Onboarding Data from Mainframe Data Files (COBOL Copybook)
Creating a Mainframe Data Files Source
For creating a Mainframe Datafiles source, see Configuring Additional Connectors. Ensure that the Source Type selected is Mainframe Data Files.
Mainframe Datafiles Configuration
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Name | The source name of the target table. The source name must be unique and must not contain space or special characters except underscore. For example, Customer_Details. |
| Source File Location | The storage systems location where your files are stored. You can select one of the following options:
|
| SFTP Host | The SFTP host from which the data will be read. |
| SFTP Port | The SFTP port where the data will be run. |
| User Name | The username to log in to the SFTP host. |
| Cloud Type | The cloud storage where the data is stored. You can select the following options for the cloud type:
|
| Container Name | The name of the container in the storage account, in which the files are stored. A container organizes a set of blobs, similar to a directory in a file system. For more details, see Create a Container. |
| Storage Account Name | The unique name of the storage account. For more details, see Create a storage account. |
| Project ID | The ID of the project in the source. For more details, see Project ID. |
| Authentication Mechanism | The authentication mechanism using which security information is stored. i. For Remote server (Using SFTP), select if you want to authenticate using private key or password. ii. For Cloud Storage, Select Access Key to authenticate using access key or select None to access data from the public cloud storage folders. |
| Password | Type the password to log in to the SFTP host. |
| Private Key | Type the private key to log into the SFTP host. It can either be a text, uploaded, or a path on the edge node. When using Private Key as authentication mechanism:
|
| Enable support for Azure Government Cloud Regions | Select this check box to enable ingestion from a source available in the Government Cloud regions. This option is not editable if the data source tables are already created. |
| Storage Account Key | The storage account access key. This option is displayed if the Authentication Mechanism used is Account Key. For more details, see Manage storage account access keys. |
| Access ID | The access ID uniquely identifies an AWS account. You can use the access ID to send authenticated requests to Amazon S3. The Access ID is a 20-character, alphanumeric string, for example, AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE. For the access ID details, contact your AWS Cloud admin. For more details, see AWS Account Access Keys. |
| Secret Key | The secret key to send requests using the AWS account. The secret access key is a 40-character string. For example, wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY. For the secret key details, contact your AWS Cloud admin. |
| Source Base Path | The bucket where all the Mainframe copybook files to be accessed are stored. For more details, see Creating a bucket. The base of all directories that will be read from the file system.
|
| Access Scheme | Scheme used to access ADLS Gen2. The available options are abfs:// and *abfss:// * This field appears only for Azure DataLake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 cloud_._ |
| File System | Provide a file system where all the data of an artifact will be stored. |
| Access Key | Provide the storage access key to connect to ADLS. |
| Application ID | Provide the ID that uniquely identifies the user application. |
| Directory ID | Provide the ID that uniquely identifies the Azure AD instance. |
| Service Credential | Provide the credential string value that the application uses to prove its identity. |
Configuring File Mappings
You can configure the File Mappings by uploading the Copybook file and providing the Source Data file details.
To configure the File Mappings using the Copybook file, perform the following steps:
- Click Add Table.
- Browse the copybook and upload the copybook file.
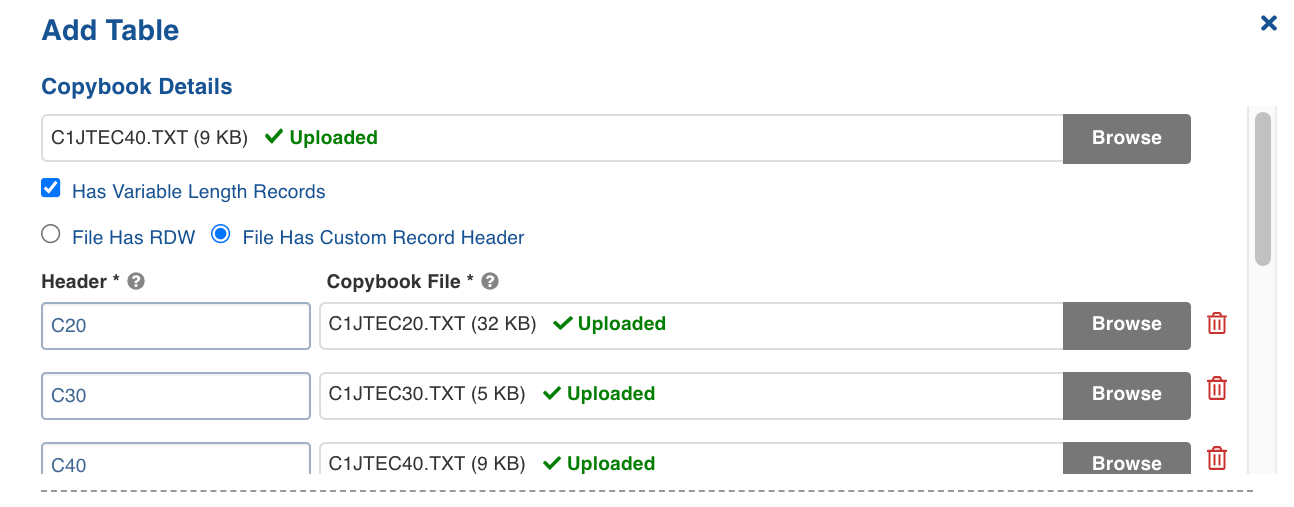
- Enter the following fields in the Copybook Details section after uploading the Copybook:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Has Variable Length Records | Select this option to specify the variable length records. If unchecked then the data file includes fixed length records. |
| File has RDW | This option is visible if the Has variable length records option is checked. The RDW stands for Record Descriptor Word that is a four byte field describing the record. The first two bytes contain the length (LL) of the logical record (including the 4 byte RDW). |
| File has Custom Record Header | This option specifies that the file includes the custom record header. |
| Record Header Encoding | This option is visible only when File Has RDW is selected. The following options are available:
Little and big endian are the two ways of storing multibyte data-types ( int, float, and so on). |
Add Copybook File for Custom Record Header
After the Copybook is uploaded, you can select File Has Custom Record Header and provide the following details:
- Header: It identifies the record uniquely in variable record length files.
- Copybook file: Provide the Copybook file related to the header.
You can also add new entries by clicking the Add button.
Configure the Data File Details
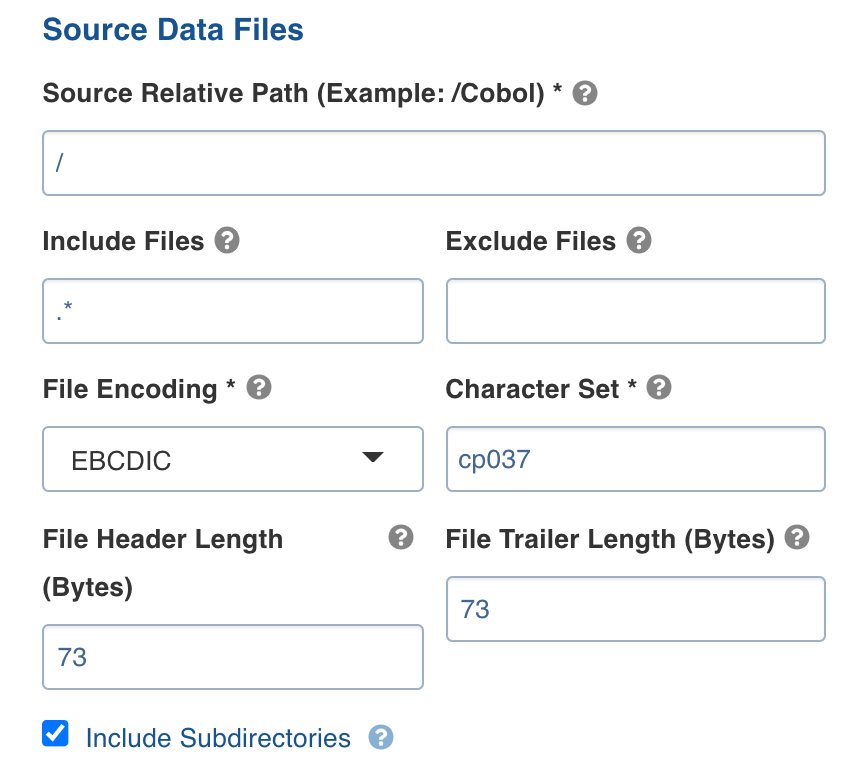
Enter the following details in the Source Data Files section for configuring the data files.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Relative Path | The path to the directory where the data files are stored (relative to the source base path). (For example, /Cobol) |
| Include Files | The regex pattern to include files. Only the files matching this Java Regex will be crawled. |
| Exclude Files | The regex pattern to exclude files. The files matching this Java Regex will not be crawled. |
| File Encoding | The encoding type for the data file that is used. EBCDIC: The EBCDIC stands for Extended Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code, data-encoding system, that uses a unique eight-bit binary code for each number and uses alphabetic characters, punctuation marks, accented letters, and non alphabetic characters. *TEXT: Specifies the simple plain text. |
| Character Set | Character encoding to be used. |
| File Header Length (Bytes) | Length of the header in bytes. |
| File Trailer length (Bytes) | Length of the footer in bytes. |
| Include sub directories | Select this option to onboard the data files present in the sub directories of the source path. |
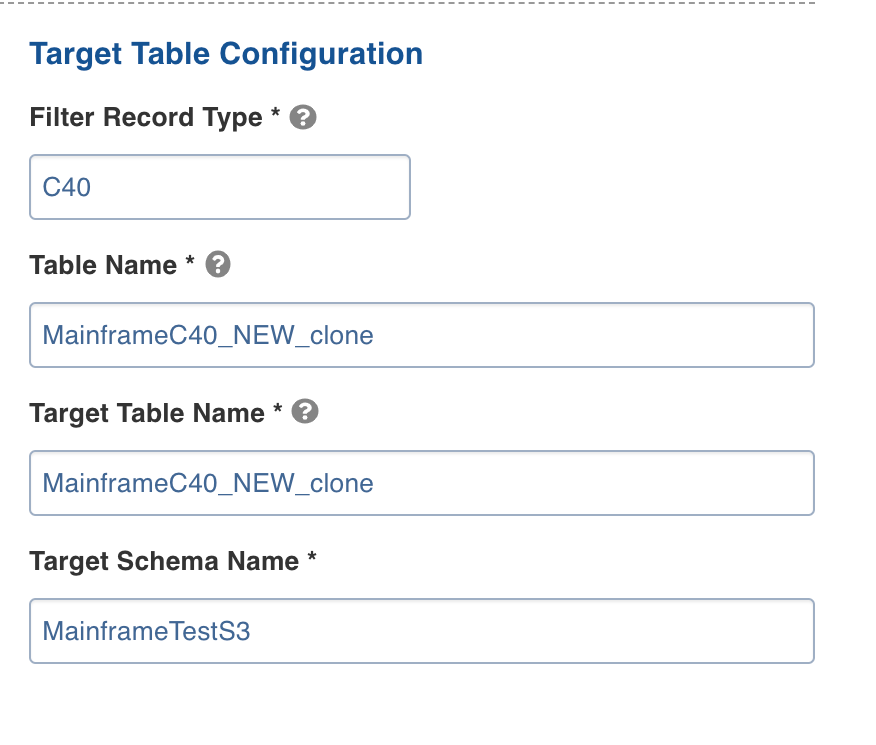
- Enter the following details in the Target Table Configuration section:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Filter Record Type | Specifies the value of the column to be extracted. |
| Filter Record Column | Specifies the column to extract the segment. |
| Table Name | The table name used to specify in the Infoworks UI. |
| Target Table Name | The target table name to be created in the Datalake. |
| Target Schema Name | The schema name of the target table. |
- Click Save and Crawl Schema to save the schema.
Edit the Schema and View Sample Data
To edit the schema and view the sample data, perform the following steps:
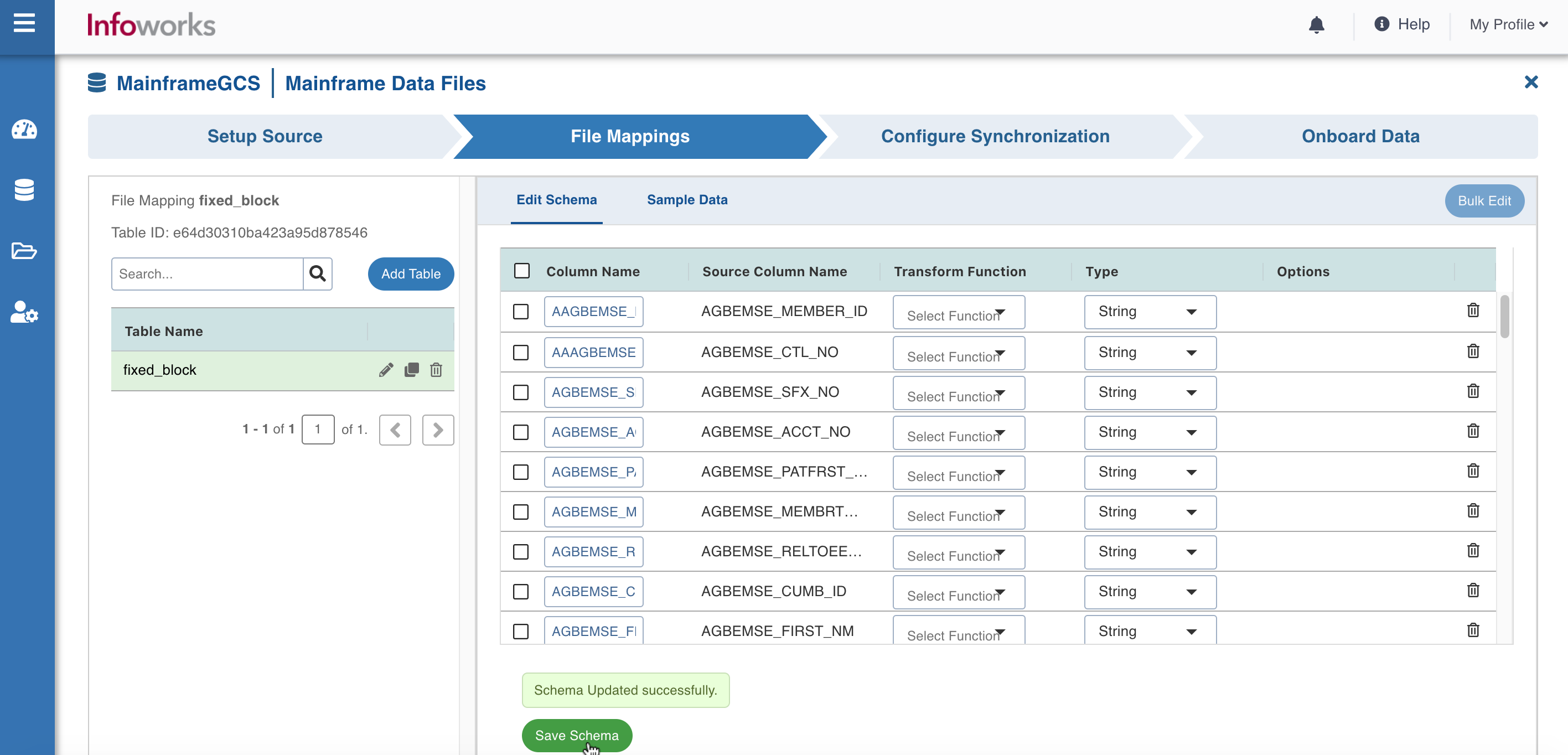
- Under File Mappings tab, enter the following details:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Column Name | Edit the column name of the table. |
| Transform Function | Select the Transform function. |
| Type | Select the data types from the drop-down. The available data types are Decimal, Integer, Float, Double, String, Boolean, Date, Timestamp, Long, and Byte. |
- Click Save Schema to save the schema successfully.
- Click Sample Data to view the sample data.
Configuring a Mainframe Datafiles Table
For configuring a Mainframe Data Files Table, see Configuring a Table.
Additional Information
- If records are not adhering to schema and there is a datatype mismatch, the job will fail.