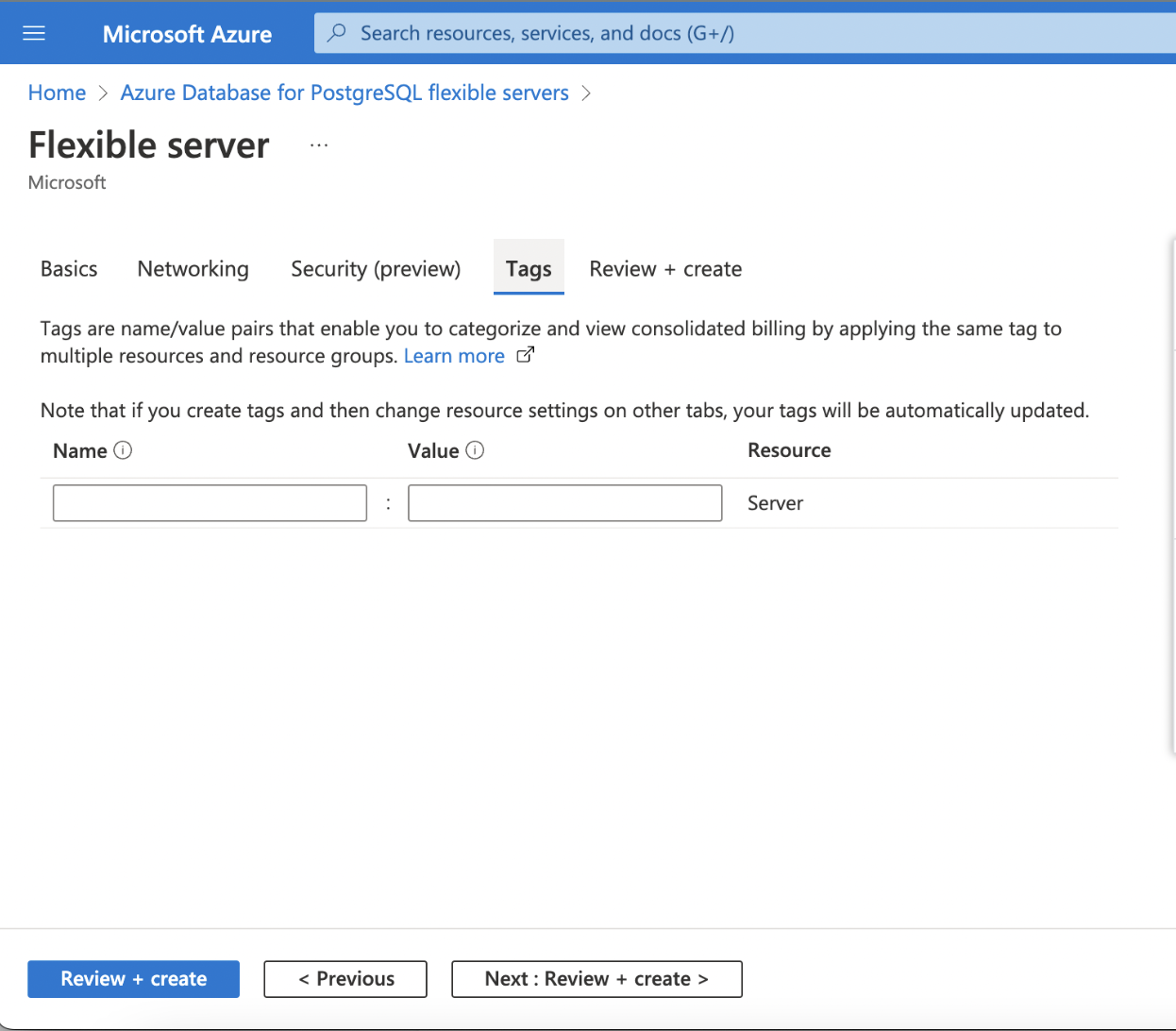
Tags
Tags are name/value pairs that enable you to categorize resources and view consolidated billing by applying the same tag to multiple resources and resource groups.
Step 1: Add the tags as per your organization's standards.
Step 2: Click Next: Review + Create >.
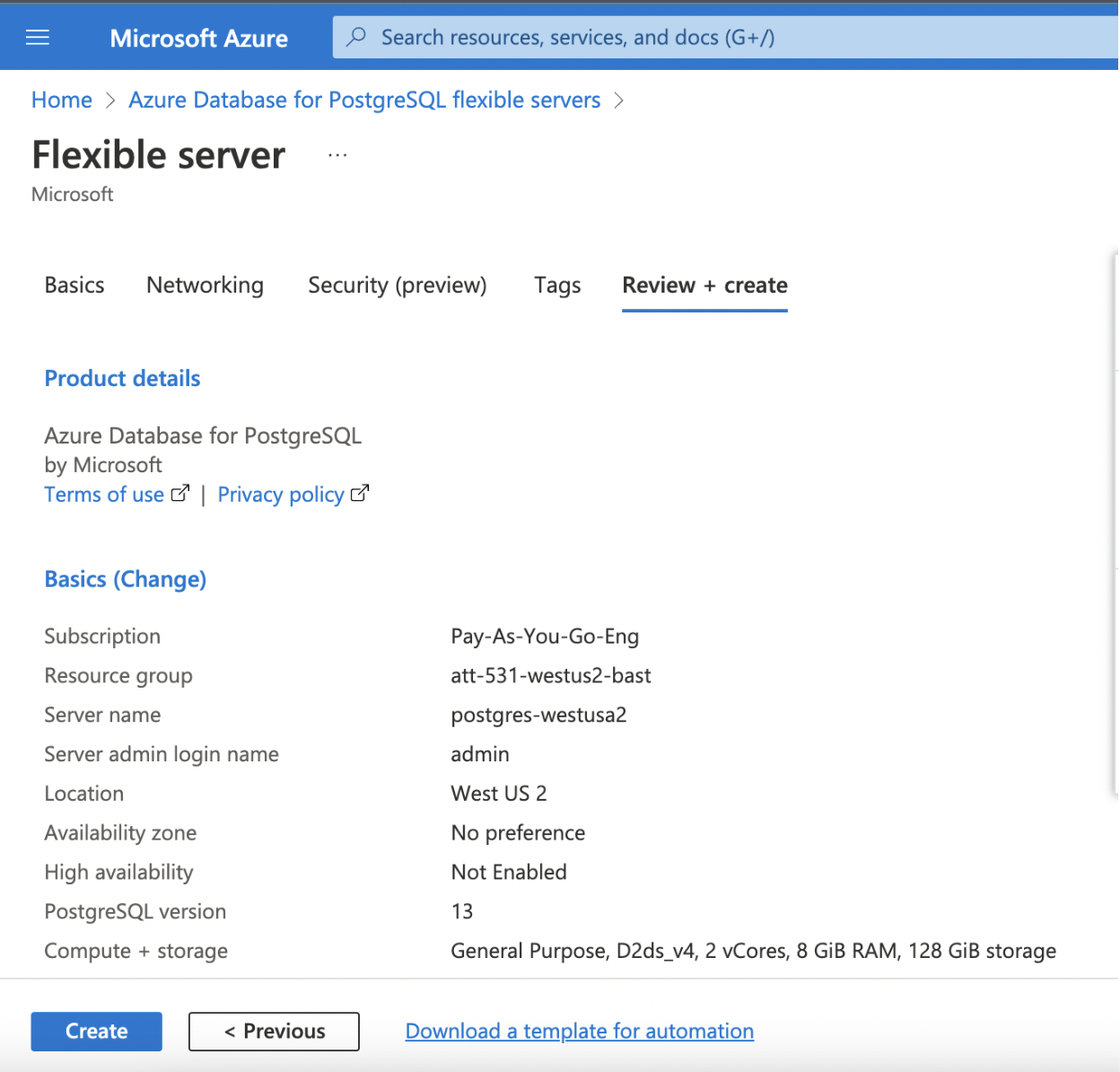
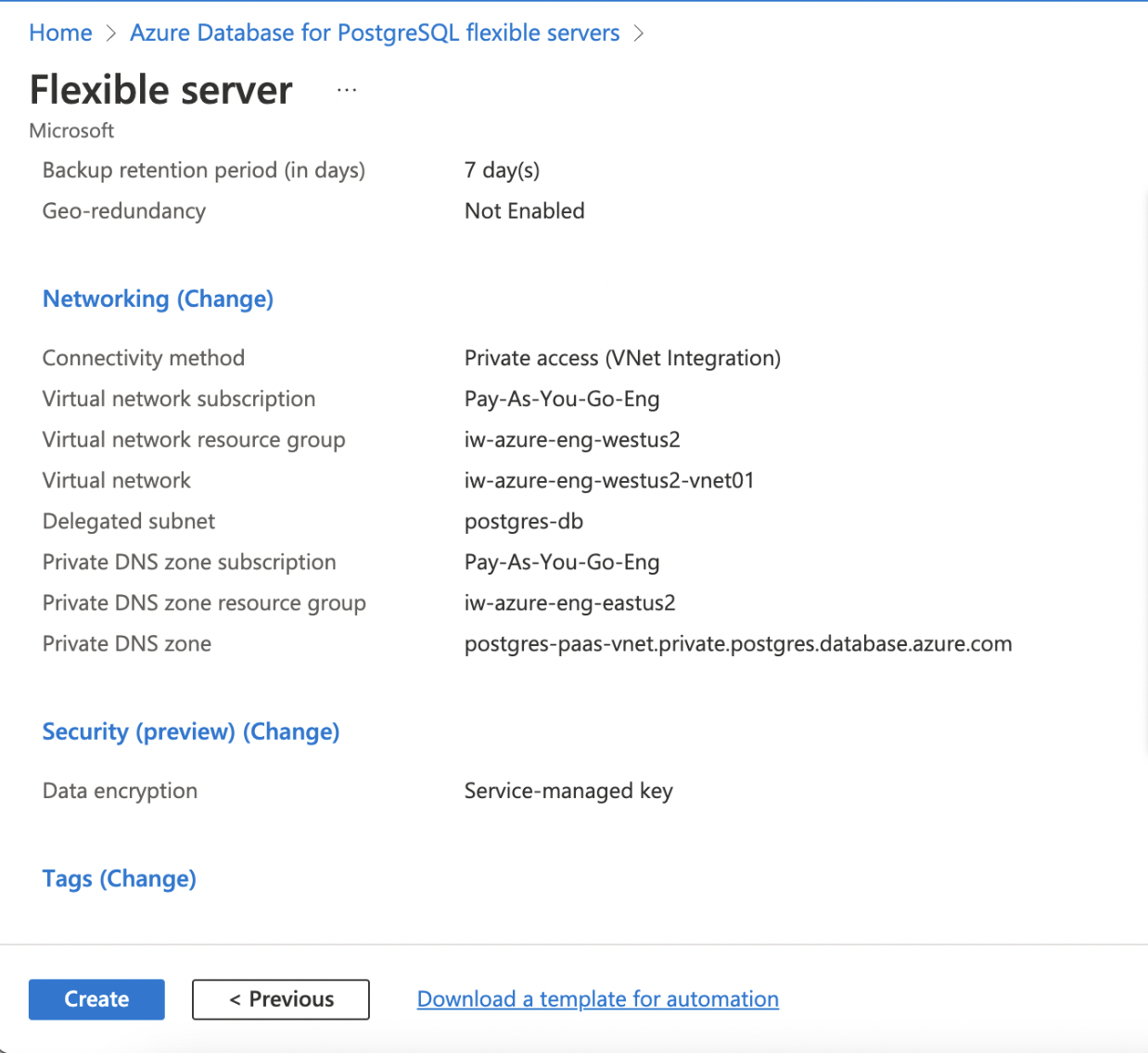
Review + Create
Verify the details and click Review + Create to complete the configurations and deploy the PostgreSQL Database.
(contd.)
High Availability
High Availability makes sure that the database service is always available and connectivity remains intact even in a scenario where one instance of the database is down or unavailable.
Infoworks recommends enabling High Availability to avoid downtime in case of an outage on the Postgres Machines.
Enabling High Availability
Enabling High Availability for a New Instance
Step 1: To enable High Availability for a new instance of PostgreSQL, navigate to Azure Console, search for Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible servers, and click it.
Step 2: Click Create.
Step 3: Under the Basics tab, click Enable High Availability checkbox.
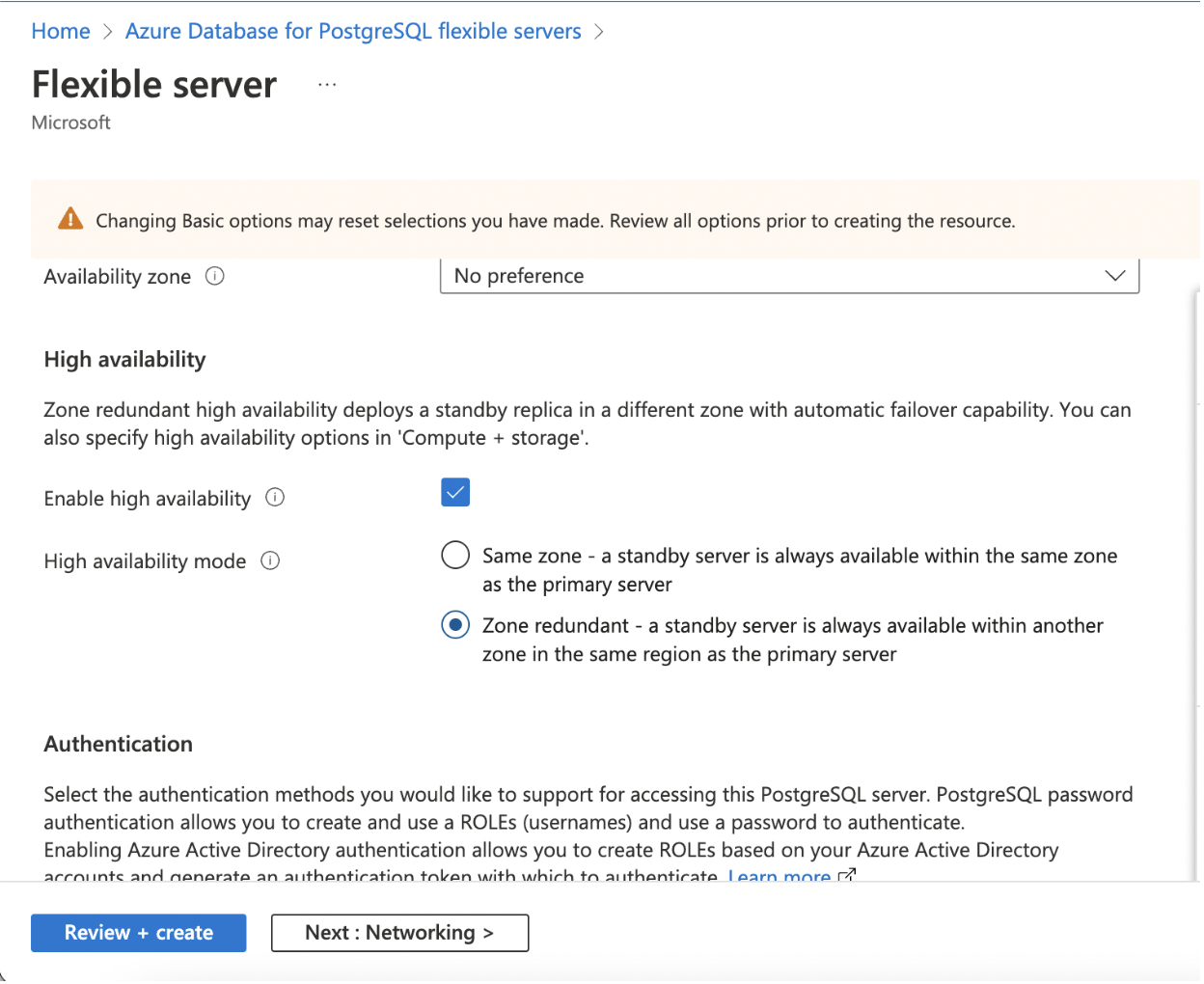
Enabling High Availability for an Existing Instance
Step 1: To enable High Availability for an existing instance of PostgreSQL, open an existing Postgres instance from the Azure portal,
Step 2: Under the Settings section, click High Availability, and click it.
Step 3: Select Enable High Availability checkbox.
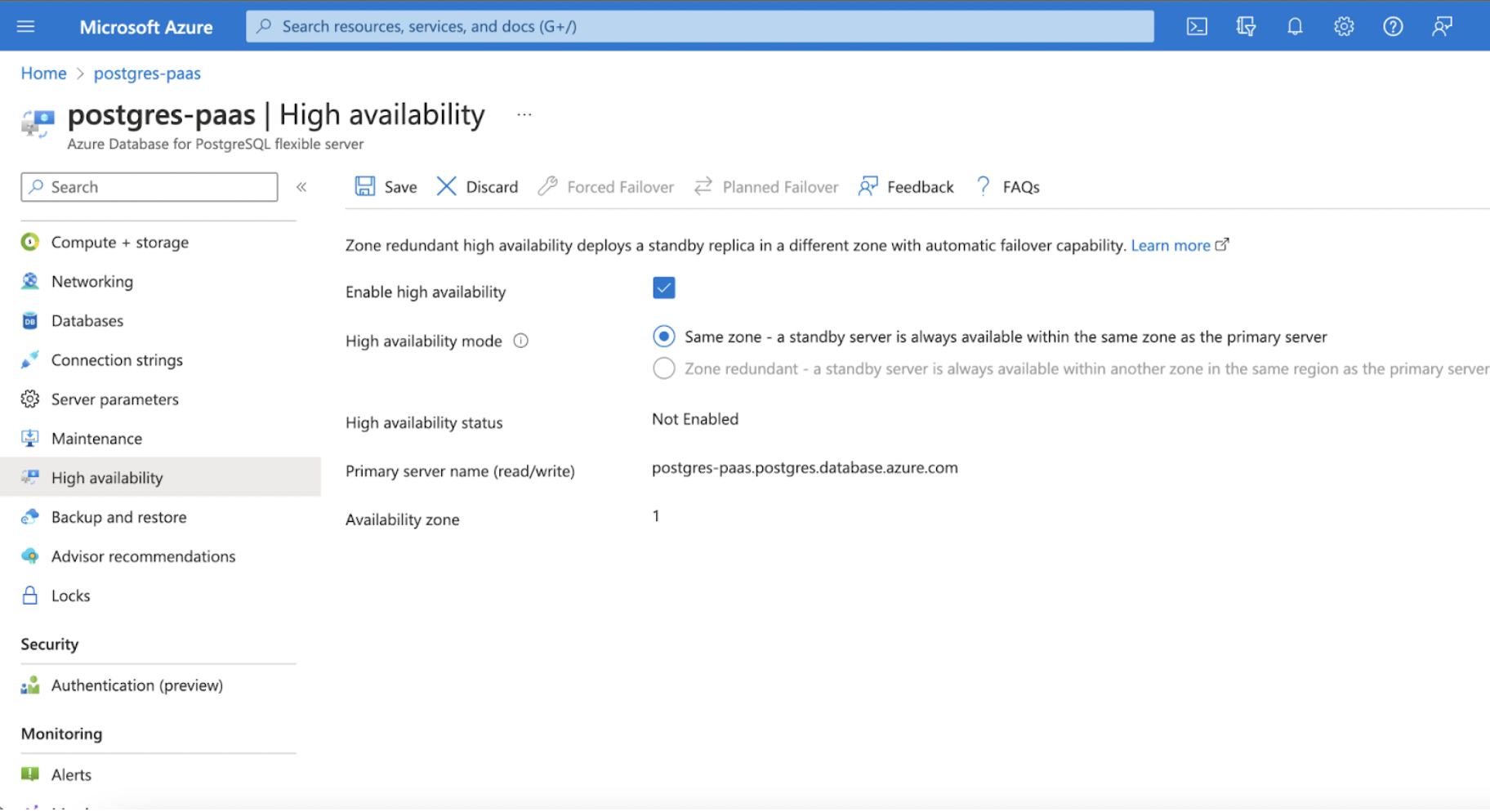
User Permissions
For Infoworks to use Postgres PaaS, considering the variables set during the installation, the given Postgres user (set in POSTGRESDB_USERNAME) needs to have the LOGIN Role. It must also have all privileges on a given database (set in INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME). For more information, refer to Infoworks Installation on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
To set the privileges:
xxxxxxxxxxCREATE USER <POSTGRESDB_USERNAME>;GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE <INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME> TO <POSTGRESDB_USERNAME>;Verifying Connection from PostgresDB to Infoworks
Verify that applications can access the PostgreSQL DB from Infoworks AKS cluster.
Use the following procedure as a reference only.
Step 1: Log in to your Bastion host where Kubernetes cluster is accessible.
Step 2: Create a pod with PostgreSQL image in the respective namespace.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl run postgres --image postgres --restart=Never --namespace <namespace> sleep 3000Step 3: Run the exec command to run bash command inside the pod.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl exec -it postgres --namespace <namespace> -- bashStep 4: Get the connection string from PostgreSQL DB. For example, consider the following command.
xxxxxxxxxxroot@postgres:/# psql --host <postgres-db-name>.postgres.database.azure.com --port 5432 --username <username> --dbname <database_name>Step 5: Provide the password.
Password for user <username>:psql (15.1 (Debian 15.1-1.pgdg110+1), server 13.7)SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)Type "help" for help.postgres=>The PostgreSQL DB and Infoworks are successfully connected. In case of any errors, refer to official Postgres Documentation.
Step 6: Once the connection between Postgres and Infoworks is successful. If you wish to delete Postgres pod, execute the following command.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl delete pods postgres --namespace <namespace>PostgresDB PaaS Backup and Restore
PostgresDB Backup and Restore are necessary steps to support rollback, since the airflow engine specific to the Infoworks Version has been upgraded. Therefore, the PostgresDB data gets upgraded to support the newer Airflow version, leaving the data incompatible with the older versioned Airflow and by association Infoworks.
Backup
PostgresDB backup may either be saved as Azure supported scheduled backup or through the pg_dump binary.
First Method: Using Azure-provided Backup Options
Azure provides an automated, scheduled backup option with a defined retention period. For more information, refer to Backup and restore in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
However, this method has the following limitations:
- This option takes a backup of the entire Server and not only of a specific Database inside the project.
- Currently, there is no on-demand backup available. Therefore any postgres data changes after a backup and before the upgrade will be lost.
- The retention period of these backups ranges from 7 to 35 days. Therefore, any backup older than the user-defined retention period is lost.
Second Method: Using pg_dump commands for Backup
To avoid the limitations of the Cloud-based approach, Postgres data backup can be done through the following pod template, which uses the pg_dump command to backup Postgres data.
Step 1: It is assumed that the environment variable IW_HOME is set to /opt/infoworks, which is the path where your current 5.4.0 charts are stored. In case it is not set, execute the following command:
xxxxxxxxxxexport IW_HOME=/opt/infoworksStep 2: Export the following Environment Variables.
xxxxxxxxxxexport IW_NAMESPACE="<your-infoworks-kubernetes-namespace>"export POSTGRESDB_HOSTNAME="<postgres-host>"export POSTGRESDB_USERNAME="<postgres-user>"export POSTGRES_PLAINTEXT_PASSWORD="<postgres-plaintext-password>"export INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME="<postgres-database>"For more details, refer to the Infoworks Installation on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) section.
Step 3: Create a directory to store the database backup dump using the command below
xxxxxxxxxxmkdir -p ${IW_HOME}/postgres_backupcd ${IW_HOME}Step 4: Clear any existing pods with the same name.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} delete po postgres-backupStep 5: Run the commands to create the required pod on the same namespace as the Kubernetes installation.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl apply -f - <<EOFapiVersion: v1kind: Podmetadata: name: postgres-backup namespace: ${IW_NAMESPACE}spec: containers: - name: postgres-backup env: - name: IW_NAMESPACE value: "${IW_NAMESPACE}" - name: POSTGRESDB_HOSTNAME value: "${POSTGRESDB_HOSTNAME}" - name: POSTGRESDB_USERNAME value: "${POSTGRESDB_USERNAME}" - name: POSTGRES_PLAINTEXT_PASSWORD value: "${POSTGRES_PLAINTEXT_PASSWORD}" - name: INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME value: "${INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME}" image: us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/iw-gcp-eng-dev/iwx-devops/infoworks-postgres-utils:psql-15 imagePullPolicy: Always command: [ "/bin/bash", "-c", "--" ] args: [ "/opt/infoworks/scripts/postgres_backup_and_restore.sh -d" ] restartPolicy: NeverEOFStep 6: Once the postgres-backup is up, run the following command to get logs
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl -n $IW_NAMESPACE logs postgres-backup -fAfter some time, you will receive the following message on your command prompt.
xxxxxxxxxxTaking Dump of PostgresTaking Postgres Dump - Enter the Parameters of the source PostgresDB ServerPG Data Dumped to postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sqlRun kubectl -n aks-upgrade-540 cp postgres-backup:postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sql postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sql to copy to your localStep 7: Copy the generated artifacts to your machine.
xxxxxxxxxxdate_time=$(date "+%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S")kubectl -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} cp postgres-backup:postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sql postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sqlcp postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sql postgres_backup/pg_dump_data_${date_time}.sqlThis should create the following files in the directory postgres _backup, $(date -I) being the current timestamp. To view the list of directories, execute the following command:
xxxxxxxxxxls postgres_backupxxxxxxxxxxpg_dump_data.sql pg_dump_data-${date_time}.sqlKeep these files safe for backup later. |
Restore
PostgresDB Restore is a necessary step to support rollback since the airflow engine specific to the Infoworks version has been upgraded. Therefore, the PostgresDB data gets upgraded to support the newer Airflow version, leaving the data incompatible with the older versioned Airflow and by association Infoworks.
PostgresDB backup may either be restored through the cloud-supported scheduled backup or manually restoring the data, as picked by the user during Backup.
First Method: Using Azure-provided Backup Options
Azure provides an automated, scheduled backup option with a defined retention period. For more information, refer to Backup and restore in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
- This option takes a backup of the entire project and not only of a specific Database inside the project.
- Currently, there is no on-demand backup available. Therefore any postgres data changes after a backup and before the upgrade will be lost.
- The retention period of these backups ranges from 7 to 35 days. Therefore any backup older than the user-defined retention period is lost.
Second Method: Using PSQL commands for Restore
To avoid the limitations of the Cloud-based approach, postgres data restore can be done through the following pod template, which uses the PSQL command to restore Postgres data.
Step 1: It is assumed that the environment variable IW_HOME is set to /opt/infoworks, which is the path where your current 5.4.0 charts are stored. In case it is not set, execute the following command
xxxxxxxxxxexport IW_HOME=/opt/infoworksStep 2: Export the following environment variables.
xxxxxxxxxxexport IW_NAMESPACE="<your-infoworks-kubernetes-namespace>"export POSTGRESDB_HOSTNAME="<postgres-host>"export POSTGRESDB_USERNAME="<postgres-user>"export POSTGRES_PLAINTEXT_PASSWORD="<postgres-plaintext-password>"export INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME="<postgres-database>"For more details regarding the above mentioned commands, refer to Infoworks Installation on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
It is recommended to take a backup of the current PostgresDB, by exporting the following variable. This requires the given user to have permission to create a new database. The pod will fail in case the backup fails, therefore do not export it to skip the backup.
This will attempt to DROP the given $INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_BACKUP_DATABASE_NAME to create a new one. |
xxxxxxxxxxexport INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_BACKUP_DATABASE_NAME="<postgres-backup-database>"Step 3: Switch to the directory where PostgresDB backups were stored.
xxxxxxxxxxcd ${IW_HOME}Step 4: Clear any existing pods with the same name.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} delete po postgres-backupStep 5: Run the commands to create the required pod on the same namespace as the Kubernetes installation.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl apply -f - <<EOFapiVersion: v1kind: Podmetadata: name: postgres-backup namespace: ${IW_NAMESPACE}spec: containers: - name: postgres-backup env: - name: IW_NAMESPACE value: "${IW_NAMESPACE}" - name: POSTGRESDB_HOSTNAME value: "${POSTGRESDB_HOSTNAME}" - name: POSTGRESDB_USERNAME value: "${POSTGRESDB_USERNAME}" - name: POSTGRES_PLAINTEXT_PASSWORD value: "${POSTGRES_PLAINTEXT_PASSWORD}" - name: INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME value: "${INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE_NAME}" - name: INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_BACKUP_DATABASE_NAME value: "${INFOWORKS_POSTGRESDB_BACKUP_DATABASE_NAME}" image: us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/iw-gcp-eng-dev/iwx-devops/infoworks-postgres-utils:psql-15 imagePullPolicy: Always command: [ "/bin/bash", "-c", "--" ] args: [ "/opt/infoworks/scripts/postgres_backup_and_restore.sh -r" ] restartPolicy: NeverEOFStep 6: Once the pod is running, run the following command to copy the backup to the pod.
xxxxxxxxxxkubectl -n ${IW_NAMESPACE} cp ${IW_HOME}/postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sql postgres-backup:postgres_backup/pg_dump_data.sqlAfter copying the above file, the restore script will automatically restore from the backup files supplied.