Creating a Pipeline
A pipeline allows you to transform the data ingested by Infoworks for various purposes like consumption by analytics tools, export to other systems, etc. |
You can perform either of the following:
- Import a Pipeline SQL or
- Create a New pipeline
Importing a Pipeline SQL
For details on importing a pipeline SQL, see Importing SQL.
Creating a New Pipeline
Following are the steps to add a new pipeline to the domain:
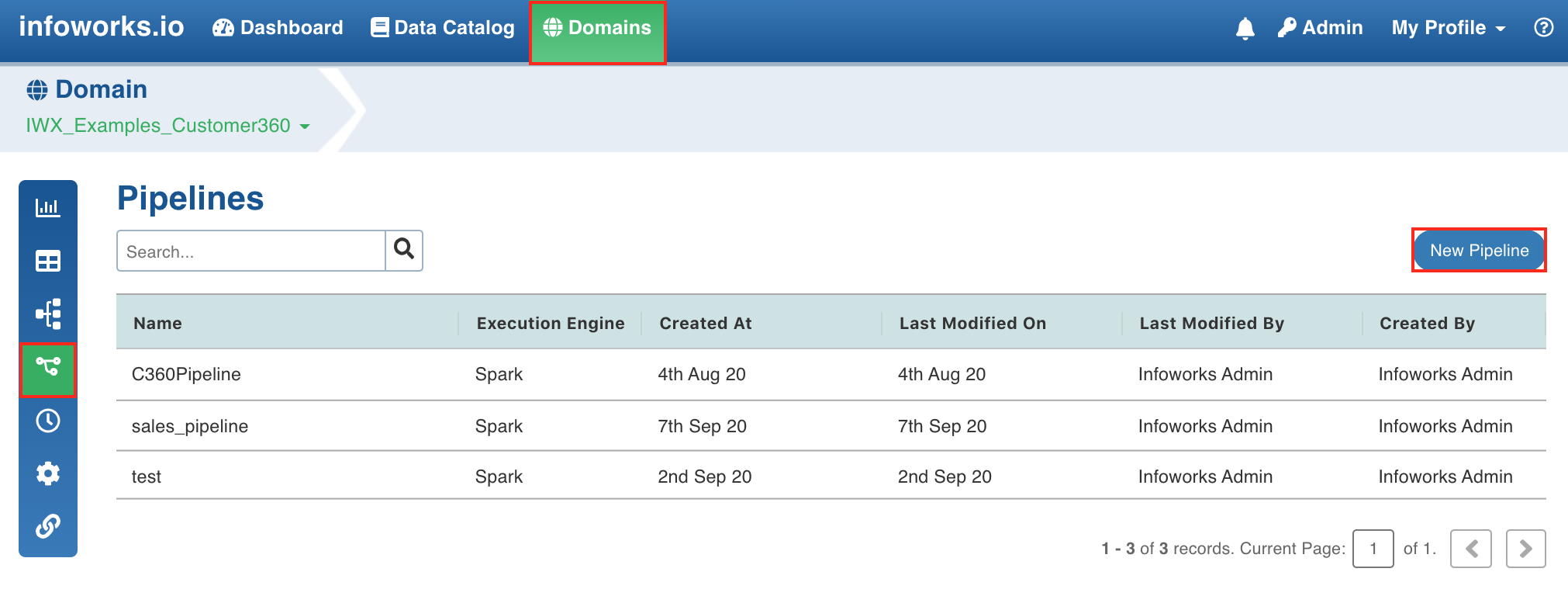
- Click the Domains menu and click the required domain from the list. You can also search for the required domain.
- Click the Pipelines icon.
- In the Pipelines page, click the New Pipeline button.
- In the New Pipeline page, select Create new pipeline in the drop-down list.
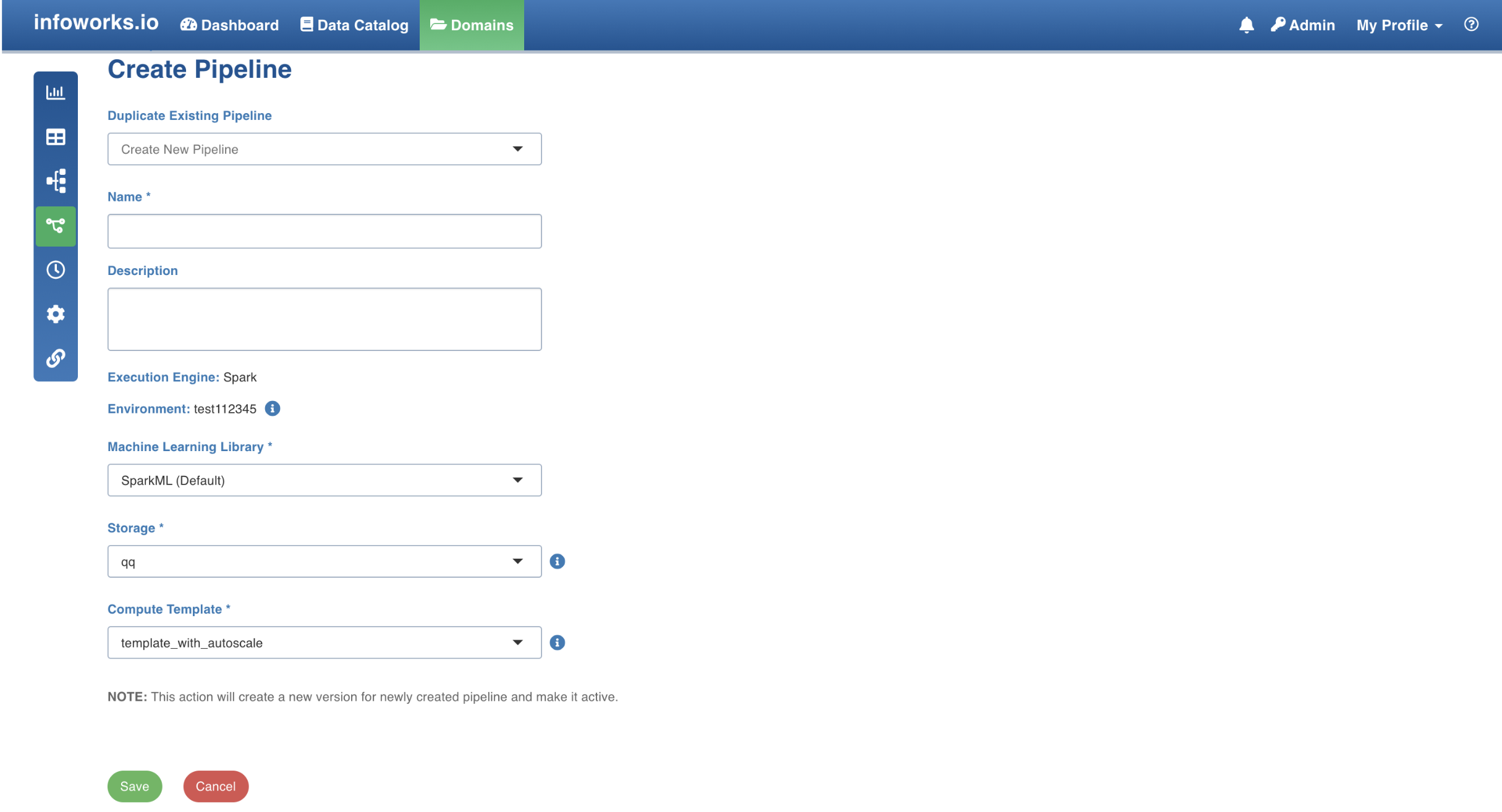
- Enter the following details:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name | The name for the pipeline. | Enter a unique name for the pipeline. |
| Description | The description for the pipeline. | Enter a description for the pipeline. |
| Execution Engine | The execution engine to communicate with Hadoop daemons such as Name node, Data nodes, and job tracker to execute the Hive query on top of Hadoop file system. | Select the Execution Engine as Spark. |
| Environment | The environment selected while creating the corresponding domain. | This is auto-assigned. |
| Machine Learning Library | The library used in machine learning. | The options include SparkML and H2O. |
| Storage | This drop-down lists the storages created by the admin. | For details on storage, see Configuring and Managing Environments. |
| Cluster Templates | This drop-down lists the cluster templates created by the admin. | For details on creating cluster, see Configuring and Managing Environments. |
- For Domains with Snowflake environment, enter the following details:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name | The name for the pipeline. | Enter a unique name for the pipeline. |
| Description | The description for the pipeline. | Enter a description for the pipeline. |
| Execution Engine | The execution engine to communicate with Hadoop daemons such as Name node, Data nodes, and job tracker to execute the Hive query on top of Hadoop file system. | This is auto-assigned. |
| Data Environment | Select from a list of snowflake environments associated with the corresponding domain. | Select the required environment. The environment selection is disabled if you clone an existing pipeline. The cloned pipeline is defaulted to use the same environment as configured in the original pipeline. |
| Run driver job on data plane | Select this checkbox to run the job on data plane. NOTE: The driver job runs on control plane by default. | Not selecting the check box implies that the job will run on control pane. |
| Compute Cluster | The compute cluster that is spin up for each table. | Select the relevant compute cluster from the dropdown list. |
| Snowflake Warehouse | Snowflake warehouse name. | Snowflake Warehouse is pre-filled from the selected snowflake environment and it can be edited. |
- For Domains with BigQuery environment, enter the following details:
| Field | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Name | The name for the pipeline. | Enter a unique name for the pipeline. |
| Description | The description for the pipeline. | Enter a description for the pipeline. |
| Execution Engine | The execution engine to communicate with Hadoop daemons such as Name node, Data nodes, and job tracker to execute the Hive query on top of Hadoop file system. | This is auto-assigned. |
| Data Environment | Select from a list of bigquery environments associated with the corresponding domain. | Select the required environment. The environment selection is disabled if you clone an existing pipeline. The cloned pipeline is defaulted to use the same environment as configured in the original pipeline. |
| Run driver job on data plane | Select this checkbox to run the job on data plane. | Not selecting the check box implies that the job will run on control pane. |
| Compute Cluster | The compute cluster that is spin up for each table. | If the Run driver job on data plane checkbox is selected, then you can select the Compute Cluster from the list of available compute clusters in the data environment. |
| Custom Tags | Tags are metadata elements that you apply to your cloud resources. They're key-value pairs that help you identify resources based on settings that are relevant to your organization. | |
| BigQuery Labels | This label enables you to add labels to your tables in BigQuery | For more information, refer to BigQuery Labels. |
- Click Save. The new pipeline will be added to the list of pipelines.
- The H2O machine learning library is not supported in interactive mode.
Using Spark
Currently, v2.0 and higher versions of Spark are supported. Spark as execution engine uses the Hive metastore to store metadata of tables. All the nodes supported by Hive and Impala are supported by the Spark engine.
- Parquet causes issues with the decimal datatype. This affects the pipeline targets that include the decimal datatype. You are recommended to cast any decimal datatype to double when using in a pipeline target.
- The number of tasks for the reduce phase can be tuned using the sql.shuffle.partitions setting. This setting controls the number of files and can be tuned per pipeline using the dt_batch_sparkapp_settings configuration in the Advanced Configuration option.
- Column names with spaces are not supported in Spark v2.2 but supported in v2.0. For example, column name as ID Number is not supported in Spark v2.2.
Best Practices
For best practices, see General Guidelines on Data Pipelines.