Creating a Source
To create a source, perform the following steps:
- Log in to Infoworks.
- In the left navigation pane, click the Data Sources icon. The Data Sources page appears.
- Click Onboard New Data. The Source Connectors page appears with the list of all available connectors.

- Click the required connector. The Setup Source page of the selected connector appears.
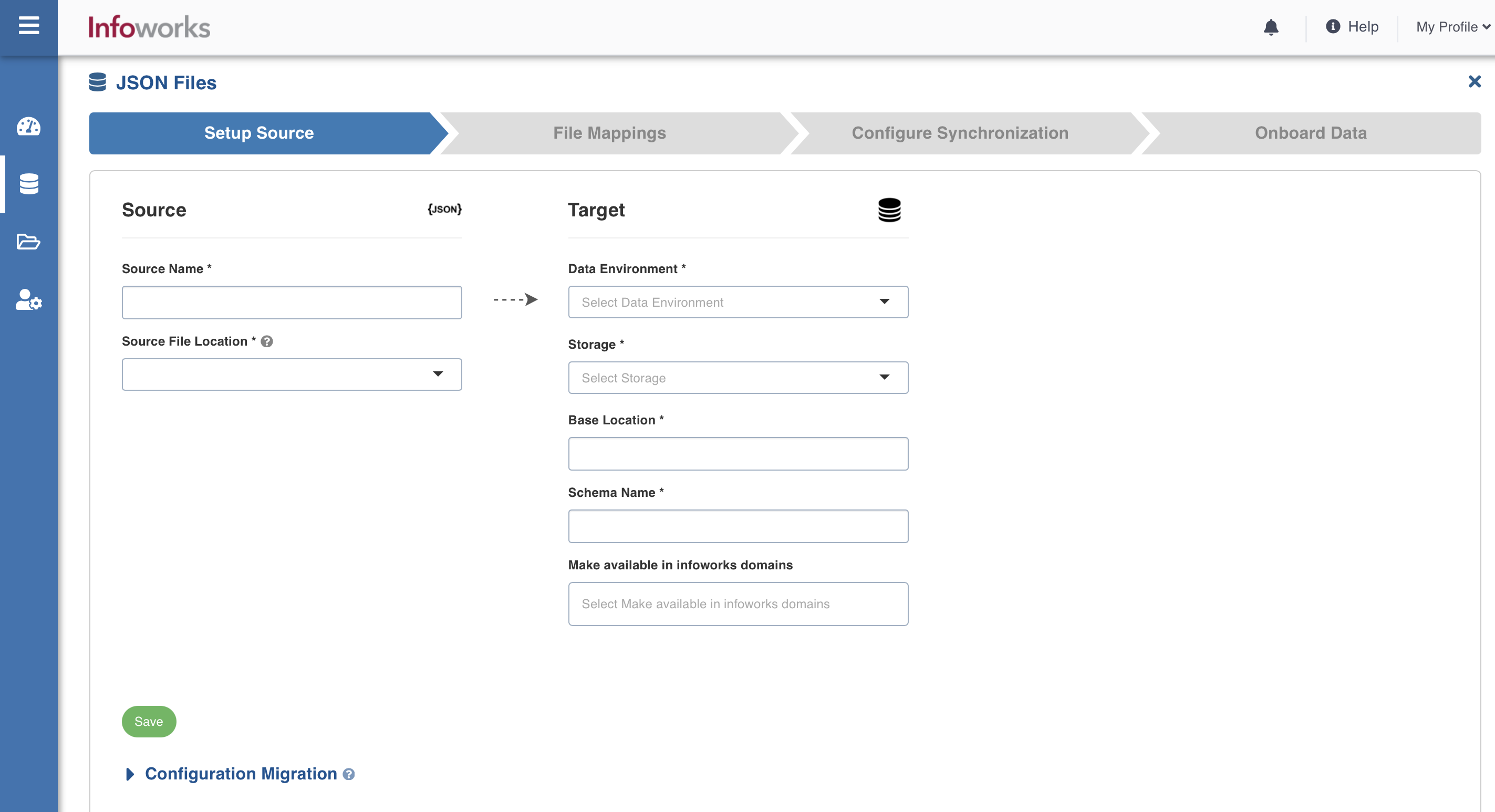
- In the Setup Source page, enter the following details:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Source Name | A name for the source that will appear in the Infoworks User Interface. | The source name must be unique and must not contain space or special characters except underscore. For example, Customer_Details. |
| Source File Location | The storage systems location where your files are stored. | You can select one of the following options:
|
| Data Environment | The environment on which the source is defined. | Select the environment from the drop-down list. The list includes the environments created by the Admin. For more details, refer to Managing Environments section. |
| Catalog Name | The name of the catalog in the data lake. | The name can only contain letters, numbers, hyphen, and underscore. |
| Schema Name | The name of the schema in the data lake. | The name can only contain letters, numbers, hyphen, and underscore. |
| Storage | The target storage where the data will be stored. | Select the storage from the drop-down list. The storage options are displayed based on the environment selected. |
| Base Location | The location of the target on the File System. | The path must start with / and must only contain letters, numbers, hyphen, and underscore. For example, /iw/sources/samplesource. |
| Staging Schema Name | The name of the schema where all the temporary tables (like CDC, segment tables etc) managed by Infoworks will be created. Ensure that Infoworks has ALL permissions assigned for this schema. This is an optional field. If staging schema name is not provided, Infoworks uses the Target Schema provided. | This field appears only when the Data Environment is snowflake. Ensure either of the following: the target table names are unique across schemas or ensure that two tables with the same name do not run in parallel. |
| BigQuery Dataset Name | Dataset name of the BigQuery target. | This field appears only when the Data Environment is BigQuery. |
| Staging Dataset Name | The name of the dataset where all the temporary tables (like CDC, segment tables, and so on) managed by Infoworks will be created. Ensure that Infoworks has ALL permissions assigned for this dataset. This is an optional field. If staging dataset name is not provided, Infoworks uses the Target dataset provided. | This field appears only when the Data Environment is BigQuery. |
6. Click Save.
BigQuery Labels
This label enables you to add labels to your tables in BigQuery.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Key | This field depicts the key for the specific BigQuery label. |
| Value | This field depicts the value for the specific BigQuery label. |
| Description | This field describes the BigQuery label |
| Actions | This field indicates the actions users can perform. For example, Add or delete |
| Add Labels | This fields adds a new BigQuery label |
| Infoworks Managed Labels | If this checkbox is selected, these labels overwrite the BigQuery label. If this checkbox is not selected, these labels will be appended to existing BigQuery labels. |
For more information, refer to BigQuery Labels.
Job Hooks
Job Hooks are external python/bash scripts that can be run before or after a source ingestion job in the data plane. These scripts can access various job properties as environment variables in the data plane. For more information about job hooks, Using a Job Hook