Configuring Infoworks with Spark on Kubernetes
Introduction
Infoworks’ Spark on Kubernetes environment enables streamlined execution of Apache Spark workloads on Kubernetes-managed clusters. Infoworks handles Kubernetes integration—submitting Spark jobs directly to the Kubernetes API so that Spark driver and executor components run as Kubernetes pods managed by Kubernetes’ native scheduler.
For more information and technical details, see the official Apache Spark documentation on running Spark on Kubernetes
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes-based deployment for Infoworks must be in place, ensuring Spark workloads can run in Kubernetes-managed containers.
- An external Hive metastore is required for managing metadata used by Spark SQL operations. This metastore must be hosted and maintained by the customer—not managed internally by Infoworks.
The platform supports two relational database backends for the Hive metastore:
- PostgreSQL
- Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL)
Infoworks provides schema setup scripts compatible with both supported databases—PostgreSQL and Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL). These scripts must be executed manually on your chosen database instance and are available at the following locations:
- PostgreSQL: hive-schema-3.1.0.postgres.sql
- MSSQL: hive-schema-3.1.0.mssql.sql
Procedure
To configure and connect to a Spark on Kubernetes environment, navigate to Admin > Manage Compute Environments, and then click the Add button under the Spark on Kubernetes option.
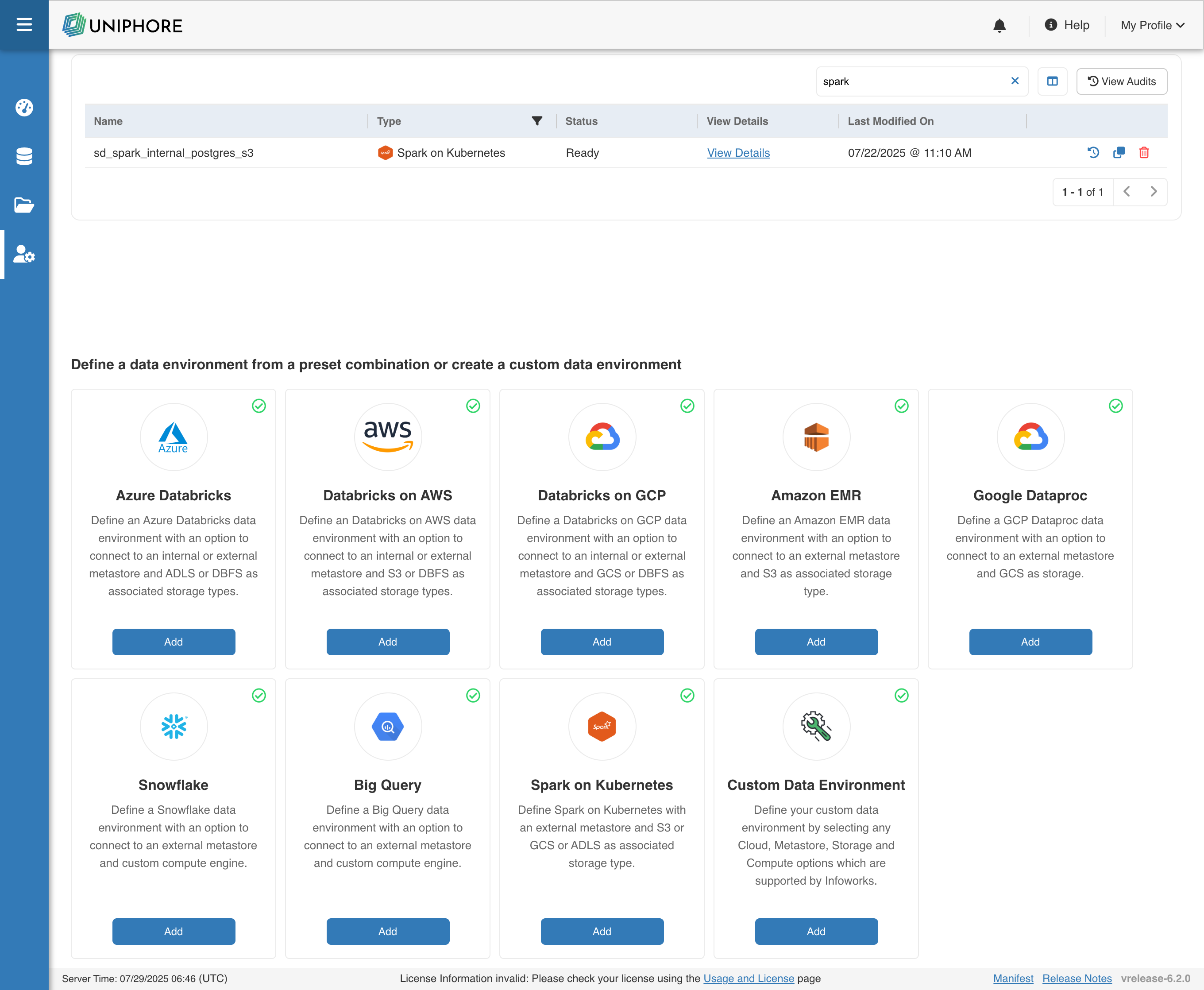
The following window appears:
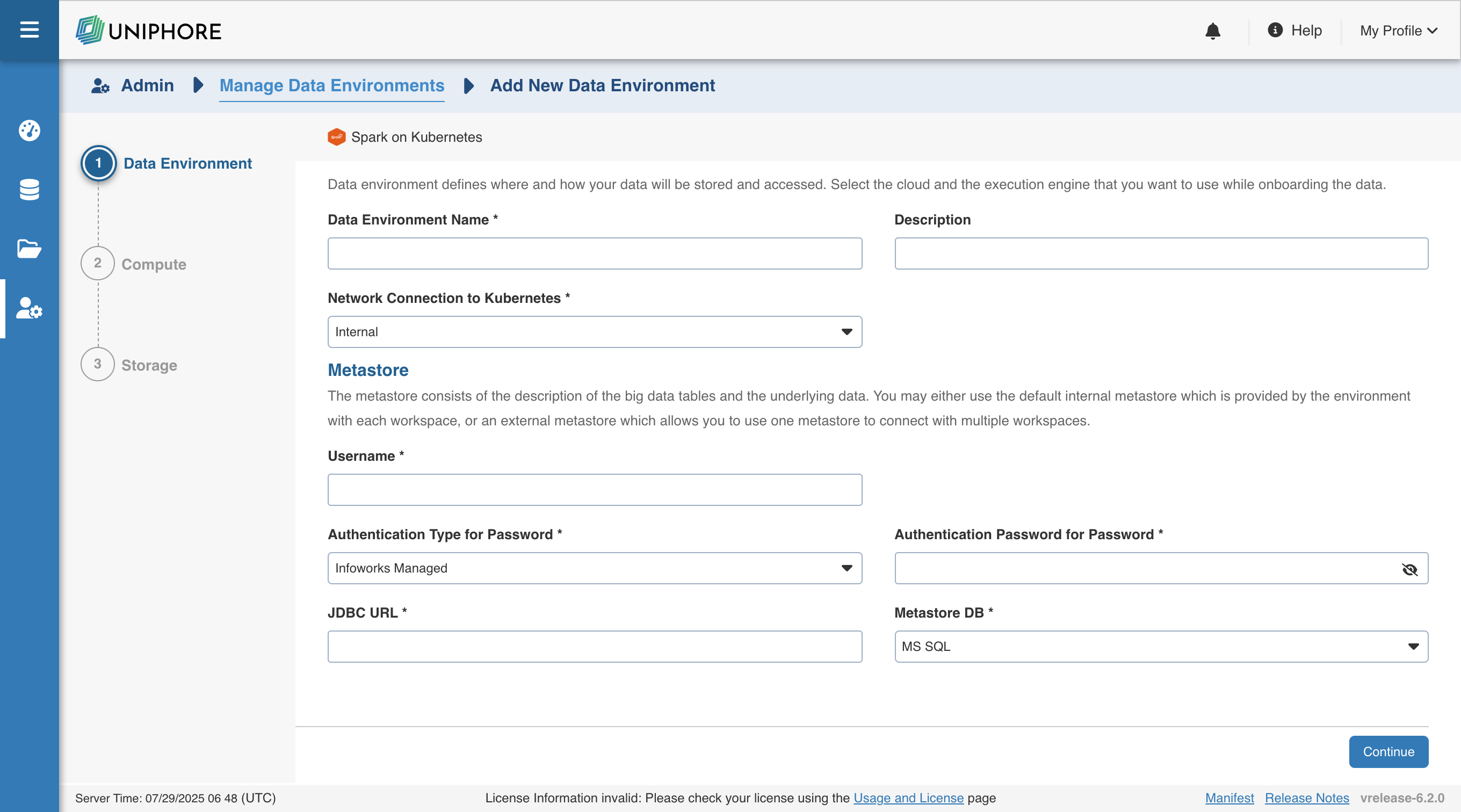
There are three tabs to be configured as follows:
Data Environment
To configure the data environment details for Spark on Kubernetes, enter values in the following fields. These settings define the compute environment parameters required for Infoworks to submit and manage Spark workloads on your Kubernetes cluster.
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Data Environment Name | Name for the Spark on Kubernetes environment. | User-defined label to identify the data environment |
| Description | Optional description for the environment | Brief notes about the purpose or scope of this environment |
| Network Connection to Kubernetes | Network route used to connect to the Kubernetes cluster | Only Internal is available currently — Infoworks services and Spark jobs run in the same Kubernetes cluster |
| Metastore DB | Type of database used to host the Hive metastore | Choose between PostgreSQL or MS SQL |
| JDBC URL | JDBC connection string to the Hive metastore database | Must follow JDBC syntax for the selected metastore database (PostgreSQL or MSSQL) |
| Username | Username for authenticating with the Hive metastore | Typically a database user with read/write permissions |
| Authentication Type for Password | How the password for the metastore user is managed. Options include Infoworks-Managed or External Secret Store | Infoworks-Managed: This field indicates that Infoworks stores the token in its database. External Secret Store: This field indicates that the password will be retrieved from External Secret Store/Keyvault as per requirement. |
| Authentication Password for Password | The password corresponding to the metastore user | Secure input field; provide the password for the metastore user. |
| Secret for Password | Reference to a secret stored in an external secret manager like Key Vault | Used when password is not managed by Infoworks; must reference a secret from an external secret store |
Compute
In the Spark on Kubernetes environment, a compute template defines the infrastructure used to execute Spark jobs directly within the Kubernetes cluster where Infoworks is installed. Spark drivers and executors run as Kubernetes pods, enabling native containerized execution.
Unlike other environments (e.g., Azure Databricks), where ephemeral clusters can be created on demand, Spark on Kubernetes supports only persistent clusters. This is because the underlying Kubernetes cluster remains continuously available and managed, providing a stable foundation for job execution.
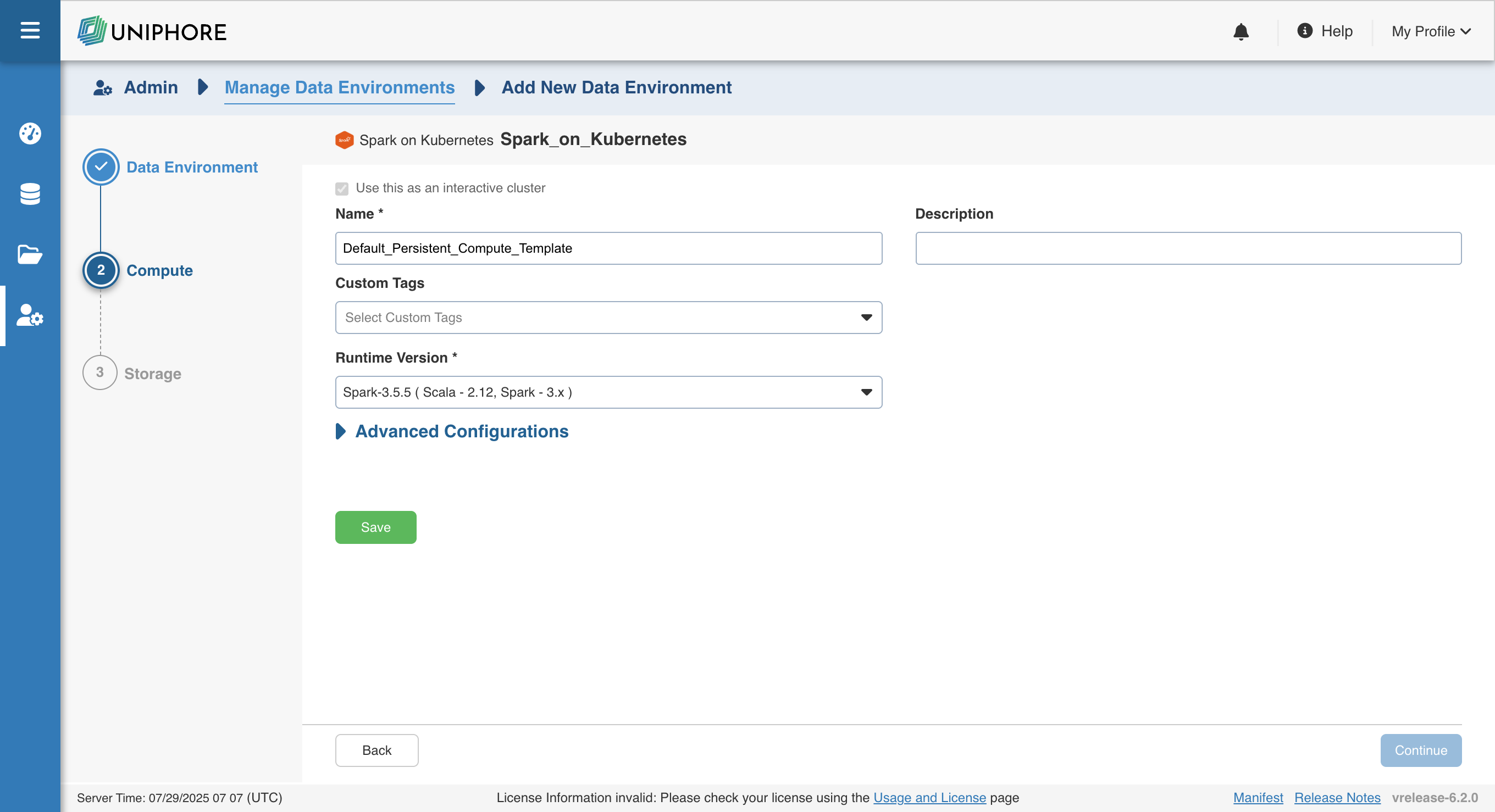
Below are the field definitions required to configure a Spark on Kubernetes compute template:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name required for the compute template that you want to use for the jobs. | User-defined. Provide a meaningful name for the compute template being configured. |
| Description | Description required for the compute template. | User-defined. Provide required description for the compute template being configured. |
| Use this as an interactive cluster | Option to designate a cluster to run interactive jobs. Interactive clusters allows you to perform various tasks such as displaying sample data for sources and pipelines. You must define only one Interactive cluster to be used by all the artifacts at any given time. | Select this check box to designate the cluster as an interactive cluster. |
| Custom Tags | Metadata tags for filtering or organization | User-defined key-value pairs for governance and automation across environments. |
| Runtime Version | Version of Apache Spark used for execution | Specify the Spark version to use. Currently, only 3.5.5 is supported. |
| Advanced Configurations | Fine-tune Spark and Kubernetes behaviour | Optional section to configure driver/executor memory, core limits, Spark config overrides, etc., for job performance tuning. |
Storage
To configure the storage details, enter values in the following fields. This defines the storage parameters, to allow Infoworks to be configured to the required Spark on Kubernetes instance:
To configure a new storage after the first time configuration, click Add button on the UI.
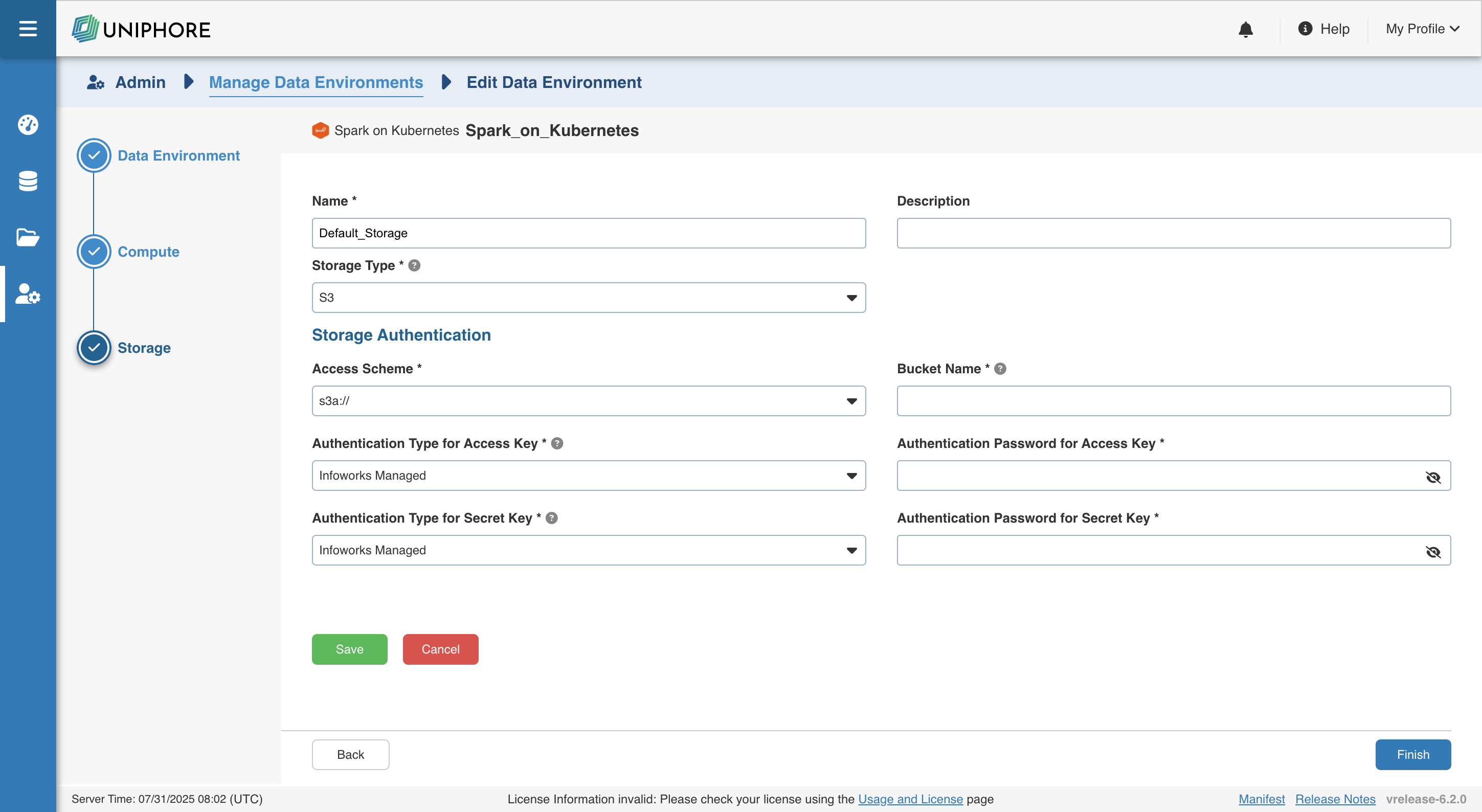
Enter the following fields under the Storage section:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Storage name must help the user to identify the storage credentials being configured. | User-defined. Provide a meaningful name for the storage set up being configured. |
| Description | Description for the storage set up being configured. | User-defined. Provide required description for the environment being configured. |
| Storage Type | Type of storage system where all the artifacts will be stored. This depends on the type of cloud/platform provider you choose in the Compute tab.
| Select the required storage type from the drop-down menu. |
Azure DataLake Storage(ADLS) Gen 2
On selecting Azure DataLake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 as the storage type, the following fields appear:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Access Scheme | Scheme used to access ADLS Gen 2. Available options are abfs:// and abfss://. | Select the required access scheme from the drop-down menu. |
| Authentication Mechanism | Mechanism using which the security information is stored. Available options are Service Principal and Access Key. | Select the required authentication mechanism from the drop-down menu. |
| File System | File system where all the data of an artifact will be stored. | Provide the required file system parameter. |
| Storage Account Name | Name of the Azure Storage Account. | Provide the required storage account name. For example, my_data_acc. |
| Application ID | ID that uniquely identifies the user application. | Provide the required application ID. |
| Directory ID | ID that uniquely identifies the Azure AD instance. | Provide the required directory ID. |
| Service Credential | Credential that the application uses to prove its identity. | Provide the credential string value. |
S3
On selecting S3 as the storage type, the following fields appear:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Access Scheme | Scheme used to access S3. Available options are s3a://, s3n://, and s3://. | Select the required access scheme from the drop-down menu. |
| Bucket Name | AWS bucket name is part of the domain in the URL. For example: http://bucket.s3.amazonaws.com. | Provide the required bucket name. This field is displayed only for S3 storage type. |
| Access Key | Unique 20-character, alphanumeric string which identifies your AWS account. For example, AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE. | Provide the required access key. |
| Secret Key | Unique 40-character string which allows you to send requests using the AWS account. For example, wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY. | Provide the required secret key. |
GCS
On selecting GCS as the storage type, the following fields appear:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Access Scheme | Scheme used to access GCS. Available option is gs:// | Select gs:// from the drop-down menu. |
| Bucket Name | Buckets are the basic containers that hold, organise, and control access to your data. | Provide the storage bucket key. Do not use gs:// for storage bucket. |
| Authentication Mechanism | Includes the authentication mechanism to access the GCP storage. | The following authentication mechanisms are available: Use system role credentials: The default credentials of the instance to identify and authorize the application. Use environment level service account credentials: The IAM Service Account defined at the environment level to identify and authorize the application. Override environment authentication mechanism: Overrides the credentials provided for the environment. |
| Service Credentials | Provide the credentials used to authenticate calls to Google Cloud APIs. | Upload File: Upload the file where the service credentials are stored. Enter File Location: Path of the file to be uploaded. You must enter the server file location. |
After entering all the required values, click Save. Click Return to Manage Environments to view and access the list of all the environments configured. Edit, Clone, and Delete actions are available on the UI, corresponding to every configured environment.