Introduction
Data Onboarding is the first step to perform data analytics on Infoworks. Onboarding refers to the process of ingesting data from various sources like RDBMS databases, structured files, SalesForce databases, and data from cloud storage like S3, into a single data lake, keeping the data synchronized with the sources, and maintained within a data governance framework. |
Data Onboarding
Data ingestion and synchronization into a cloud or big data environment is harder than most people think. Loading large volumes of data at high speed and managing the incremental ingestion and synchronization of data at scale into an on-premise or cloud data lake can present significant technical challenges.
Data onboarding with Infoworks automates the following:
- Data Ingestion - from all enterprise and external data sources,
- Data Synchronization - CDC (Changed Data Capture) to keep data synchronized with the source,
- Data Governance - cataloging, data lineage, metadata management, audit, and history. Infoworks automates data onboarding for batch and streaming.
Infoworks Onboarding Architecture
The Infoworks onboarding process is illustrated here:
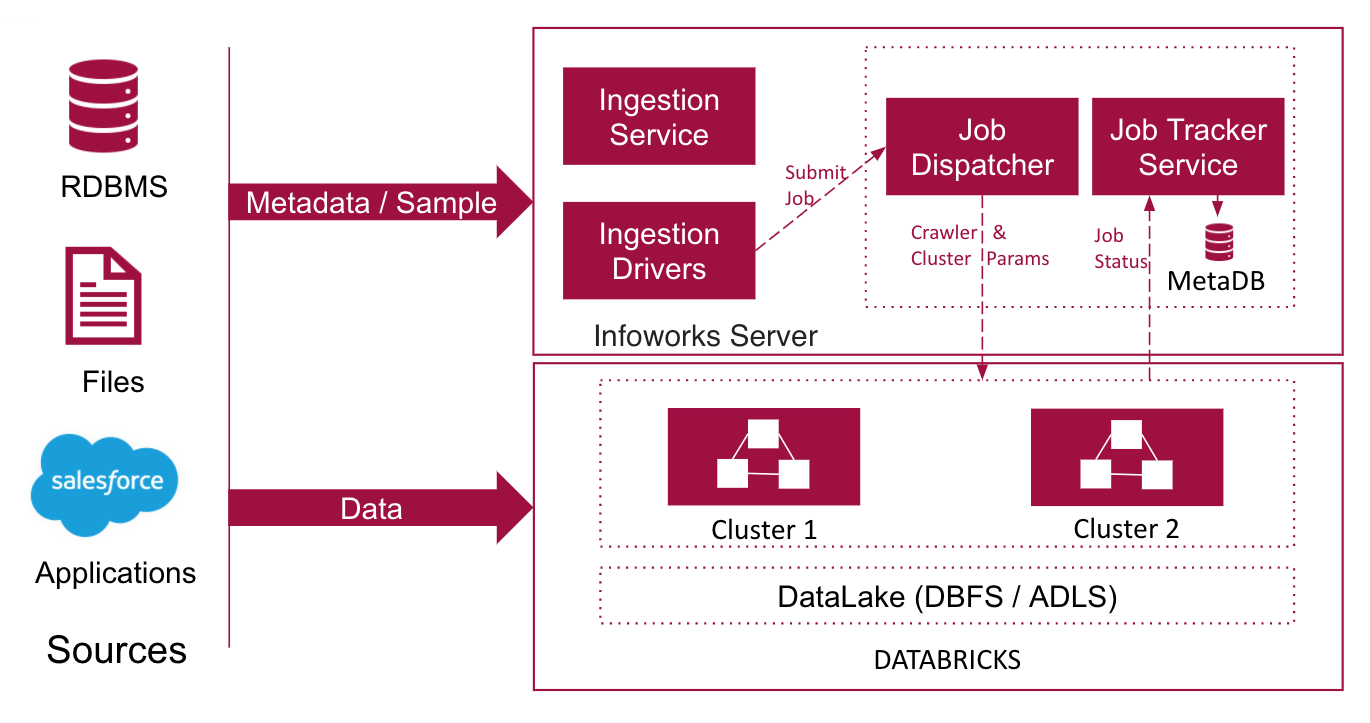
- Infoworks ingests data from data sources using Spark jobs. Your source can be an RDBMS database like Oracle, or a structured file like CSV or an application database like Salesforce. File sources can be located in a file system like DBFS or cloud object storage like S3. You can also parallelize the process of reading data from the sources for faster ingestion. Infoworks supports inter-table and intra-table parallelization.
- Before reading the source data, Infoworks crawls the source metadata which includes a list of all the tables, table definitions, column names, and column data types. All metadata are automatically tracked and cataloged.
- The data read is processed using Spark as the processing engine. On-demand clusters are automatically launched and data is split into multiple processes on different worker nodes, running concurrent executions in parallel.
The data processed is stored in S3 or ADLS data lake. Infoworks supports storing data in Avro or Delta formats.
- Avro (write-optimized) is a compact, binary data format, with rich data structures and dynamically typed schema, which allows the data to be written faster to the target data store.
- Delta (read-optimized) stores data in the form of differences (deltas) between sequential data rather than complete files. The differences are recorded in discrete files called deltas. Delta format is faster for querying.
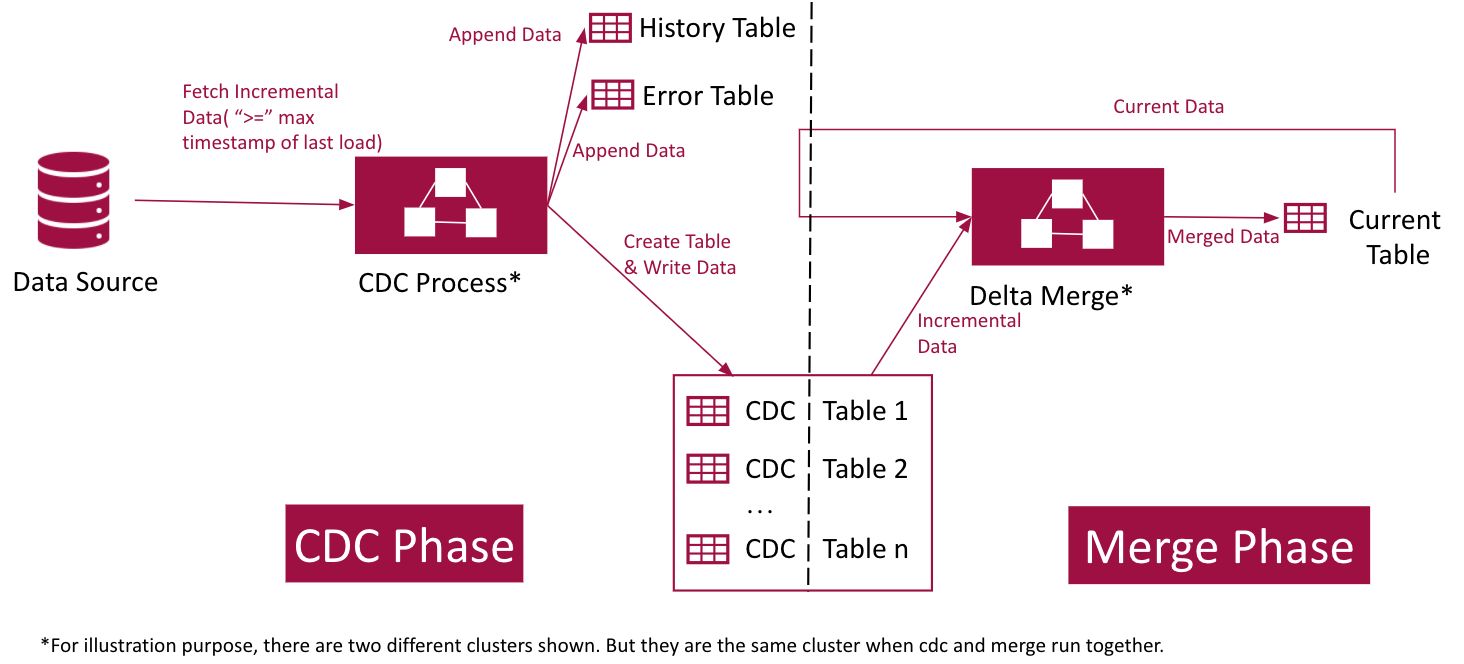
The ingested data includes a set of tables.
- The data of the table being crawled is stored in the current table.
- The data that cannot be parsed is stored in the error table.
- If the source data is modified after performing ingestion, you can perform incremental ingestion, where only the changed data is captured and merged with the existing data. The changed data is stored in the CDC table.
- The data from all the CDC runs are stored in the History table. This table contains the entire data that has been crawled in every data load.
In a nutshell,
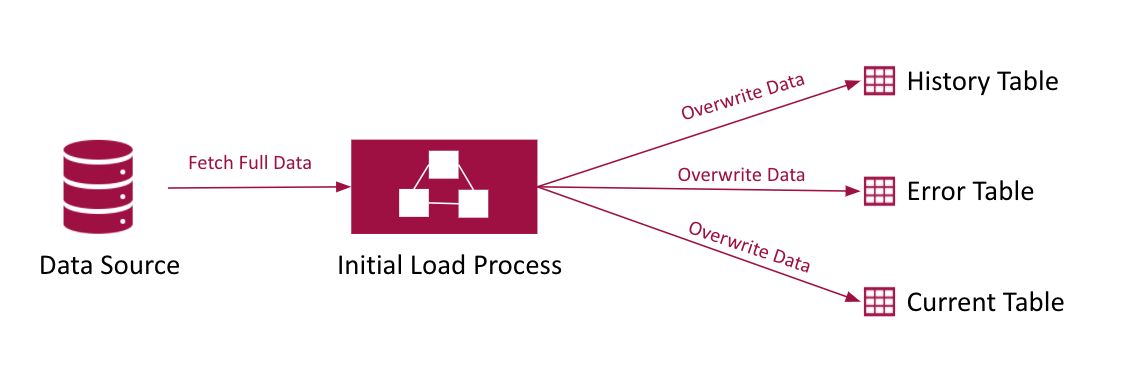
Full Refresh Ingestion Architecture
Full Refresh refers to the process of fetching the complete data. You can perform full refresh when you ingest the data for the first time.
Incremental Ingestion Architecture
Incremental ingestion refers to the process of fetching the complete data only in the first run and fetching only the changed data in subsequent runs. You can perform incremental ingestion when an ingested source is being updated or modified.